Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -induced total reaction cross sections based on the intranuclear cascade model
-induced total reaction cross sections based on the intranuclear cascade modelNakano, Masahiro*; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Furuta, Toshimasa*; Uozumi, Yusuke*
Physical Review C, 110(6), p.064620_1 - 064620_5, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Alpha-induced total reaction cross sections in the low-energy region below 400 MeV are investigated using an intranuclear cascade model based on the extended framework for nucleon- and deuteron-induced reactions. Experimental data for  C,
C,  Si,
Si,  Ca, and
Ca, and  Pb targets are reproduced well by calculations performed with reasonable parameters close to those determined in other studies. It is shown that two effects, namely, discrete level constraint (DLC) and the Coulomb effect, provide important contributions that depend on the incident- energy and target. The DLC effect is limited to a narrow region of low-energy and is very important in light targets. The Coulomb effect is decisive on cross sections in
Pb targets are reproduced well by calculations performed with reasonable parameters close to those determined in other studies. It is shown that two effects, namely, discrete level constraint (DLC) and the Coulomb effect, provide important contributions that depend on the incident- energy and target. The DLC effect is limited to a narrow region of low-energy and is very important in light targets. The Coulomb effect is decisive on cross sections in  Pb, while the DLC contribution for the heavy target is small. It is concluded that this trend in the contribution of both effects is consistent with proton- and deuteron-induced total reaction cross sections.
Pb, while the DLC contribution for the heavy target is small. It is concluded that this trend in the contribution of both effects is consistent with proton- and deuteron-induced total reaction cross sections.
Okita, Shoichiro; Sakurai, Tatsuhiro*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Takagi, Katsuyuki*; Nakano, Takayuki*; Hino, Masahiro*
KURNS Progress Report 2023, P. 97, 2024/07
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Nakano, Masahiro*; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Uozumi, Yusuke*
Physical Review C, 106(1), p.014612_1 - 014612_8, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.31(Physics, Nuclear)Deuteron-induced nonelastic cross sections are studied in an extended intranuclear cascade (INC) model. A three-body framework of proton, neutron, and target is introduced into the INC model to incorporate naturally the decomposition and capture reactions from weakly bound deuterons. This framework includes three types of interaction potential, namely proton-target, neutron-target, and proton-neutron, the last of which causes the two nucleons in the deuteron to oscillate and play an important role in its breakup. The calculated results reproduce well the experimental data for  C,
C,  Ca,
Ca,  Ni, and
Ni, and  Pb targets with almost the same parameters as those determined previously for nucleon-induced nonelastic reactions.
Pb targets with almost the same parameters as those determined previously for nucleon-induced nonelastic reactions.
Nakano, Masanao; Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Kubota, Tomohiro; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-040, 118 Pages, 2021/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2020. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Sato, Tomonori; Komatsu, Atsushi; Nakano, Junichi*; Yamamoto, Masahiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.457 - 461, 2021/12
The Primary Containment Vessel (PCV) in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (1F) have been exposed to a corrosive environment containing seawater components under irradiation condition. In such conditions, the hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) is generated by water radiolysis as an oxidant in addition to dissolved oxygen. The H
) is generated by water radiolysis as an oxidant in addition to dissolved oxygen. The H O
O concentration is able to be estimated by radiolysis calculations. The corrosion tests under gamma-ray irradiation was performed. As the results, it was confirmed that the N
concentration is able to be estimated by radiolysis calculations. The corrosion tests under gamma-ray irradiation was performed. As the results, it was confirmed that the N gas purging performed in the PCV is effective in inhibiting the corrosion of carbon steel under irradiation conditions. The weight loss of carbon steel obtained in the corrosion test under gamma-ray irradiations, are evaluated using calculated O
gas purging performed in the PCV is effective in inhibiting the corrosion of carbon steel under irradiation conditions. The weight loss of carbon steel obtained in the corrosion test under gamma-ray irradiations, are evaluated using calculated O and H
and H O
O concentrations obtained by radiolysis calculations. As a results, it is confirmed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel under irradiation is determined by the sum of diffusion limiting currents of O
concentrations obtained by radiolysis calculations. As a results, it is confirmed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel under irradiation is determined by the sum of diffusion limiting currents of O and H
and H O
O as well as that of carbon steel in the O
as well as that of carbon steel in the O and H
and H O
O coexistent conditions under non-irradiation.
