Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakajima, Toru; Ogata, Manabu; Uchida, Mao; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Tanaka, Kiriha; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-035, 29 Pages, 2024/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2024. The objectives and contents of this research are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ishikawa, Norito
2023-Nendo Daigaku Kenkyu Josei Gijutsu Kenkyu Hokokusho, p.123 - 134, 2024/03
Evaluation of corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement is important in the quality control of stainless steel and the development of next steel materials assuming a high-pressure hydrogen environment. Typically, a secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS) is used to analyze hydrogen in steel materials. The hydrogen concentration of conventional standard substance for hydrogen analysis is as small as 1wt-ppm, which has been a problem in hydrogen analysis. We use a hydrogen-implant method to create a locally higher hydrogen concentration than that of the conventional. Hydrogen concentration analysis has been evaluated using the nuclear reaction analysis (NRA) method at a tandem accelerator. We have succeeded in creating a sample with a higher hydrogen concentration of about 1,900 wt-ppm than that of the conventional in locally.
Ishikawa, Norito; Fukuda, Shoma; Nakajima, Toru; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Fujimura, Yuki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Materials, 17(3), p.547_1 - 547_21, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.76(Chemistry, Physical)Natural monoclinic zirconia (baddeleyite) was irradiated with 340-MeV Au ions, and the irradiation-induced nanostructures (i.e., ion tracks and nanohillocks) were observed using transmission electron microscopy. The diameter of the nanohillocks is approximately 10 nm, which is similar to the maximum molten region size calculated using the analytical thermal spike model. Ion tracks are imaged as strained regions that maintain their crystalline structure. The cross-sections of most of the ion tracks are imaged as parallelopiped or rectangular contrasts as large as 10 nm. These results strongly indicate that the molten region is recrystallized anisotropically, reflecting the lattice structure. Furthermore, low-density track cores are formed in the center of the ion tracks. The formation of low-density track cores can be attributed to the ejection of molten matter toward the surface.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Fujita, Natsuko; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Fukuda, Shoma; Nakajima, Toru; Kagami, Saya; Ogata, Manabu; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-017, 27 Pages, 2023/10
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2023. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2023 are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Ishihara, Takanori; Ogawa, Hiroki; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Tsuyoshi; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogata, Manabu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2023-005, 78 Pages, 2023/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 1st fiscal year of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
 irradiated with swift heavy ions at grazing incidence
irradiated with swift heavy ions at grazing incidenceIshikawa, Norito; Fujimura, Yuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Szabo, G. L.*; Wilhelm, R. A.*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Nanotechnology, 33(23), p.235303_1 - 235303_10, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:53.46(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A single crystal of SrTiO doped with niobium (Nb-STO) was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at grazing incidence. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used to study the relation between irradiation-induced change of surface topography and corresponding material property changes. As expected, multiple hillocks as high as 5-6 nm are imaged by AFM observation. It is also found that the region in between the adjacent hillocks is slightly elevated rather than depressed. Line-like contrasts along the ion paths are found in both AFM phase images and SEM images, indicating the formation of continuous ion tracks in addition to multiple hillocks. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation shows that the ion tracks in the near-surface region are found to be relatively large, whereas buried ion tracks in the deeper region are relatively small. The results suggest that recrystallization plays an important role in the formation of small ion tracks in the deep region, whereas formation of large ion tracks in the near-surface region is likely due to the absence of recrystallization.
doped with niobium (Nb-STO) was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at grazing incidence. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used to study the relation between irradiation-induced change of surface topography and corresponding material property changes. As expected, multiple hillocks as high as 5-6 nm are imaged by AFM observation. It is also found that the region in between the adjacent hillocks is slightly elevated rather than depressed. Line-like contrasts along the ion paths are found in both AFM phase images and SEM images, indicating the formation of continuous ion tracks in addition to multiple hillocks. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation shows that the ion tracks in the near-surface region are found to be relatively large, whereas buried ion tracks in the deeper region are relatively small. The results suggest that recrystallization plays an important role in the formation of small ion tracks in the deep region, whereas formation of large ion tracks in the near-surface region is likely due to the absence of recrystallization.
