Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 generation of two strains of
generation of two strains of  var.
var. 
Honda, Kazushige*; Taneichi, Shuhei*; Maeda, Tomoo*; Goto, Satoshi*; Shikanai, Yasuhiro*; Sasaki, Kazuya*; Nozawa, Shigeki; Hase, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 107, 2016/02
no abstracts in English
Ono, Yutaka; Hase, Yoshihiro; Sato, Katsuya; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issey*
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (138), p.17 - 20, 2015/06
no abstracts in English
Kawasaki, Michio*; Kikyo, Shogo*; Nozawa, Shigeki; Akita, Yusuke*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issey*
Nihon Sakumotsu Gakkai Tohoku Shibu Kaiho, (57), p.61 - 62, 2014/12
no abstracts in English
Iimure, Takashi*; Hoki, Takehiro*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issey*; Kihara, Makoto*; Ogushi, Kensuke*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 109, 2014/03
Matsuo, Yoichiro*; Izumi, Yoshinobu*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Sakamoto, Ayako; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issey*; Shimizu, Kikuo*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 112, 2014/03
Tanaka, Atsushi; Nozawa, Shigeki; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issey*; Ishikawa, Hidetaka*; Koike, Aki*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 103, 2014/03
Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Asami, Itsuo*; Tanogashira, Yuki*; Matsuo, Yoichi*; Kanazawa, Akira*; Honda, Kazushige*; Narumi, Issey*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 102, 2014/03
Zaiton, A.*; Affrida, A. H.*; Shakinah, S.*; Nurul Hidayah, M.*; Nozawa, Shigeki*; Narumi, Issey*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Ono, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 104, 2014/03
Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issey*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 105, 2014/03
 mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt tolerance
mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt toleranceAriga, Hirotake*; Katori, Taku*; Yoshihara, Ryohei*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Iuchi, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Masatomo*; Tezuka, Kenji*; Sakata, Yoichi*; et al.
Plant Signaling & Behavior (Internet), 8(7), p.e24779_1 - e24779_5, 2013/07
Based on analysis of the salinity tolerance among 354  accessions, some accessions showed greater salt shock tolerance compared with a reference accession, Col-0 on a typical assay with drastic change in NaCl concentration from 0 mM to 225 mM. On the other hand, several accessions including Zu-0 exhibited marked acquired salt tolerance, which is induced after exposure to moderate salt stress (salt acclimation ability). It is likely that Arabidopsis plants have at least two types of tolerance abilities, salt shock tolerance and salt acclimation. To dissect the salt tolerance mechanisms of the salt tolerant accessions, we isolated a salt-sensitive mutant from ion beam-mutagenized Zu-0 seedlings. The mutant showed severe growth inhibition under salt shock stress due to a single base deletion in SOS1 gene as well-known salt shock tolerance gene, even more salt sensitive than Col-0. Nevertheless, the mutant was able to survive on the salt acclimation with 100 mM NaCl for 7 days followed with 750 mM sorbitol for 20 days (salt acclimation assay) as well as the Zu-0 wild type, whereas Col-0 showed apparent chlorosis under the condition. We propose that a gene for salt acclimation ability is different from a gene for salt shock tolerance and plays an important role in acquisition for marked salt- or osmotic tolerance.
accessions, some accessions showed greater salt shock tolerance compared with a reference accession, Col-0 on a typical assay with drastic change in NaCl concentration from 0 mM to 225 mM. On the other hand, several accessions including Zu-0 exhibited marked acquired salt tolerance, which is induced after exposure to moderate salt stress (salt acclimation ability). It is likely that Arabidopsis plants have at least two types of tolerance abilities, salt shock tolerance and salt acclimation. To dissect the salt tolerance mechanisms of the salt tolerant accessions, we isolated a salt-sensitive mutant from ion beam-mutagenized Zu-0 seedlings. The mutant showed severe growth inhibition under salt shock stress due to a single base deletion in SOS1 gene as well-known salt shock tolerance gene, even more salt sensitive than Col-0. Nevertheless, the mutant was able to survive on the salt acclimation with 100 mM NaCl for 7 days followed with 750 mM sorbitol for 20 days (salt acclimation assay) as well as the Zu-0 wild type, whereas Col-0 showed apparent chlorosis under the condition. We propose that a gene for salt acclimation ability is different from a gene for salt shock tolerance and plays an important role in acquisition for marked salt- or osmotic tolerance.
