Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 IrSi
IrSiOnuki, Yoshichika*; Kaneko, Yoshio*; Aoki, Dai*; Nakamura, Ai*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Nakashima, Miho*; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.065002_1 - 065002_2, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -Mn and
-Mn and  -Mn
-MnOnuki, Yoshichika*; Aoki, Dai*; Nakamura, Ai*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Nakashima, Miho*; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.065001_1 - 065001_2, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) and EuAu
and EuAu with the characteristic hexagonal structure
with the characteristic hexagonal structureMatsuda, Shinya*; Ota, Joji*; Nakaima, Kenri*; Iha, Wataru*; Gochi, Jun*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; Nakashima, Miho*; Amako, Yasushi*; Honda, Fuminori*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Philosophical Magazine, 100(10), p.1244 - 1257, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Si
Si single crystal grown by the flux method
single crystal grown by the flux methodTakeuchi, Tetsuya*; Haga, Yoshinori; Taniguchi, Toshifumi*; Iha, Wataru*; Ashitomi, Yosuke*; Yara, Tomoyuki*; Kida, Takanori*; Tahara, Taimu*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Nakashima, Miho*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(3), p.034705_1 - 034705_15, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Onuki, Yoshichika*; Kakihana, Masashi*; Iha, Wataru*; Nakaima, Kenri*; Aoki, Dai*; Nakamura, Ai*; Honda, Fuminori*; Nakashima, Miho*; Amako, Yasushi*; Gochi, Jun*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 29, p.012001_1 - 012001_9, 2020/02
Iha, Wataru*; Kakihana, Masashi*; Matsuda, Shinya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Nakashima, Miho*; Amako, Yasushi*; Gochi, Jun*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 788, p.361 - 366, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:45.49(Chemistry, Physical) Si
Si
Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Yara, Tomoyuki*; Ashitomi, Yosuke*; Iha, Wataru*; Kakihana, Masashi*; Nakashima, Miho*; Amako, Yasushi*; Honda, Fuminori*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(7), p.074709_1 - 074709_14, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:62.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yagmur, A.*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Ihara, Kazuki*; Ioka, Ikuo; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Ono, Madoka*; Endo, Junichi*; Kashiwagi, Kimiaki*; Nakashima, Tetsuya*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 109(24), p.243902_1 - 243902_4, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.39(Physics, Applied)Thermoelectric devices based on the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) were irradiated with gamma ( ) rays with the total dose of around 3
) rays with the total dose of around 3 10
10 Gy in order to investigate the
Gy in order to investigate the  -radiation resistance of the devices. To demonstrate this, Pt/Ni
-radiation resistance of the devices. To demonstrate this, Pt/Ni Zn
Zn Fe
Fe O
O /Glass and Pt/Bi
/Glass and Pt/Bi Y
Y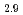 Fe
Fe O
O /Gd
/Gd Ga
Ga O
O SSE devices were used. We confirmed that the thermoelectric, magnetic, and structural properties of the SSE devices are not affected by the
SSE devices were used. We confirmed that the thermoelectric, magnetic, and structural properties of the SSE devices are not affected by the  -ray irradiation. This result demonstrates that SSE devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in high radiation environments.
-ray irradiation. This result demonstrates that SSE devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in high radiation environments.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.63 - 69, 2016/09
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. PHITS users apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some new models such as muon-induced nuclear reaction model and a  de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 82, p.110 - 115, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:94.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)The general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through a collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is responsible for managing the entire project. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. This paper briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions useful for particular purposes, such as an event generator mode and beam transport functions.
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Iida, Hiromasa*; Itoga, Toshio*; Okumura, Keisuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Konno, Chikara; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Nakamura, Takashi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Hoshasen Shahei Handobukku; Kisohen, p.299 - 356, 2015/03
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.69 - 74, 2015/02
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. All components of PHITS such as its source, executable and data-library files are assembled in one package and then distributed to many countries. More than 1,000 researchers apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions for specific applications, such as an event generator mode and a radiation damage calculation function.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(9), p.913 - 923, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:609 Percentile:99.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)An upgraded version of the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS 2.52, was developed and released to public. The new version has been greatly improved from the previous released version, PHITS 2.24, in terms of not only the code itself but also the contents of its package such as attached data libraries. Owing to these improvements, PHITS became a more powerful tool for particle transport simulation applicable to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
RIST News, (54), p.14 - 24, 2013/01
Features of the latest version of the PHITS code (version 2.52) is described.
