Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
植田 祥平; 水田 直紀; 深谷 裕司; 後藤 実; 橘 幸男; 本田 真樹*; 齋木 洋平*; 高橋 昌史*; 大平 幸一*; 中野 正明*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 357, p.110419_1 - 110419_10, 2020/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:8.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)固有の安全性に優れ高効率なプルトニウムの利用が可能なプルトニウム燃焼高温ガス炉が提案されている。プルトニウム燃焼高温ガス炉に用いるセキュリティ強化型安全(3S-TRISO)燃料においては、イットリア安定化ジルコニア(YSZ)を不活性母材とするPuO -YSZ燃料核へ、遊離酸素ゲッターの特性を有する炭化ジルコニウム(ZrC)を直接被覆する。本論文では、プルトニウム燃焼高温ガス炉の成立性および3S-TRISO燃料の研究開発について報告する。
-YSZ燃料核へ、遊離酸素ゲッターの特性を有する炭化ジルコニウム(ZrC)を直接被覆する。本論文では、プルトニウム燃焼高温ガス炉の成立性および3S-TRISO燃料の研究開発について報告する。
永井 崇之; 小林 秀和; 嶋村 圭介; 大山 孝一; 捧 賢一; 岡本 芳浩; 塩飽 秀啓; 山中 恵介*; 太田 俊明*
JAEA-Research 2018-005, 72 Pages, 2018/09
ガラス固化プロセスで製造されるガラス固化体中の原料ガラス成分や廃棄物成分の局所構造は、固化体に含まれる廃棄物成分による影響を受ける。本研究は、リン添加ホウケイ酸ガラスを原料ガラスに用いて模擬廃棄物ガラス試料を作製し、放射光XAFS測定によりガラス成分の軽元素や廃棄物成分の希土類元素等の化学状態及び局所構造を評価した。
北条 公伸*; 林 翔太郎*; 西 亘*; 釜谷 昌幸*; 勝山 仁哉; 眞崎 浩一*; 永井 政貴*; 岡本 年樹*; 高田 泰和*; 吉村 忍*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 3(4), p.16-00083_1 - 16-00083_16, 2016/08
鋳造ステンレス鋼に対する非破壊検査が計画されているが、鋳造ステンレス鋼のような二相ステンレス鋼では、超音波の低い透過性などの理由から、許容欠陥寸法が定められていない。鋳造ステンレス鋼の許容欠陥寸法を合理的に決定するためには、確率論的破壊力学(PFM)は有用である。本研究では、鋳造ステンレス鋼配管を対象に、PFM解析コードの適用性や信頼性に係るベンチマーク問題を提案した。破損モードとしては、疲労亀裂進展、塑性崩壊、及び延性亀裂進展を考慮し、それらの相互作用を考慮した条件でPFM解析を行った。6機関が参加して実施されたベンチマーク解析による破損確率の比較を行った。その結果、各機関で様々なPFM解析コードで得られた破損確率はよく一致し、鋳造ステンレス鋼配管に対するPFMの適用性が確認された。
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*; et al.
Proceedings of 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '14) (Internet), p.28 - 33, 2014/07
Three-dimensional (3D) cooling of 40-keV  Mg
Mg ion beams with Doppler laser cooling and the coupling resonance has been demonstrated in the storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University toward the production of ultralow-emittance beams, in other words, ultracold beams and so-called crystalline beams. So far, the transverse temperatures of 6 K and 2 K have been experimentally attained in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, at a low beam intensity of about
ion beams with Doppler laser cooling and the coupling resonance has been demonstrated in the storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University toward the production of ultralow-emittance beams, in other words, ultracold beams and so-called crystalline beams. So far, the transverse temperatures of 6 K and 2 K have been experimentally attained in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, at a low beam intensity of about 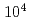 ions in the ring. These temperatures are the lowest ever attained by laser cooling of ion beams. Systematic molecular dynamics simulations predict the realization of further lower temperatures,
ions in the ring. These temperatures are the lowest ever attained by laser cooling of ion beams. Systematic molecular dynamics simulations predict the realization of further lower temperatures,  1 mK and
1 mK and  0.1 K in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, if the laser spot size and detuning are properly adjusted even with such a low laser power (
0.1 K in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, if the laser spot size and detuning are properly adjusted even with such a low laser power ( 10 mW) as utilized in the experiments at S-LSR. A 3D ordered state of the beam with 3D laser cooling is also predicted. Recent experimental achievements and latest simulation results are presented.
