Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirata, Yuho; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Parisi, A.*; Uritani, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(7), p.915 - 924, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:88.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)The reliability of dose assessment with radiation detectors is an important feature in various fields, such as radiotherapy, radiation protection, and high-energy physics. However, many detectors irradiated by high linear energy transfer (LET) radiations exhibit decreased efficiency called the quenching effect. This quenching effect depends not only on the particle LET but strongly on the ion species and its microscopic pattern of energy deposition. Recently, a computational method for estimating the relative efficiency of luminescence detectors was proposed following analysis of microdosimetric specific energy distributions simulated using the particle and heavy ion transport code system (PHITS). This study applied the model to estimate the relative optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) efficiency of BaFBr:Eu detectors. Additionally, we measured the luminescence intensity of BaFBr:Eu detectors exposed to  He,
He,  C and
C and  Ne ions to verify the calculated data. The model reproduced the experimental data in the cases of adopting a microdosimetric target diameter of approximately 30-50 nm. The calculated relative efficiency exhibit ion-species dependence in addition to LET. This result shows that the microdosimetric calculation from specific energy is a successful method for accurately understanding the results of OSL measurements with BaFBr:Eu detectors irradiated by various particles.
Ne ions to verify the calculated data. The model reproduced the experimental data in the cases of adopting a microdosimetric target diameter of approximately 30-50 nm. The calculated relative efficiency exhibit ion-species dependence in addition to LET. This result shows that the microdosimetric calculation from specific energy is a successful method for accurately understanding the results of OSL measurements with BaFBr:Eu detectors irradiated by various particles.
Wakui, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Naoe, Takashi; Hanano, Kohei*; Haga, Katsuhiro; Shimada, Tsubasa*; Kanomata, Kenichi*
Materials Science Forum, 1024, p.145 - 150, 2021/03
To realize a high beam power operation at the J-PARC, a mercury target vessel covered with water shroud was developed. In the first step, to realize an operation at 500 kW, the basic structure of the initial design was followed and the connection method between the mercury vessel and the water shroud was changed. Additionally, the operation at a beam power of 500 kW was realized in approximately eight months. In the second step, to realize the operation at 1 MW, the new structure in which only rear ends of vessels were connected was investigated. Cooling of the mercury vessel is used to reduce thermal stress and thick vessels of the water shroud are used to increase stiffness for the internal pressure; therefore, it was adopted. The stress in each vessel was lower than the allowable stress based on the pressure vessel code criteria prescribed in the Japan Industrial Standard, and confirmation was obtained that the operation with a beam power of 1 MW could be conducted.
Wakui, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Naoe, Takashi; Hanano, Kohei; Haga, Katsuhiro; Takada, Hiroshi; Shimada, Tsubasa*; Kanomata, Kenichi*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.081002_1 - 081002_6, 2020/02
A mercury target vessel of J-PRAC is designed with a triple-walled structure consisting of the mercury vessel and a double-walled water shroud with internal and external vessels. During the beam operation at 500 kW in 2015, small water leakages from a water shroud of the mercury target vessel occurred twice. Design, fabrication and inspection processes were improved based on the lessons learned from the target failures. The total length of welding lines at the front of the mercury target vessel decreases drastically to approximately 55% by adopting monolithic structure cut out from a block of stainless steel by the wire-electrical discharge machining. Thorough testing of welds by radiographic testing and ultrasonic testing was conducted. The fabrication of the mercury target vessel #8 was finished on September 2017 and the beam operation using it started. Stable beam operation at 500 kW has been achieved and it could experience the maximum beam power of 1 MW during a beam test.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Yasue, Kenichi*; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Saiga, Atsushi; Shimizu, Mayuko; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-008, 83 Pages, 2018/12
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 2nd fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Wakui, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi; Naoe, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro; Takada, Hiroshi; Shintaku, Yohei*; Li, T.*; Kanomata, Kenichi*
Choompa Techno, 30(5), p.16 - 20, 2018/10
A mercury target vessel has been used for the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. It has a complicated multi-layered structure composed of a mercury target and a surrounding double-walled water shroud, which is assembled with thin plates (minimum thickness of 3 mm) by welding. Thus, welding inspection during the manufacturing process is important. We investigated the applicability of new ultrasonic inspections using specimens (thickness of 3 mm) with defects to improve the accuracy of welding inspection for the mercury target vessel. Immersion ultrasonic testing using a probe (frequency of 50 MHz) could detect a spherical defect with a diameter of 0.2 mm. The size was smaller than target value of 0.4 mm. The length of unwelded region estimated using the phased array ultrasonic testing corresponded with the actual length (0.8 - 1.5 mm).