Nemoto, Miho*; Ebine, Noriya; Okamoto, Akiko; Hosaka, Yasuhisa*; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Terada, Hiroaki; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Togawa, Orihiko
JAEA-Technology 2021-013, 41 Pages, 2021/08
When North Korea has carried out nuclear tests, Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) predicts atmospheric dispersion of radionuclides by using the WSPEEDI-II upon requests from Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) and submits the predicted results to NRA in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Center (NSEC). This is a part of the activity of NEAT supporting the Japanese Government in emergency responses. The WSPEEDI-II automatic calculation system specialized for responses to nuclear tests by North Korea was developed by NSEC and was used for responses to three nuclear tests from February 2013 to September 2017. This report describes the transfer and installation of the calculation system to NEAT, and the subsequent maintenance and operation. Future issues for responses to nuclear tests are also described in this report.
 in NaCl
in NaClAoyama, Takahito; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Metals, 11(3), p.511_1 - 511_13, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effect of Cu in bulk solution on pitting corrosion resistance of extra high purity type 316 stainless steel was investigated. Pitting occurred in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
in bulk solution on pitting corrosion resistance of extra high purity type 316 stainless steel was investigated. Pitting occurred in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl whereas pitting was not initiated in 0.1 M NaCl. Although deposition of Cu
whereas pitting was not initiated in 0.1 M NaCl. Although deposition of Cu on the surface occurred regardless of potential region in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
on the surface occurred regardless of potential region in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl , Cu
, Cu in bulk solution had no influence on the passive film formation. The decrease in pitting corrosion resistance in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
in bulk solution had no influence on the passive film formation. The decrease in pitting corrosion resistance in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl resulted from the deposited Cu or Cu compound and continuous supply of Cu
resulted from the deposited Cu or Cu compound and continuous supply of Cu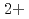 on the surface.
on the surface.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ioka, Ikuo
QST-M-29; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2019, P. 71, 2021/03
The objective of our research is to clarify corrosion acceleration mechanism of materials under the gamma-ray radiation environment. The irradiation experiment was conducted for 30 mins at the gamma-ray irradiation facility of Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute of QST. During the gamma-ray irradiation, pH decreases, and also the electric conductivity showed a tendency to increase. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide in water was measured after irradiation and was about 3.5 10
10 wt%. When the concentration is less than 10 wt%, the pH value decreases with increasing the concentration. A pH of 3.5
wt%. When the concentration is less than 10 wt%, the pH value decreases with increasing the concentration. A pH of 3.5 10
10 wt% hydrogen peroxide water was 5.58. This was almost same as the pH value (5.56) of purified water. It seems that the decrease of pH after irradiation is not able to explain by the production of hydrogen peroxide.
wt% hydrogen peroxide water was 5.58. This was almost same as the pH value (5.56) of purified water. It seems that the decrease of pH after irradiation is not able to explain by the production of hydrogen peroxide.
Fujimoto, Shinji*; Tsuchiya, Hiroaki*; Ogawa, Soma*; Iida, Yoshihisa; Taniguchi, Naoki
Materials and Corrosion, 72(1-2), p.333 - 338, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of pure copper in bentonite was examined by a slow strain rate test (SSRT). The bentonite was swollen with pure water or aqueous solutions containing NH of 0.05 M and 0.1 M. The thick corrosion films and particulate deposits were formed on copper surface after SSRT. Typical tarnish rupture type SCC occurred on pure copper in swollen bentonite with and without NH
of 0.05 M and 0.1 M. The thick corrosion films and particulate deposits were formed on copper surface after SSRT. Typical tarnish rupture type SCC occurred on pure copper in swollen bentonite with and without NH . Crack propagation rate was enhanced by NH
. Crack propagation rate was enhanced by NH . It is confirmed thick oxide layer is formed on copper during plastic deformation which resulting in the tarnish crack type SCC. The many particulate deposits observed on the surface might be formed as a results of rapid dissolution of Cu
. It is confirmed thick oxide layer is formed on copper during plastic deformation which resulting in the tarnish crack type SCC. The many particulate deposits observed on the surface might be formed as a results of rapid dissolution of Cu to form porous CuO at locallized deformed sites.
to form porous CuO at locallized deformed sites.
Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Ogawa, Hiroaki
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(4), p.43_1 - 43_14, 2020/12
Amorphizable ceramics were irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions, and the as-irradiated samples were observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ion track diameter and hillock diameter are similar for all the amorphizable ceramics. For SrTiO and niobium-doped STO, 200 MeV Au ion irradiation and TEM observation were also performed. The ion track diameters in these materials are found to be markedly smaller than the hillock diameters. The ion tracks in these materials exhibit inhomogeneity, which is similar to that reported for non-amorphizable ceramics. On the other hand, the hillocks appear to be amorphous, and the amorphous feature is in contrast to the crystalline feature of hillocks observed in non-amorphizable ceramics. No marked difference is recognized between the nanostructures in STO and those in Nb-STO.
and niobium-doped STO, 200 MeV Au ion irradiation and TEM observation were also performed. The ion track diameters in these materials are found to be markedly smaller than the hillock diameters. The ion tracks in these materials exhibit inhomogeneity, which is similar to that reported for non-amorphizable ceramics. On the other hand, the hillocks appear to be amorphous, and the amorphous feature is in contrast to the crystalline feature of hillocks observed in non-amorphizable ceramics. No marked difference is recognized between the nanostructures in STO and those in Nb-STO.
Aihara, Jun; Yasuda, Atsushi*; Ueta, Shohei; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Honda, Masaki*; Ohira, Koichi*; Tachibana, Yukio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 18(4), p.237 - 245, 2019/12
Development of fabrication and inspection technologies of oxidation resistant fuel element for improvement of safety of high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs) in severe oxidation accident was carried out. Simulated coated fuel particles (CFPs), alumina particles, were over-coated with mixed powder of Si, C and small amount of resin to form over-coated particles, and over-coated particles were molded and hot-pressed to sinter simulated oxidation resistant fuel elements with SiC/C mixed matrix. Simulated oxidation resistant fuel elements with matrix whose Si/C mole ratio is 1.00 were fabricated. Failure fraction of CFPs in fuel elements is one of very important inspection subjects of HTGR fuel. It is essential that CFPs are extracted from fuel elements without additional failure. Development of method for extraction of CFPs was carried out. Desolation of SiC by KOH method or pressurized acidolysis method should be applied to extraction of CFPs.
Aihara, Jun; Honda, Masaki*; Ueta, Shohei; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ohira, Koichi*; Tachibana, Yukio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 18(1), p.29 - 36, 2019/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency carried out development of fabrication technology of oxidation resistant fuel element for improvement of safety of high temperature gas-cooled reactors in serious oxidation accident, based on precursor research in former JAEA. Dummy coated fuel particles (alumina particles) were over-coated with mixed powder of Si, C and small amount of resin to form over-coated particles, and over-coated particles were molded and hot-pressed to sinter dummy oxidation resistant fuel elements with SiC/C mixed matrix. We fabricated dummy oxidation resistant fuel elements with matrix whose Si/C mole ratio (about 0.551) is three times as large as that in precursor research. Si peak was not detected by X-ray diffraction of matrix. Better oxidation resistant was confirmed with oxidation test in 20% O at 1673 K than that of ordinal fuel compact with ordinal graphite/carbon matrix. All dummy coated fuel particles were held in specimen after 10 h oxidation.
at 1673 K than that of ordinal fuel compact with ordinal graphite/carbon matrix. All dummy coated fuel particles were held in specimen after 10 h oxidation.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Uchibori, Yosuke*; Wakeshima, Makoto*; Hinatsu, Yukio*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Yano, Masahiro; Asaoka, Hidehito
RSC Advances (Internet), 8(66), p.37600 - 37605, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:39.98(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We present a quantitative study on the effect of a newly obtained thermal history on the formation of Fe-N-C catalytic sites. A short and repeated heating process is employed as the new thermal history, where short heating (1 min) followed by quenching is applied to a sample with arbitrary repetition. Through electrochemical quantitative analysis, it is found that the new process effectively increases the Fe-N-C mass-based site density (MSD) to almost twice that achieved using a conventional continuous heating process, while the turn-over frequency (TOF) is independent of the process. Elemental analysis shows that the new process effectively suppresses the thermal desorption of Fe and N atoms during the initial formation stage and consequently contributes to an increase in the Fe-N-C site density. The resultant catalytic activity (gravimetric kinetic current density (0.8 V vs. RHE)) is 1.8 times higher than that achieved with the continuous heating process.