10 mW) as utilized in the experiments at S-LSR. A 3D ordered state of the beam with 3D laser cooling is also predicted. Recent experimental achievements and latest simulation results are presented.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.143 - 145, 2014/06
We have experimentally demonstrated transverse indirect laser cooling utilizing synchro-betatron resonance coupling in the ion accumulation cooler ring S-LSR. However, its efficiency was rather poor for relatively high beam intensity of 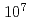 ions in the ring due to beam heating by intra-beam scattering and its cooling time was as long as 100 s. By application of beam scraping and optimization of laser detuning together with equilibrium deceleration with the use of an induction accelerator, we could reach the lowest transverse temperatures ever attained by laser cooling as 7.0 K and 2.1 K for the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The prospect of generating an ultra-low-temperature beam and realizing beam crystallization will be discussed on the basis of the present result.
ions in the ring due to beam heating by intra-beam scattering and its cooling time was as long as 100 s. By application of beam scraping and optimization of laser detuning together with equilibrium deceleration with the use of an induction accelerator, we could reach the lowest transverse temperatures ever attained by laser cooling as 7.0 K and 2.1 K for the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The prospect of generating an ultra-low-temperature beam and realizing beam crystallization will be discussed on the basis of the present result.
佐藤 猛; 武藤 重男; 奥野 浩; 片桐 裕実; 秋山 聖光; 岡本 明子; 小家 雅博; 池田 武司; 根本内 利正; 斉藤 徹; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-046, 65 Pages, 2014/02
原子力機構は、指定公共機関として、国及び地方公共団体その他の機関に対し、災害対策又は武力攻撃事態等への対処において、防災業務計画及び国民保護業務計画に則り、技術支援をする責務を有している。原子力緊急時支援・研修センターは、緊急時には、専門家の派遣、防災資機材の提供、防護対策のための技術的助言等の支援活動を行う。また、平常時には、我が国の防災対応体制強化・充実のために、自らの訓練・研修の他、国、地方公共団体、警察、消防、自衛隊等の原子力防災関係者のための訓練・研修、原子力防災に関する調査研究及び国際協力を実施する。平成24年度においては、上記業務を継続して実施するとともに、国の原子力防災体制の抜本的見直しに対し、これまでに培った経験及び東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故への対応を通じた教訓等を活かし、国レベルでの防災対応基盤の強化に向け、専門家として技術的な支援を行うとともに、当センターの機能の維持・運営及び国との連携を図った自らの対応能力強化などに取り組んだ。なお、福島事故への対応については、人的・技術的な支援活動の主たる拠点が福島技術本部に移行することとなったため、平成24年9月をもって終了した。
榊 泰直; 西内 満美子; 前田 祥太; 匂坂 明人; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; 小倉 浩一; 深見 智代; 松川 兼也*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A705_1 - 02A705_4, 2014/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:10.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)高強度レーザーとプラズマの相互作用によるイオン発生において、電子特性の計測は不可欠である。そのため、様々な計測手法が提案されているが、今回我々は、光核中性子反応による中性子を計測することで、精度よく電子特性の計測を行う新規性の高い手法を提案する。この手法は、イオン加速エネルギー計測と共にピークパワー1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm のJ-KARENレーザーによって実証された。イオン加速エネルギーと本手法による計測結果は極めて相関をもつことがわかり、改良を重ねて行けば非常に良い計測器になり得ることがわかった。
のJ-KARENレーザーによって実証された。イオン加速エネルギーと本手法による計測結果は極めて相関をもつことがわかり、改良を重ねて行けば非常に良い計測器になり得ることがわかった。
百合 庸介; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; He, Z.*; 想田 光*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '13) (Internet), p.162 - 165, 2013/11
Efficient transverse laser cooling of a low-intensity heavy-ion beam has been recently accomplished experimentally by means of the resonant coupling method at the cooler storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University. In parallel with the experimental effort, multi-dimensional laser cooling of the ion beam has been studied also numerically with the molecular dynamics (MD) simulation code in which the stochastic interaction between ions and laser photons is incorporated in order to search optimum laser-cooling conditions and verify the results of the experiment. The present MD result demonstrates that, in spite of the limited experimental conditions of the cooling laser such as low power, fixed frequency, and short cooling section, a three-dimensionally low-temperature beam of 40-keV  Mg
Mg can be obtained through resonant coupling at a low intensity of
can be obtained through resonant coupling at a low intensity of 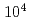 ions in the ring, which is consistent with the experimental result.