coexistent conditions under non-irradiation.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Kubota, Tomohiro; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-070, 120 Pages, 2021/02
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2019. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.67(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Sato, Yuji*; Tsukamoto, Masahiro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yamashita, Yoshihiro*; Yamagata, Shuto*; Nishi, Takaya*; Higashino, Ritsuko*; Okubo, Tomomasa*; Nakano, Hitoshi*; Abe, Nobuyuki*
Applied Physics A, 124(4), p.288_1 - 288_6, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamics of titanium (Ti) melted by laser irradiation was investigated in a synchrotron radiation experiment. As an indicator of wettability, the contact angle between a selective laser melting (SLM) baseplate and the molten Ti was measured by synchrotron X-rays at 30 keV during laser irradiation. As the baseplate temperature increased, the contact angle decreased, down to 28 degrees at a baseplate temperature of 500 C. Based on this result, the influence of wettability of a Ti plate fabricated by SLM in a vacuum was investigated. It was revealed that the improvement of wettability by preheating suppressed sputtering generation, and a surface having a small surface roughness was fabricated by SLM in a vacuum.
C. Based on this result, the influence of wettability of a Ti plate fabricated by SLM in a vacuum was investigated. It was revealed that the improvement of wettability by preheating suppressed sputtering generation, and a surface having a small surface roughness was fabricated by SLM in a vacuum.
 -ray irradiated neutral water condition
-ray irradiated neutral water conditionYamamoto, Masahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of 17th Asian Pacific Corrosion Control Conference (APCCC-17) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2016/01
In Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, decommissioning procedures are continuing more than 30 years until fuel debris removal. It is important to keep soundness of primary container vessel (PCV), made of carbon steel, during these procedures. Corrosion of carbon steel is well-known to be controlled by cathodic reaction, in usual, oxygen reduction reaction. Corrosion of carbon steel could be mitigated by nitrogen injection procedure. However, a lot of radioactive materials exist in cooling water, an effect of radiolysis product on corrosion is an important problem. Clarifying an irradiation effect for corrosion of carbon steel, corrosion test was conducted in  Co
Co  -ray irradiated condition. Electrochemical measurements were conducted to determine cathodic current density of samples. Corrosion rates of carbon steel decrease with time in both
-ray irradiated condition. Electrochemical measurements were conducted to determine cathodic current density of samples. Corrosion rates of carbon steel decrease with time in both  -ray irradiated and non-irradiated conditions. Measured values of cathodic current density gradually decreased with time and then stayed at constant value.
-ray irradiated and non-irradiated conditions. Measured values of cathodic current density gradually decreased with time and then stayed at constant value.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(3), p.181 - 188, 2015/09
In relation to the consideration for long-term storage of spent Cs adsorption vessels containing zeolites in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, corrosion of the vessel material in the spent Cs adsorption vessel is one of important issues. We performed electrochemical tests of stainless steel (SUS 316L) in the zeolites containing artificial seawater under  -ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential (
-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential ( ) and critical pitting potential (
) and critical pitting potential (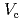 ), of SUS 316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after
), of SUS 316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after  -ray irradiation. The
-ray irradiation. The  , defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing
, defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing  was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H
was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H O
O in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H
in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H O
O . There was good relationship between
. There was good relationship between  and the concentration of H
and the concentration of H O
O . The
. The 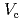 of SUS 316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl
of SUS 316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the
ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the 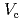 in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing
in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing  under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolite can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS 316L.
under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolite can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS 316L.
 -ray irradiated condition
-ray irradiated conditionYamamoto, Masahiro; Sato, Tomonori; Komatsu, Atsushi; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of European Corrosion Congress 2015 (EUROCORR 2015) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2015/09
In Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, decommissioning procedures are continuing and it will take more than 30 years. As some structures are made of carbon steel, degradation by corrosion is large problem for structural reliability. To clarify an irradiation effect for corrosion of carbon steel, corrosion test was con-ducted in  Co
Co  -ray irradiated condition. Corrosion test results showed that corrosion rates of
-ray irradiated condition. Corrosion test results showed that corrosion rates of  -ray irradiated condition increased with
-ray irradiated condition increased with  -ray dose rates. The oxidant concentrations were also increased with
-ray dose rates. The oxidant concentrations were also increased with  -ray dose rate. From these results, a new estimation method for corrosion rate of carbon steel in water with
-ray dose rate. From these results, a new estimation method for corrosion rate of carbon steel in water with  -ray irradiated condition using radiolysis calculation is introduced and discussed.
