Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nemoto, Takahiro; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Arakawa, Ryoki; Choyama, Yuya; Nagasumi, Satoru; Hasegawa, Toshinari; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Onishi, Takashi; Kawamoto, Taiki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-003, 17 Pages, 2024/06
In order to investigate the cause of the increase in differential pressure in the primary helium circulator filter that occurred during the RS-14 cycle, a clogged filter was investigated. As a result of the investigation, deposits caused by silicone oil were confirmed on the surface of the filter element. These results revealed that the cause of filter clogging was silicone oil mixed into the primary system due to performance deterioration of the charcoal filter in the gas circulator of primary helium purification system. As a measure to prevent the recurrence of this event, in addition to the conventional management based on operating hours for replacing of charcoal filter in the gas circulator of primary helium purification system, we have established a new replacement plan for every three years.
Nemoto, Takahiro; Arakawa, Ryoki; Kawakami, Satoru; Nagasumi, Satoru; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Onishi, Takashi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Furusawa, Takayuki; Inoi, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-005, 33 Pages, 2023/05
During shut down of the HTTR (High Temperature engineering Test Reactor) RS-14 cycle, an increasing trend of filter differential pressure for the helium gas circulator was observed. In order to investigate this phenomenon, the blower of the primary helium purification system was disassembled and inspected. As a result, it is clear that the silicon oil mist entered into the primary coolant due to the deterioration of the charcoal filter performance. The replacement and further investigation of the filter are planning to prevent the reoccurrence of the same phenomenon in the future.
Sano, Yuichi; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Misumi, Ryuta*; Kunii, Kanako*; Todoroki, Kei*; Nishi, Kazuhiko*; Kaminoyama, Meguru*
Kagaku Kogaku Rombunshu, 44(6), p.335 - 340, 2018/11
Concerning an annular centrifugal contactor which has high throughput and separation performance, the effect of operational condition on fluidic and dispersion behavior, which are important to improve the contactor performance, was investigated by computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis based on the turbulence model, and the calculated results were validated by experimental data. The liquid phase in the annular zone was gradually divided into two regions vertically with increasing the rotor speed and decreasing the flowrate, and the liquid flow moved toward the center of the housing bottom was generated in the lower annular zone under any operational condition. The droplet size of the dispersed phase in the annular zone decreased with increasing the rotor speed and decreasing the flowrate. These calculation results showed a good agreement with experimental data. The CFD analysis considering mass transfer between aqueous and organic phases was also attempted, and it was confirmed that the change of extraction performance with the rotor speed showed the same tendency as the experimental result.
Misumi, Ryuta*; Todoroki, Kei*; Kunii, Kanako*; Nishi, Kazuhiko*; Kaminoyama, Meguru*; Sano, Yuichi; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Kagaku Kogaku Rombunshu, 44(5), p.285 - 291, 2018/09
Annular centrifugal extractors have been anticipated for use as extractors in spent nuclear fuel recycling. The extraction rate and the liquid-liquid dispersion are related to the flow pattern in the vessel. However, no study has clarified flow patterns in vessels of various scales. For this study, flow pattern characteristics are quantified for extractors of two scales. An extractor has a mixing zone around the vessel bottom and a separation zone in the cylindrical rotor. For this experiment, distilled water was fed into the vessel. Flow behavior in the mixing zone was observed from a side view using a digital video camera at various rotor speeds and supply flow rates for extractors of two scales. In some cases, the liquid horizontal velocity vectors in the mixing zone were measured using particle image velocimetry. Results demonstrate that flow behaviors in the mixing zone in both scales of extractors are classifiable as three types, changing with operational conditions: Type A, Type B, and a Transition regime. For the Type A state, the mixing zone is fully filled with liquid from the vessel bottom up to the lower edge of the rotor. In the Type B state, the zone with existing liquid is vertically divisible into two regions. Lower rotor speeds and higher flow rates tend to produce Type A state flow behavior. The boundary operational condition between Type A and the Transition regime are correlated with the normalized supply flow rate and pumping capacity of the rotor, which is evaluated from liquid surface level in a rotor formed by centrifugal force. Furthermore, the fluid velocity in the mixing zone is roughly proportional to the rotor surface circumferential speed irrespective of the vessel scale.