ions in the ring, which is consistent with the experimental result.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '13) (Internet), p.157 - 161, 2013/11
We have tried to approach to the lowest attainable beam temperature with laser cooling of a 40-keV  Mg
Mg ion beam at a cooler storage ring S-LSR, which has a superperiodicity of six and is designed to be tough against resonant perturbation to the circulating beam. The capability of active indirect transverse laser cooling has been experimentally demonstrated with the use of the theoretically-proposed synchro-betatron resonance coupling scheme. For the reduction of beam heating due to intrabeam scattering, an additional scheme has been established to control the intensity of the circulating beam down to
ion beam at a cooler storage ring S-LSR, which has a superperiodicity of six and is designed to be tough against resonant perturbation to the circulating beam. The capability of active indirect transverse laser cooling has been experimentally demonstrated with the use of the theoretically-proposed synchro-betatron resonance coupling scheme. For the reduction of beam heating due to intrabeam scattering, an additional scheme has been established to control the intensity of the circulating beam down to 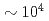 ions by scraping the outskirt of the beam with the use of a horizontally-moving scraper, which could cool the horizontal and vertical beam temperature down to
ions by scraping the outskirt of the beam with the use of a horizontally-moving scraper, which could cool the horizontal and vertical beam temperature down to 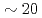 K and
K and 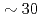 K, respectively, at an operation tune without horizontal-vertical (H-V) coupling. In the present paper, we would like to also present our recent results with H-V coupling in addition to longitudinal-horizontal coupling toward further reduction of the transverse beam temperature.
K, respectively, at an operation tune without horizontal-vertical (H-V) coupling. In the present paper, we would like to also present our recent results with H-V coupling in addition to longitudinal-horizontal coupling toward further reduction of the transverse beam temperature.