Wakui, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi; Naoe, Takashi; Shintaku, Yohei*; Li, T.*; Murakami, Kazuya*; Kanomata, Kenichi*; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro; Takada, Hiroshi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 506, p.3 - 11, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.93(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The mercury target vessel is designed as multi-walled structure with thin wall (min. 3 mm), and assembled by welding. In order to estimate the structural integrity of the vessel, it is important to measure the defects in welding accurately. For nondestructive tests of the welding, radiographic testing is applicable but it is difficult to detect for some defect shapes. Therefore it is effective to do ultrasonic testing together with it. Because ultrasonic methods prescribed in JIS inspect on the plate with more than 6 mm in thickness, these methods couldn't be applied as the inspection on the vessel with thin walls. In order to develop effective method, we carried out measurements using some testing method on samples with small defect whose size is specified. In the case of the latest phased array method, measured value agreed with actual size. It was found that this method was applicable to detect defects in the thin-walled structure for which accurate inspection was difficult so far.
Furuta, Takuya; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Ishikawa, Kenichi*; Noda, Shigeho*; Takagi, Shu*; Maeyama, Takuya*; Fukunishi, Nobuhisa*; Fukasaku, Kazuaki*; et al.
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Mathematics and Computation, Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and the Monte Carlo Method (M&C + SNA + MC 2015) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2015/04
In Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System PHITS, two parallel computing functions are prepared to reduce the computational time. One is the distributed-memory parallelization using message passing interface (MPI) and the other is the shared-memory parallelization using OpenMP directives. Each function has advantages and disadvantages, and thus, by adopting both functions in PHITS, it is possible to conduct parallel computing suited for needs of users. It is also possible to conduct the hybrid parallelization by the intra-node OpenMP parallelization and the inter-node MPI parallelization in supercomputer systems. Each parallelization functions were explained together with some application results obtained using a workstation and a supercomputer system, K computer at RIKEN.
 C-photoassimilate flow using positron-emitting tracer imaging system
C-photoassimilate flow using positron-emitting tracer imaging systemSuzui, Nobuo; Kawachi, Naoki; Ishii, Satomi; Yin, Y.-G.; Iwasaki, Aya*; Ogawa, Kenichi*; Fujimaki, Shu
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 105, 2015/03
Iguchi, Masahide; Saito, Toru; Kawano, Katsumi; Chida, Yutaka; Nakajima, Hideo; Ogawa, Tsuyoshi*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Ogata, Hiroshige*; Minemura, Toshiyuki*; Tokai, Daisuke*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(9-10), p.2520 - 2524, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:64.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)ITER TFC structures are large welding structures made of heavy thick stainless steels. JAEA plans to apply narrow gap TIG welding with FMYJJ1 which is full austenitic stainless filler material to manufacture TFC structure. FMYJJ1 is specified in "Codes for Fusion Facilities -Rules on Superconducting Magnet Structure (2008)". In order to evaluate effect of base material combinations and thickness of welded joint on tensile properties at 4 K, tensile tests were conducted at 4 K by using tensile specimens taken from 40 mm thickness weld joints of four combinations and 200 mm thickness ones of two combinations of base materials. These weld joints were manufactured by one side narrow gap TIG welding with FMYJJ1. As the results, it was confirmed that yield and tensile strengths of welded joint at 4K were decreased with decreasing of nitrogen of base material, and there were no large distribution of strengths at 4 K along the thickness of welded joints of 200 mm thickness.
Kurihara, Kenichi; Ogawa, Yuichi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 55(4), p.225 - 230, 2013/04
, 55(4), p.225 - 230, 2013/04
no abstracts in English
Kawachi, Naoki; Koyanagi, Atsushi*; Suzui, Nobuo; Ishii, Satomi; Yin, Y.-G.; Yamazaki, Haruaki; Iwasaki, Aya*; Ogawa, Kenichi*; Fujimaki, Shu
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 93, 2013/01
Iguchi, Masahide; Chida, Yutaka; Takano, Katsutoshi; Kawano, Katsumi; Saito, Toru; Nakajima, Hideo; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Minemura, Toshiyuki*; Ogata, Hiroshige*; Ogawa, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 22(3), p.4203305_1 - 4203305_5, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:48.95(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has responsibility to procure 19 structures for ITER toroidal field (TF) coils as in-kind components. JAEA plans to use materials specified in the material section of "Codes for Fusion Facilities; Rules on Superconducting Magnet Structure (2008)" issued by the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers (JSME) in 2008. Large forged products were produced and their mechanical properties at 4K were evaluated. In addition, the following activities have been performed; (1) to optimize the design of each weld type identified in the manufacturing sequence, (2) to qualify typical welding procedure including repair, (3) to establish welding techniques other than narrow gap TIG welding with FMYJJ1, (4) to demonstrate the manufacturing procedures through manufacture of 1-m mockups and full-scale segments of TFC structure. This paper describes the results of material qualification and industrialization activities of manufacturing processes of ITER TFC structure.