Misumi, Ryuta*; Kunii, Kanako*; Todoroki, Kei*; Nishi, Kazuhiko*; Kaminoyama, Meguru*; Sano, Yuichi; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Kagaku Kogaku Rombunshu, 44(3), p.135 - 141, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.27(Engineering, Chemical)Annular centrifugal extractors have been used in spent nuclear fuel reprocessing, but the relation between the extraction rate and flow pattern in the vessel remains unclear. This study quantifies characteristics of the flow pattern to clarify this relation. An extractor produces a mixing zone around the vessel bottom and a separation zone in the rotor. The horizontal velocity of the liquid in the mixing zone was measured using particle image velocimetry at various rotor speeds and supply flow rates. Flow behaviors in the mixing zone are of three types, changing with operational conditions: Type A, Type B, and a transition regime. At lower rotor speeds and high supply flow rates, the mixing zone is fully filled with liquid from the vessel bottom up to the lower edge of the rotor: the Type A flow state. At high rotor speeds and low supply flow rates, the zone with existing liquid is vertically divisible into two regions: near the vanes and around the bottom of the rotor, which is the Type B flow state. A transition regime is also observed between Type A and Type B state. In each region surrounding the two vanes on the vessel bottom and the vessel wall, the liquid flowed in the direction of rotor rotation along the vessel wall. Liquid flow altered by the vane flowed toward the center of vessel bottom. The liquid then entered the separation zone through the orifice at the rotor bottom. For the Type A state, the horizontal velocity distribution was roughly proportional to the rotor speed. For the Type B state, the horizontal velocities around the vessel bottom were lower than those of Type A and were not proportional to the rotor speed. Presumably, the liquid fed into the vessel went directly to the rotor instead of passing between the two vanes attached to the vessel bottom.
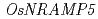 -knockdown rice is a promising candidate for Cd phytoremediation in paddy fields
-knockdown rice is a promising candidate for Cd phytoremediation in paddy fieldsTakahashi, Ryuichi*; Ishimaru, Yasuhiro*; Shimo, H.*; Bashir, K.*; Senoura, Takeshi*; Sugimoto, Kazuhiko*; Ono, Kazuko*; Suzui, Nobuo; Kawachi, Naoki; Ishii, Satomi; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 9(6), p.e98816_1 - e98816_7, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:85.62(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:70.56(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Katanishi, Shoji; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 237(12-13), p.1372 - 1380, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:76.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)One of the unique safety design concepts of a Gas Turbine High Temperature Reactor (GTHTR300) is that events with frequency of occurrence of higher than 10 /reactor-year are evaluated as design basis events (DBEs) in order to show that the frequency of large amount of FP release is less than 10
/reactor-year are evaluated as design basis events (DBEs) in order to show that the frequency of large amount of FP release is less than 10 /reactor-year. According to this concept, a depressurization accident is postulated as a DBE. This accident is one of the most serious accidents in the high temperature gas-cooled reactors from the view point of loss of coolability. The safety evaluation on the accident was conducted based on the actual design of the system. The fuel temperature behavior, internal pressure of the reactor building, oxidation behavior of fuels and graphite structures were evaluated and exposure dose of general public was also estimated using the results of evaluations of temperature and fuel failure. All of the results meet the safety criteria and feasibility of the GTHTR300 was shown by this study.
/reactor-year. According to this concept, a depressurization accident is postulated as a DBE. This accident is one of the most serious accidents in the high temperature gas-cooled reactors from the view point of loss of coolability. The safety evaluation on the accident was conducted based on the actual design of the system. The fuel temperature behavior, internal pressure of the reactor building, oxidation behavior of fuels and graphite structures were evaluated and exposure dose of general public was also estimated using the results of evaluations of temperature and fuel failure. All of the results meet the safety criteria and feasibility of the GTHTR300 was shown by this study.