 (R: Rare earth)
(R: Rare earth)Hieu, N. V.*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Tonohiro, Chie*; Yamada, Tsutomu*; Nakashima, Hiroshi*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Settai, Rikio*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 76(6), p.064702_1 - 064702_16, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:85.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary) without inversion symmetry in the crystal structure
without inversion symmetry in the crystal structureKawai, Tomoya*; Okuda, Yusuke*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Thamizhavel, A.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Nakashima, Miho*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Hedo, Masato*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 76(1), p.014710_1 - 014710_6, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.21(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in growing a single crystal of CePtSi by the Sn-flux method. CePtSi
by the Sn-flux method. CePtSi is found to be an antiferromagnet with two transitions at 4.8 and 2.4 K. Magnetic easy direction was [100] direction with an ordered moment of 1.15
is found to be an antiferromagnet with two transitions at 4.8 and 2.4 K. Magnetic easy direction was [100] direction with an ordered moment of 1.15 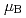 /Ce. The anisotropy is similar to that of CeIrSi
/Ce. The anisotropy is similar to that of CeIrSi in which the pressure-induced superconductivity was observed.
in which the pressure-induced superconductivity was observed.
 , TbRhIn
, TbRhIn , DyRhIn
, DyRhIn , and HoRhIn
, and HoRhIn
Hieu, N. V.*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Thamizhavel, A.*; Nakashima, Hiroshi*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Settai, Rikio*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(7), p.074708_1 - 074708_6, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:70.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We grew single crystals of NdRhIn , TbRhIn
, TbRhIn , DyRhIn
, DyRhIn , and HoRhIn
, and HoRhIn with the tetragonal crystal structure and measured the magnetic susceptibility and magnetization. NdRhIn
with the tetragonal crystal structure and measured the magnetic susceptibility and magnetization. NdRhIn is an antiferromagnet with a Neel temperature
is an antiferromagnet with a Neel temperature 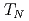 = 11.6 K. Below
= 11.6 K. Below 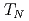 , magnetization reveals two metamagnetic transitions at Hm1 = 70 kOe and Hm2 = 93 kOe for the magnetic field along the [001] direction. The saturation moment of 2.5
, magnetization reveals two metamagnetic transitions at Hm1 = 70 kOe and Hm2 = 93 kOe for the magnetic field along the [001] direction. The saturation moment of 2.5 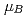 /Nd is in good agreement with the staggered Nd moment determined by the neutron diffraction experiment. These metamagnetic transitions correspond to the change of the magnetic structure. TbRhIn
/Nd is in good agreement with the staggered Nd moment determined by the neutron diffraction experiment. These metamagnetic transitions correspond to the change of the magnetic structure. TbRhIn , DyRhIn
, DyRhIn and HoRhIn
and HoRhIn are found to be antiferromagnets with
are found to be antiferromagnets with 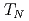 = 47.3, 28.1, and 15.8 K, respectively. The magnetization curves of these compounds are also quite similar to those of NdRhIn
= 47.3, 28.1, and 15.8 K, respectively. The magnetization curves of these compounds are also quite similar to those of NdRhIn , revealing two metamagnetic transitions. The magnetic structures in magnetic fields are proposed by considering the exchange interactions based on the crystal structure.
, revealing two metamagnetic transitions. The magnetic structures in magnetic fields are proposed by considering the exchange interactions based on the crystal structure.