He, Z.*; Wei, J.*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of 25th North American Particle Accelerator Conference (NA-PAC '13) (Internet), p.1298 - 1300, 2013/09
The power of the cooling laser currently available in a compact ion cooler ring S-LSR, Kyoto University, is quite limited for generating ultralow-temperature ion beams. Therefore, parameters of laser cooling should be carefully determined in order to approach the lowest possible temperature in the experiment. This paper mainly concerns optimization of laser-cooling parameters and prediction of a possible lower limit of beam temperature in S-LSR, based on systematic molecular dynamics simulations. The adiabatic capture process of the ion beam was introduced to prevent the emittance from blowing up during bunching. The spot size of the laser was optimized with the total laser power limited. An optimum solenoid field strength was obtained for three-dimensional cooling. The lowest beam temperature achievable in S-LSR was predicted by choosing the parameters optimized.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; He, Z.*; Grieser, M.*; 野田 章*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(3), p.030202_1 - 030202_4, 2013/03
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:21.67(Physics, Applied)The efficiency of indirect transverse laser cooling of a heavy-ion beam using synchro-betatron resonant coupling (SBRC) was improved by the reduction of the beam intensity through scraping the tail part of the beam. In order to measure the beam size at low beam intensity, a new scheme was established where the beam profile was determined from the beam survival ratio by changing the insertion position of a beam scraper. At a beam intensity of 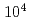 particles in the ring, the transverse cooling time of the beam was reduced to 1.2 s, and horizontal and vertical minimum beam sizes were 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm, corresponding to the beam temperatures of 20 K and 29 K, respectively. The cooling time was much improved compared with that of our previous experiment, 100 s at
particles in the ring, the transverse cooling time of the beam was reduced to 1.2 s, and horizontal and vertical minimum beam sizes were 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm, corresponding to the beam temperatures of 20 K and 29 K, respectively. The cooling time was much improved compared with that of our previous experiment, 100 s at 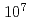 particles (Nakao et al.). The transverse temperature was comparable to that in other work (Madsen et al.), in spite of the limitation in the experimental conditions such as low laser power and short laser-cooling section. This suggests that the present SBRC scheme has a potential capacity for attaining a lower-temperature beam or even Coulomb crystallization.
particles (Nakao et al.). The transverse temperature was comparable to that in other work (Madsen et al.), in spite of the limitation in the experimental conditions such as low laser power and short laser-cooling section. This suggests that the present SBRC scheme has a potential capacity for attaining a lower-temperature beam or even Coulomb crystallization.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; Meshkov, I.*; Smirnov, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd Russian Particle Accelerator Conference (RuPAC 2012) (Internet), p.48 - 52, 2012/09
Various approaches to attaining low-temperature beams have been continued in the cooler storage ring S-LSR at Kyoto University. One-dimensional ordering of electron-cooled 7-MeV protons was realized with an abrupt longitudinal temperature jump from 2 K to 0.3 K at a particle number of around 2000. Laser cooling has been applied to 40-keV  Mg
Mg beams toward the realization of crystalline beams. For a coasting beam, the lowest longitudinal temperature of 3.6 K was attained at
beams toward the realization of crystalline beams. For a coasting beam, the lowest longitudinal temperature of 3.6 K was attained at 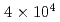 ions. The temperature was limited due to intra-beam scattering (IBS). On the other hand, the transverse temperature of the beam indirectly cooled through IBS was saturated at 500 K for
ions. The temperature was limited due to intra-beam scattering (IBS). On the other hand, the transverse temperature of the beam indirectly cooled through IBS was saturated at 500 K for 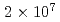 ions. In order to cool the transverse direction further, synchro-betatron resonance coupling has been applied to a bunched Mg beam. The transverse temperature has been reduced to the order of
ions. In order to cool the transverse direction further, synchro-betatron resonance coupling has been applied to a bunched Mg beam. The transverse temperature has been reduced to the order of 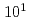 K at the beam intensity of
K at the beam intensity of 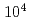 ions by the reduction of the beam intensity using a scraper.
ions by the reduction of the beam intensity using a scraper.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.72 - 74, 2012/08
Laser cooling of 40-keV Mg ion has been performed at S-LSR. Indirect transverse laser cooling of a bunched beam with the use of synchro-betatron resonance coupling (SBRC) has been experimentally indicated. However, it is not so efficient due to heating by intra-beam scattering for the ion number of 10 . For attaining very low-temperature beam, it is inevitable to reduce the beam intensity without deterioration of beam detection signal. For this purpose, we have applied controlled scraping of a laser-cooled beam. After beam injection, the beam tail is cut off by a scraper moving in the horizontal direction and laser-cooled both in the longitudinal and horizontal directions with SBRC. Then, the horizontal beam size was measured with another scraper moving also in the horizontal direction. With this scheme, the beam intensity could be reduced from 10
. For attaining very low-temperature beam, it is inevitable to reduce the beam intensity without deterioration of beam detection signal. For this purpose, we have applied controlled scraping of a laser-cooled beam. After beam injection, the beam tail is cut off by a scraper moving in the horizontal direction and laser-cooled both in the longitudinal and horizontal directions with SBRC. Then, the horizontal beam size was measured with another scraper moving also in the horizontal direction. With this scheme, the beam intensity could be reduced from 10 to 10
to 10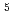 , which resulted in rather efficient indirect transverse laser cooling with the cooling time of about 1 sec.