Sakai, Kenji; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Seki, Masakazu; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Naoe, Takashi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Tatsumoto, Hideki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-039, 121 Pages, 2012/03
This report investigates the behavior, damage and restoration of a neutron source station of the MLF at the Great East Japan Earthquake and verified the safety design for emergency accidents in the neutron source station. In the MLF, after an occurrence of the Earthquake, strong quakes were detected at the instruments, the external power supply was lost, all of the circulators shut down automatically, and the hydrogen gas was released. The leakages of mercury, hydrogen and radio-activation gases did not occur. While, the quakes made gaps between the shield blocks and ruptured external pipe lines by subsidence around the building. But significant damages to the components were not found though the pressure drop of compressed air lines influenced on a target trolley lock system and so on. These results substantiated the validity of the safety design for emergency accidents in the source station, and suggested several points of improvement.
Sakai, Kenji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Takada, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Seki, Masakazu; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of 20th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-20) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/03
This report investigates behaviors and damages of each component in a neutron target station of the MLF at the J-PARC at the time of the Great East Japan Earthquake (GEJE). At the date of the GEJE, in the MLF, strong quakes were detected at several instruments, an external power supply were lost, all of the circulation systems were shut down automatically, and a hydrogen gas was released as planned. Leakage of activation liquids and gases did not occur. While, the quakes made gaps between shield blocks and ruptured external pipe lines for air and water by subsidence. But significant damages on the components of the target station were not found though a loss of compressed air supply affected lock systems with air cylinders and pneumatic operation values. These results substantiated a validity of safety design on the target station for emergency accidents.
Iguchi, Masahide; Chida, Yutaka; Nakajima, Hideo; Ogawa, Tsuyoshi*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Ogata, Hiroshige*; Minemura, Toshiyuki*; Miyabe, Keisuke*; Tokai, Daisuke*; Niimi, Kenichiro*
Teion Kogaku, 47(3), p.193 - 199, 2012/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted qualification and rationalization activities in Japan in order to rationalize manufacturing procedure of ITER Toroidal Field (TF) coil structures. The activities included qualification of structural materials and qualification of welding procedure according to Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers (JSME) code constituted for fusion devices, demonstration of the manufacturing method and procedures through full-scale segments of TF coil structure. From results of these activities, JAEA confirmed applicability of JSME code to actual series TF coil structures as quality control method hence the quality of structural materials and weld joints of Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) were satisfied ITER requirement. In addition, JAEA obtained knowledge of welding deformation of actual TF coil structures. This paper describes results of these qualification and development activities for TF coil structure.
Kawachi, Naoki; Suzui, Nobuo; Ishii, Satomi; Yamazaki, Haruaki; Iwasaki, Aya*; Ogawa, Kenichi*; Fujimaki, Shu
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 93, 2012/01
Torii, Tatsuo; Sugita, Takeshi; Kamogawa, Masashi*; Watanabe, Yasuyuki*; Kusunoki, Kenichi*
Geophysical Research Letters, 38(24), p.L24801_1 - L24801_5, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:83.48(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We identify a migrating source of high energy radiation, lasting for several minutes, attributed to thunderstorm activities through the observations of radiation, atmospheric electric field, and meteorological radar echoes at several points. Our findings indicate that the energetic radiation is emitted continuously from a downward hemispherical surface without lightning, the bottom of which is about 300 m above sea level, and this source of radiation moves from north to south above the observation site at a speed of about 7 m/s. The radiation source probably moves along with the negatively charged region of the cloud at the height of around 1 km, because the estimated migration of the radiation source is consistent with the observed movement of atmospheric electric field variation between ground-based observation sites and with the wind speed and direction at about 1 km altitude. This movement implies that the intensive electric field produced by the charged region in the thundercloud generates a radiation source. In addition, our results suggest that the low altitude of radiation source is related to no lightning activity during the energetic radiation emission.
 C translocation using positron-emitting tracer imaging system
C translocation using positron-emitting tracer imaging systemKawachi, Naoki; Suzui, Nobuo; Ishii, Satomi; Ito, Sayuri; Ishioka, Noriko; Yamazaki, Haruaki; Iwasaki, Aya*; Ogawa, Kenichi*; Fujimaki, Shu
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 648(Suppl.1), p.S317 - S320, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.40(Instruments & Instrumentation) collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 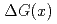 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.