 B
B and GdRh
and GdRh B
B
Obiraki, Yoshiko*; Nakashima, Hiroshi*; Galatanu, A.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Settai, Rikio*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(6), p.064702_1 - 064702_8, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.85(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in growing single crystals of ferromagnets NdRh B
B and GdRh
and GdRh B
B with the hexagonal structure, and measured the electrical resistivity, specific heat, magnetic susceptibility and magnetization. From these measurements, the Curie temperature
with the hexagonal structure, and measured the electrical resistivity, specific heat, magnetic susceptibility and magnetization. From these measurements, the Curie temperature 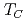 is determined as
is determined as 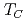 =10.2 K in NdRh
=10.2 K in NdRh B
B and TC=93 K in GdRh
and TC=93 K in GdRh B
B . The magnetic moments of about 2.5
. The magnetic moments of about 2.5 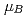 in NdRh
in NdRh B
B and 7.7
and 7.7 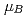 in GdRh
in GdRh B
B are oriented in the basal plane. The crystalline electric field scheme is proposed for NdRh
are oriented in the basal plane. The crystalline electric field scheme is proposed for NdRh B
B on the basis of the experimental results of Schottky anomaly in the specific heat and anisotropic susceptibility and magnetization. The Fermi surface in NdRh
on the basis of the experimental results of Schottky anomaly in the specific heat and anisotropic susceptibility and magnetization. The Fermi surface in NdRh B
B is very similar to that in a non-4 f reference compound LaRh
is very similar to that in a non-4 f reference compound LaRh B
B , possessing the quasi-one dimensional electronic character.
, possessing the quasi-one dimensional electronic character.
 Ni
Ni Ge
Ge single crystal
single crystalThamizhavel, A.*; Sugitani, Ichiro*; Obiraki, Yoshiko*; Nakashima, Miho*; Okuda, Yusuke*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Settai, Rikio*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 378-380, p.841 - 842, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have succeeded in growing single crystals of Ce Ni
Ni Ge
Ge , which crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal structure, by the flux method and studied the anisotropic physical properties by measuring the electrical resistivity, magnetic susceptibility and specific heat. The results of these measurements indicate that Ce
, which crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal structure, by the flux method and studied the anisotropic physical properties by measuring the electrical resistivity, magnetic susceptibility and specific heat. The results of these measurements indicate that Ce Ni
Ni Ge
Ge undergoes two antiferromagnetic transitions at
undergoes two antiferromagnetic transitions at 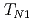 =4.9 K and
=4.9 K and 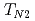 =4.3 K. The electrical resistivity and susceptibility measurements reveal strong anisotropic magnetic properties. From the specific heat measurement the electronic specific heat coefficient was found to be 90mJ/K
=4.3 K. The electrical resistivity and susceptibility measurements reveal strong anisotropic magnetic properties. From the specific heat measurement the electronic specific heat coefficient was found to be 90mJ/K mol.
mol.
 Ni
Ni Ge
Ge
Thamizhavel, A.*; Nakashima, Hiroshi*; Obiraki, Yoshiko*; Nakashima, Miho*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Settai, Rikio*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(10), p.2843 - 2848, 2005/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:62.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Single crystals of a pressure-induced superconductor Ce Ni
Ni Ge
Ge have been successfully grown by the flux method. The anisotropic magnetic properties due to the orthorhombic crystal structure have been studied precisely by the electrical resistivity, specific heat, magnetic susceptibility, and high-field magnetization measurements. The results of these measurements confirmed two antiferromagnetic transitions at T
have been successfully grown by the flux method. The anisotropic magnetic properties due to the orthorhombic crystal structure have been studied precisely by the electrical resistivity, specific heat, magnetic susceptibility, and high-field magnetization measurements. The results of these measurements confirmed two antiferromagnetic transitions at T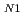 =5.0 K and T
=5.0 K and T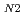 =4.3 K. The electronic specific heat coefficient obtained from the low-temperature specific heat data amounts to 90 mJ/K
=4.3 K. The electronic specific heat coefficient obtained from the low-temperature specific heat data amounts to 90 mJ/K mol Ce. The high-field magnetization for H //[100] shows four magnetic transitions at 11.8, 12.9, 17.5 and 23.9 T with a saturation moment of 0.73
mol Ce. The high-field magnetization for H //[100] shows four magnetic transitions at 11.8, 12.9, 17.5 and 23.9 T with a saturation moment of 0.73 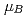 /Ce at 1.3 K. We have also performed the crystalline electric field (CEF) analysis on the magnetic susceptibility and magnetization to understand the magnetocrystalline anisotropy, where the splitting energies of two excited doublets in the CEF scheme are estimated to be 140 and 576 K, respectively.
/Ce at 1.3 K. We have also performed the crystalline electric field (CEF) analysis on the magnetic susceptibility and magnetization to understand the magnetocrystalline anisotropy, where the splitting energies of two excited doublets in the CEF scheme are estimated to be 140 and 576 K, respectively.