-ray irradiated condition using radiolysis calculation is introduced and discussed.
 -ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral water
-ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral waterYamamoto, Masahiro; Nakano, Junichi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Sato, Tomonori; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 19th International Corrosion Congress (19th ICC) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/11
Corrosion protection of RPV and PCV is an important issue for the long term maintenance until the end of the decommissioning procedures. One of the uncertain factors for the issue is an effect of radioactivity on corrosion of LAS and CS. Corrosion tests using LAS and CS were conducted in  -rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by
-rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by  -rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with
-rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with  -ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H
-ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H O
O was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in
was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in  -ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
-ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
 atmosphere on the corrosion of reactor vessel steels in diluted seawater under
atmosphere on the corrosion of reactor vessel steels in diluted seawater under  -rays irradiation
-rays irradiationNakano, Junichi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.977 - 986, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Seawater was injected into the reactor cores in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Corrosion of reactor vessel steels is considered to progress. To evaluate durability of the reactor vessel steels, corrosion tests were conducted in diluted seawater at 50  C under
C under  -rays irradiation. 10 mg/L and 100 mg/L N
-rays irradiation. 10 mg/L and 100 mg/L N H
H were added to diluted seawater. Without addition of N
were added to diluted seawater. Without addition of N H
H , weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 0.2 kGy/h dose rate was comparable with those without irradiation and weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 4.4 kGy/h dose rate was higher than those without irradiation. Under irradiation, weight loss in the vessel steels in diluted seawater containing N
, weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 0.2 kGy/h dose rate was comparable with those without irradiation and weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 4.4 kGy/h dose rate was higher than those without irradiation. Under irradiation, weight loss in the vessel steels in diluted seawater containing N H
H was comparable with that in diluted seawater without N
was comparable with that in diluted seawater without N H
H . When gas phase in the flask was replaced with N
. When gas phase in the flask was replaced with N , weight loss in the vessel steels, and O
, weight loss in the vessel steels, and O and H
and H O
O concentrations in the diluted seawater decreased.
concentrations in the diluted seawater decreased.
 -rays irradiation
-rays irradiationNakano, Junichi; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(1), p.1 - 6, 2014/03
The seawater was injected into reactor cores of Units 1, 2 and 3 in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. To investigate effects of  rays irradiation on corrosion of carbon steel and low alloy steel, corrosion tests were performed in the diluted seawater at 50
rays irradiation on corrosion of carbon steel and low alloy steel, corrosion tests were performed in the diluted seawater at 50  C under
C under  rays irradiation with dose rates of 4.4 kGy/h and 0.2 kGy/h. Hydrazine (N
rays irradiation with dose rates of 4.4 kGy/h and 0.2 kGy/h. Hydrazine (N H
H ) was added to the diluted seawater. In the diluted seawater without N
) was added to the diluted seawater. In the diluted seawater without N H
H , the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 0.2 kGy/h were similar to those of the unirradiated steels, and the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 4.4 kGy/h increased to approximate 1.7 times of those of the unirradiated steels. The weight losses of the steels irradiated in the diluted seawater containing N
, the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 0.2 kGy/h were similar to those of the unirradiated steels, and the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 4.4 kGy/h increased to approximate 1.7 times of those of the unirradiated steels. The weight losses of the steels irradiated in the diluted seawater containing N H
H were similar to those in the diluted seawater without N
were similar to those in the diluted seawater without N H
H . When N
. When N was introduced to gas phase in the flasks during
was introduced to gas phase in the flasks during  rays irradiation, the weight losses of the steels decreased.