, which resulted in rather efficient indirect transverse laser cooling with the cooling time of about 1 sec.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 野田 章*; 神保 光一*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.388 - 390, 2012/08
京都大学化学研究所のイオン蓄積・冷却リングS-LSRでは、シンクロ・ベータトロン共鳴によって重イオンビームの運動の進行方向と水平方向の振動を結合させ、レーザー冷却によって横方向を間接的に冷却する実験を進めている。冷却の過程において、粒子数が多い場合Intra-beam散乱による自己加熱作用によって冷却が阻害されるため、スクレイパーによってビーム外縁部の粒子を除去することによって冷却効率を高めている。このとき、2枚のスクレイパーを用い、1枚目のスクレイパーで粒子数を減らした後、2枚目のスクレイパーの挿入距離を変えてビームの残存率を測定することで、ビーム中心からの距離とその内側にある粒子の割合が得られ、この関係から冷却後のビームサイズを測定した。その結果、40keV  Mg
Mg ビームについて、水平・鉛直ベータトロンチューン、及びシンクロトロンチューンがそれぞれ(2.074, 1.120, 0.072)、1枚目のスクレイパーをビーム中心から0.3mmまで挿入して粒子数を1
ビームについて、水平・鉛直ベータトロンチューン、及びシンクロトロンチューンがそれぞれ(2.074, 1.120, 0.072)、1枚目のスクレイパーをビーム中心から0.3mmまで挿入して粒子数を1 10
10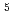 まで減少させた条件で、水平方向ビームサイズが0.3mm、温度に換算して52Kまで冷却されていることを観測した。この時、ビームサイズが1/eになるまでの冷却時間は1.25秒であった。
まで減少させた条件で、水平方向ビームサイズが0.3mm、温度に換算して52Kまで冷却されていることを観測した。この時、ビームサイズが1/eになるまでの冷却時間は1.25秒であった。
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 野田 章*; 頓宮 拓*; 伊藤 清一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.397 - 399, 2012/05
The longitudinal temperature of 40 keV  Mg
Mg beams was measured through bunch length measurement during laser cooling at S-LSR. The bunch length was measured as time-domain signals from a pair of parallel-plate electrostatic pickups. Injected non-cooled beams gave a bunch length of 2.5 m and cooled beams had two components of broad and sharp distributions. The broad distribution had a longitudinal length of 2.2 m, which is close to that of the initial beam. The length of the sharp distribution shrunk to 0.25 m and is expected as a cooled part. The capture efficiency of cooling, which represents the ratio of particle numbers of the cooled part and the total particle number, varied with laser detuning. With a scanning range of 2 GHz, it was improved from 66% to 92%, while the bunch became longer by 10% with scanning. A new scheme for improving the capture efficiency will be applied to attain a strong signal from a low-current low-temperature beam.