Azad, M. A. K.*; Mazumdar, M. N. N.*; Chaki, A. K.*; Ali, M.*; Hakim, M. L.*; Mamun, A. N. K.*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Tanaka, Atsushi; Koike, Aki*; et al.
SABRAO Journal of Breeding and Genetics, 45(2), p.179 - 186, 2013/06
no abstracts in English
 -rays and carbon ion beams in
-rays and carbon ion beams in  seedlings
seedlingsYoshihara, Ryohei*; Nozawa, Shigeki; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Hidema, Jun*; Sakamoto, Ayako
Journal of Radiation Research, 54(6), p.1050 - 1056, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:69.64(Biology)Zaiton, A.*; Affrida, A. H.*; Shakinah, S.*; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Ono, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 97, 2013/01
Tanaka, Atsushi; Nozawa, Shigeki; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Ishikawa, Hidetaka*; Koike, Aki*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 96, 2013/01
Hase, Yoshihiro; Yoshihara, Ryohei*; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 98, 2013/01
Matsuo, Yoichiro*; Izumi, Yoshinobu*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Sakamoto, Ayako; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Shimizu, Kikuo*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 105, 2013/01
 spp.
spp.Uyama, Yoshihide*; Oya, Hirotaka*; Amano, Yoshinori*; Kashimoto, Koichi*; Hatano, Shoji*; Nozawa, Shigeki; Yoshihara, Ryohei*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 102, 2013/01
Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Okada, Tomoyuki*; Asami, Itsuo*; Nagatani, Takeshi*; Matsuo, Yoichi*; Kanazawa, Akira*; Honda, Kazushige*; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 95, 2013/01
Hase, Yoshihiro; Yoshihara, Ryohei; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 731(1-2), p.41 - 47, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:69.59(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)To gain insight into the mutagenic effects of accelerated heavy ions in plants, the mutagenic effects of carbon ions near the range end (mean LET: 425 keV/ m) were compared with the effects of carbon ions penetrating the seeds (mean LET: 113 keV/
m) were compared with the effects of carbon ions penetrating the seeds (mean LET: 113 keV/ m). Mutational analysis by plasmid rescue of
m). Mutational analysis by plasmid rescue of 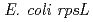 from irradiated Arabidopsis plants showed a 2.7-fold increase in mutant frequency for 113 keV/
from irradiated Arabidopsis plants showed a 2.7-fold increase in mutant frequency for 113 keV/ m carbon ions, whereas no enhancement of mutant frequency was observed for carbon ions near the range end. This suggested that carbon ions near the range end induced mutations that were not recovered by plasmid rescue. An Arabidopsis DNA ligase IV mutant, deficient in non-homologous end-joining repair, showed hyper-sensitivity to both types of carbon-ion irradiation. The difference in radiation sensitivity between the wild type and the repair-deficient mutant was greatly diminished for carbon ions near the range end, suggesting that these ions induce irreparable DNA damage. Mutational analysis of the Arabidopsis
m carbon ions, whereas no enhancement of mutant frequency was observed for carbon ions near the range end. This suggested that carbon ions near the range end induced mutations that were not recovered by plasmid rescue. An Arabidopsis DNA ligase IV mutant, deficient in non-homologous end-joining repair, showed hyper-sensitivity to both types of carbon-ion irradiation. The difference in radiation sensitivity between the wild type and the repair-deficient mutant was greatly diminished for carbon ions near the range end, suggesting that these ions induce irreparable DNA damage. Mutational analysis of the Arabidopsis 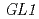 locus showed that while the frequency of generation of glabrous mutant sectors was not different between the two types of carbon-ion irradiation, large deletions (
locus showed that while the frequency of generation of glabrous mutant sectors was not different between the two types of carbon-ion irradiation, large deletions (
 30 kb) were six times more frequently induced by carbon ions near the range end. This suggests that the proportion of large deletions increases with LET in plants.
30 kb) were six times more frequently induced by carbon ions near the range end. This suggests that the proportion of large deletions increases with LET in plants.
Shakinah, S.*; Zaiton, A.*; Affrida, A. H.*; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Hase, Yoshihiro; Ono, Yutaka
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 102, 2012/01