rays irradiation, the weight losses of the steels decreased.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 444(1-3), p.454 - 461, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cracking growth tests were conducted in high-temperature water containing hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) at 561 to 423 K to evaluate the effects of H
) at 561 to 423 K to evaluate the effects of H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel (SS) at temperature lower than the boiling water reactor (BWR) operating temperature. Small compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 SS. Despite the observation of only a small portion intergranular SCC (IGSCC) near the side groove of the CT specimen at 561 K in high-temperature water containing 100 ppb of H
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel (SS) at temperature lower than the boiling water reactor (BWR) operating temperature. Small compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 SS. Despite the observation of only a small portion intergranular SCC (IGSCC) near the side groove of the CT specimen at 561 K in high-temperature water containing 100 ppb of H O
O , the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens at 423 and 453 K. Effects of H
, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens at 423 and 453 K. Effects of H O
O on SCC appeared intensely at temperature lower than the BWR operating temperature. To estimate the environment in the cracks, outer oxide distribution on the fracture surface and fatigue pre-crack were examined by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
on SCC appeared intensely at temperature lower than the BWR operating temperature. To estimate the environment in the cracks, outer oxide distribution on the fracture surface and fatigue pre-crack were examined by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 441(1-3), p.348 - 356, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Crack growth tests were performed in high-temperature water containing hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) to evaluate the relationships between the crevice structure and H
) to evaluate the relationships between the crevice structure and H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) growth morphology of stainless steel (SS). Small compact tension (CT) specimens with different fatigue pre-crack lengths were prepared. 20
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) growth morphology of stainless steel (SS). Small compact tension (CT) specimens with different fatigue pre-crack lengths were prepared. 20 300 ppb H
300 ppb H O
O was injected into the high-temperature water at 561 K. Intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only near the side grooves of the CT specimens. Owing to pre-crack shortening, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens. The effects of H
was injected into the high-temperature water at 561 K. Intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only near the side grooves of the CT specimens. Owing to pre-crack shortening, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens. The effects of H O
O on SS appeared intensely near the surfaces exposed to high levels of H
on SS appeared intensely near the surfaces exposed to high levels of H O
O . The calculations for the percentage of H
. The calculations for the percentage of H O
O remaining showed that the effects of H
remaining showed that the effects of H O
O flowed from both sides of the crack were more obvious than those flowed from the crack mouth.
flowed from both sides of the crack were more obvious than those flowed from the crack mouth.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 2012 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2012) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2012/09
It has been reported that the corrosion behavior of stainless steels in high temperature water with hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) was different from those with O
) was different from those with O . To evaluate the effect of H
. To evaluate the effect of H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC), SCC growth tests were conducted in high temperature water injected with H
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC), SCC growth tests were conducted in high temperature water injected with H O
O . In 100 ppb H
. In 100 ppb H O
O at 561 K, an intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only small portion of area near the side grooves of the CT specimen. In 100 ppb H
at 561 K, an intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only small portion of area near the side grooves of the CT specimen. In 100 ppb H O
O at 453 K, however, IGSCC extended to the central region of the CT specimen. Effects of H
at 453 K, however, IGSCC extended to the central region of the CT specimen. Effects of H O
O on SCC growth behavior appeared stronger at lower temperature due to a reduction of the thermal decomposition of H
on SCC growth behavior appeared stronger at lower temperature due to a reduction of the thermal decomposition of H O
O . Moreover, outer oxide layer of oxide film formed on the crack of the CT specimen was examined to estimate environmental situations in the cracks and a thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
. Moreover, outer oxide layer of oxide film formed on the crack of the CT specimen was examined to estimate environmental situations in the cracks and a thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
Yamamoto, Masahiro; Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsujikawa, Shigeo*; Hattori, Shigeo*; Yoshii, Tsuguyasu*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-007, 404 Pages, 2012/03
There are many LWRs which have been operated for more than 20 years in Japan and it is expected that technique corresponding to aging plants are necessary established for safety operation in LWRs. A lot of troubles related to SCC are reported and many investigations are concerned with SCC mechanism and technical evaluation. In this paper, those research data were collected as possible widely and reviewed systematically. Current circumstances concerned with SCC in LWRs were reviewed specifically as follows: SCC incidents, SCC evaluation methods for crack initiation and propagation, the investigations concerned with SCC mechanism and monitoring technique for corrosive environment. Influences with reactor types (BWR, PWR), materials (stainless steels, Ni alloys) and SCC evaluating methods (laboratories and actual plants) were summarized as graphs and tables easy to understand in common/difference points concerned with SCC. From these arranged results, future themes were considered and remarked SCC phenomenon was summarized in actual plants. As for SCC evaluations under the accelerate conditions in the laboratory test, it was suggested that a computational prediction and modeling including statistical technique and microscopic analysis in crack initiation were important. Furthermore it was suggested that monitoring techniques predicting SCC initiation and grasping plant circumstance in operation and feasibility in actual plants were important.