beams was measured through bunch length measurement during laser cooling at S-LSR. The bunch length was measured as time-domain signals from a pair of parallel-plate electrostatic pickups. Injected non-cooled beams gave a bunch length of 2.5 m and cooled beams had two components of broad and sharp distributions. The broad distribution had a longitudinal length of 2.2 m, which is close to that of the initial beam. The length of the sharp distribution shrunk to 0.25 m and is expected as a cooled part. The capture efficiency of cooling, which represents the ratio of particle numbers of the cooled part and the total particle number, varied with laser detuning. With a scanning range of 2 GHz, it was improved from 66% to 92%, while the bunch became longer by 10% with scanning. A new scheme for improving the capture efficiency will be applied to attain a strong signal from a low-current low-temperature beam.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 伊藤 清一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.394 - 396, 2012/05
Mg ion beams have been successfully laser-cooled both in longitudinal and transverse directions at S-LSR in ICR, Kyoto University. The cooling rate, however, is not strong enough to realize a crystalline beam due to heating from intra-beam scattering (IBS). Reduction of the beam intensity is inevitable to suppress this IBS effect, which, however, had resulted in poor S/N ratio for observation of the transverse beam size. We, therefore, describe a new beam-scraping scheme: The scheme selects out ions in the distribution tail of the transverse phase space, keeping the beam density in the core part by simultaneous application of multi-dimensional laser cooling and beam scraping. The strategy to realize the scheme effectively has been searched by combination of the beam experiments and computer simulations.
岡本 清美*; 佐藤 正寛*; 奥西 巧一*; 坂井 徹; 糸井 千岳*
Physica E, 43(3), p.769 - 772, 2011/01
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:23.95(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)3本の量子スピン鎖が結合したスピンナノチューブの磁化過程について、有限系の数値的厳密対角化と密度行列繰り込み群法によって理論的に解析した。その結果、鎖間の結合が十分に大きい場合には、飽和磁化の3分の1のところに磁化プラトーが現れることがわかった。また、鎖間の結合が非対称になる格子ひずみがある場合には、磁化プラトー形成のメカニズムが2種類あることも判明し、メカニズムの違いによる磁化プラトーの相図を得ることに成功した。
坂井 徹; 佐藤 正寛*; 岡本 清美*; 奥西 巧一*; 糸井 千岳*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 22(40), p.403201_1 - 403201_13, 2010/10
被引用回数:37 パーセンタイル:39.53(Physics, Condensed Matter)スピンナノチューブについての最近の理論的研究をレビューする。特に、S=1/2 3本鎖スピンチューブに焦点をあてる。3本鎖スピンラダーと違って、正三角形のユニットセルを持つスピンチューブはスピンギャップが開いている。ハバード模型に基づく有効理論によると、このユニットセルが二等辺三角形になる格子ひずみによりスピンギャップが消失する量子相転移が起きることが予測される。このことは、数値対角化と密度行列繰り込み群による数値解析により立証された。さらに、われわれは新しい磁場誘起秩序として、ネール秩序,ダイマー秩序,カイラル秩序,不均一秩序などが生じることや、新しいメカニズムによる磁化プラトー現象が起きることも、理論的に示すことに成功した。最近合成された実際のスピンチューブ物質についても簡単にレビューする。
坂井 徹; 奥西 巧一*; 岡本 清美*; 糸井 千岳*; 佐藤 正寛*
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 159(1-2), p.55 - 59, 2010/04
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:36.06(Physics, Applied)S=1/2三本鎖スピンナノチューブに対する数値的厳密対角化と密度行列繰り込み群による数値解析により、この系の非対称性によって異なる二つのメカニズムにより、飽和磁化の3分の1のところに磁化プラトーが現れることが判明した。
岡田 耕一*; 近藤 恵太郎; 落合 謙太郎; 佐藤 聡; 今野 力; 岡本 敦*; 小渕 隆*; 北島 純男*; 笹尾 真実子*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.8, p.666 - 669, 2009/09
ITERにおける燃焼制御のために燃料イオン密度比測定が求められている。この燃料イオン比はリアルタイムでフィードバックされなければならないので、燃料イオン比測定のための中性子計測システムには高い計数率が求められる。ITERの通常運転時では、DT中性子はDD中性子の200倍発生すると見積もられている。われわれはTOFスペクトロメータを用いた中性子計測システムを開発し、原子力機構FNSのDD中性子をわずかに含むDT中性子ビームに適用した。燃料イオン比を測定するために、それぞれの中性子からの信号を弁別するウィンドウを用いたシステムを構築し、DT中性子とDD中性子の分離計測に成功した。