Takamura, Shuichi*; Kado, Shinichiro*; Fujii, Takashi*; Fujiyama, Hiroshi*; Takabe, Hideaki*; Adachi, Kazuo*; Morimiya, Osamu*; Fujimori, Naoji*; Watanabe, Takayuki*; Hayashi, Yasuaki*; et al.
Kara Zukai, Purazuma Enerugi No Subete, P. 164, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Takei, Masanobu*; Kosugiyama, Shinichi*; Mori, Tomoaki; Katanishi, Shoji; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 5(2), p.109 - 117, 2006/06
no abstracts in English
Takada, Shoji; Katanishi, Shoji; Yan, X.; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Koon Gakkai-Shi, 32(1), p.54 - 62, 2006/01
Design and development of the high temperature gas cooled reactor with a gas turbine electric generation system, the GTHTR300, was carried out by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute. The GTHTR300 is expected to be a new electric generation system in the early 2010s. Design originalities of the GTHTR300 are a horizontally mounted highly efficient gas turbine system and an ultimately simplified safety system such as no containment building and no active emergency core cooling. These design originalities are proposed based on design and operational experiences in conventional gas turbine systems and Japanese first high temperature gas cooled reactor HTTR so that many R&Ds are not required for the development. Except these original design features, devised core design, fuel design and plant design are adopted to meet design requirements and attain a target cost. This paper describes the unique design features of the GTHTR300 and its deployment plan.
Katanishi, Shoji; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Maekawa, Isamu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(3), p.257 - 267, 2004/09
no abstracts in English
Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Katanishi, Shoji; Takada, Shoji; Takizuka, Takakazu; Yan, X.; Kosugiyama, Shinichi
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.261 - 267, 2004/05
The GTHTR300 aiming at electric generation with its thermal efficiency of 46 % is a safe and economically competitive HTGR in 2010s. A helium gas turbine system connected with the reactor is designed based on existing technologies developed for fossil gas turbine systems. However, there are some uncertainties in performance of a helium gas compressor, electric magnetic bearings and control system. In order to confirm these technical uncertainties, a 1/3 scale model of the compressor and 1/3 scale magnetic bearings will be manufactured and tested in the simulated condition of the GTHTR300. This paper describes R&D plans focusing on the 1/3 scale compressor model test as well as unique design features of the GTHTR300.
Katanishi, Shoji; Takei, Masanobu; Nakata, Tetsuo*; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(1), p.67 - 75, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Katanishi, Shoji; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(1), p.76 - 87, 2004/03
The Gas Turbine High Temperature Reactor 300 (GTHTR300) composed of an inherent safe 600MWt reactor and a closed gas turbine power conversion system is a high efficient and economically competitive HTGR to be deployed in 2010s. To analyze the plant dynamics and the thermal hydraulics of the GTHTR300, a new analytical code (Conan-GTHTR) based on 'RELAP5/MOD3' has been developed and applied to heat transfer calculations of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) for its verification. The results proved that the new code was available for transient simulations in Higt Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor systems.
Takei, Masanobu; Katanishi, Shoji; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Izumiya, Toru*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(4), p.490 - 499, 2003/12
no abstracts in English
Nakata, Tetsuo*; Katanishi, Shoji; Takada, Shoji; Yan, X.; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(4), p.478 - 489, 2003/12
no abstracts in English
Kosugiyama, Shinichi; Takizuka, Takakazu; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Yan, X.; Katanishi, Shoji; Takada, Shoji
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(3), p.319 - 331, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Katanishi, Shoji; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(1), p.55 - 67, 2003/01
no abstracts in English
Takada, Shoji; Takizuka, Takakazu; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Yan, X.; Katanishi, Shoji; Kosugiyama, Shinichi; Minatsuki, Isao*; Miyoshi, Yasuyuki*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 1(4), p.341 - 351, 2002/12
no abstracts in English