Ishizaki, Shuhei; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Terada, Hiroaki; Togawa, Orihiko
JAEA-Technology 2018-007, 43 Pages, 2018/10
When North Korea has carried out a nuclear test, by a request from Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) predicts atmospheric dispersion of radionuclides by WSPEEDI-II system in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Center (NSEC), and submits the predicted results to NRA as the activity to assist responses by the Japanese Government. This report explains frameworks of the Japanese Government and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to cope with nuclear tests by North Korea, and describes a series of activities by NEAT regarding predictions of atmospheric dispersion of radionuclides in response to the 5th and 6th nuclear tests carried out by North Korea in September 2016 and September 2017. Future plans and issues to be solved for responses to nuclear tests are also described in this report, together with an outline of a computer program system used in the predictions.
Hino, Ryutaro; Takegami, Hiroaki; Yamazaki, Yukie; Ogawa, Toru
JAEA-Review 2016-038, 294 Pages, 2017/03
In the aftermath of the Fukushima nuclear accident, safety measures against hydrogen in severe accident have been recognized as a serious technical problem in Japan. Therefore, efforts have begun to form a common knowledge base between nuclear engineers and experts on combustion and explosion, and to secure and improve future nuclear energy safety. As one of such activities, we have prepared the "Handbook of Advanced Nuclear Hydrogen Safety" under the Advanced Nuclear Hydrogen Safety Research Program funded by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. The concepts of the handbook are as follows: to show advanced nuclear hydrogen safety technologies that nuclear engineers should understand, to show hydrogen safety points to make combustion-explosion experts cooperate with nuclear engineers, to expand information on water radiolysis considering the situation from just after the Fukushima accidents and to the waste management necessary for decommissioning after the accident, etc.
Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Hatae, Takaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Takeuchi, Masaki; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.1012 - 1016, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Domestic Agency (JADA) is responsible for six diagnostic systems in the ITER project. We have successfully developed an instrumentation and control (I&C) system for the diagnostic systems. The I&C system manages internal operations for measurement such as health checks of sensors, configuration of measurement parameters, and consistency checks between measurement parameters. We developed a conversion tool to convert operational flowcharts to EPICS records. The sequencing management function coordinates the execution of operation steps by monitoring changes in the record values. It was designed so that the relationship between the records and steps is determined automatically according to the flowcharts as much as possible. We validated the performance of the I&C system for the thermocouple measurement system, and are continuing the development of even more complex I&C systems for other JADA diagnostic systems.
Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Maruyama, Toshiyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Itami, Kiyoshi; Casal, N.*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10(Sp.2), p.3402044_1 - 3402044_4, 2015/04
Takeuchi, Masaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ishikawa, Masao; Shimada, Takahiko; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 8(Sp.1), p.2402147_1 - 2402147_5, 2013/11
Divertor IR Thermography is one of the diagnostics which Japan is in charge of development in ITER project. The conceptual design has been performed so far, and the progress is reported here. By reducing the size of mirrors, and making the optical path a labyrinthine structure, the design of a new optics that fills requirements of both spatial resolution and neutron shielding has been advanced. To achieve the required measurement accuracy, the detected signal and the noises such as bremsstrahlung light, detector noise and thermal noise of optical components were evaluated. Higher photons than the bremsstrahlung light are obtained, excluding the low temperature range. The simulation calculation of reflection from wall was started. Detailed method of data processing of deriving the profiles of surface temperature in the divertor plates from the observed signals and in-situ calibration strategies of the optical system are important issues and will be discussed.
Okayasu, Yuichi*; Tomizawa, Hiromitsu*; Matsubara, Shinichi*; Sato, Takahiro*; Ogawa, Kanade*; Togashi, Tadashi*; Takahashi, Eiji*; Minamide, Hiroaki*; Matsukawa, Ken*; Aoyama, Makoto; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2012) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2012/10
no abstracts in English