Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Okuno, Koichi*
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 43(11), p.3916 - 3920, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.7(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In the present study a comparison between simulations using the PHITS code and activated material analysis of JT-60U has been performed. Neutron transport have been simulated using the Monte Carlo methods PHITS to determine the neutron fluency at the irradiation position. The Activated analysis has been complemented by the foil-activation technique. The preliminary result of these PHITS simulations has been confirmed by comparing the reaction rates of gold, cobalt, and nickel foils activation. The simulation results by PHITS consisted with the measured reaction rate of each foils near the device.
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Iida, Hiromasa*; Itoga, Toshio*; Okumura, Keisuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Konno, Chikara; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Nakamura, Takashi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Hoshasen Shahei Handobukku; Kisohen, p.299 - 356, 2015/03
no abstracts in English
Okuno, Koichi*; Iikura, Hiroshi
Nuclear Science and Techniques, 25(S1), p.S010604_1 - S010604_5, 2014/12
no abstracts in English
Sato, Takeshi; Muto, Shigeo; Okuno, Hiroshi; Katagiri, Hiromi; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Okamoto, Akiko; Koie, Masahiro; Ikeda, Takeshi; Nemotochi, Toshimasa; Saito, Toru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-046, 65 Pages, 2014/02
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has the responsibility of providing technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire stations and nuclear operators etc., because the JAEA has been designated as the Designated Public Institution under the Basic Act on Disaster Control Measures and the Act on Response to Armed Attack Situations, etc.. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, dispatches specialists as required, and supplies the National Government and local governments with emergency equipments and materials. NEAT provides various exercise and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention to those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal times. The tasks of NEAT, with its past experiences as a designated public institution including the responses to TEPCO's Fukushima Accident, have been shifted to technical supports to the national government for strengthening its abilities to emergency responses; the NEAT therefore focused on maintenance and operation of its functions, and strengthening its response abilities in cooperation with the national government. This annual report summarized these activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2012.
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Anayama, Yoshimasa*; Okuno, Koichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kaminaga, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.850 - 853, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:82.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A flexible heat resistant neutron shielding material has been developed, which consists of polymer resin with 1 weight % boron. The neutron shielding performance of the developed resin, examined by the  Cf neutron source is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The outgas of H
Cf neutron source is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The outgas of H , H
, H O, CO and CO
O, CO and CO from the resin have been measured at 250
from the resin have been measured at 250  C environment. The resin will be applied around the port of the vacuum vessel as an additional shielding material and prevented the effects on the neutron streaming of the superconducting tokamak device such as JT-60SA.
C environment. The resin will be applied around the port of the vacuum vessel as an additional shielding material and prevented the effects on the neutron streaming of the superconducting tokamak device such as JT-60SA.
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Kawasaki, Hiromitsu*; Okuno, Koichi*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.375 - 381, 2011/10
A complete 3D neutrons and photons transport analysis by Monte Carlo transport code system PHITS (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System) have been performed for superconducting tokamak fusion device such as JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60SA). It is possible to make use of PHITS in the port streaming analysis around the devices for the tokamak fusion device, the duct streaming analysis in the building where the device is installed, and the sky shine analysis for the site boundary. The neutron transport analysis by PHITS makes it clear that the shielding performance of the superconducting tokamak fusion device with the cryostat is improved by the graphical results. From the standpoint of the port streaming and the duct streaming, it is necessary to calculate by 3D codes for the neutronics analysis of superconducting tokamak fusion device.
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Okuno, Koichi*; Kawasaki, Hiromitsu*
RIST News, (51), p.20 - 29, 2011/07
no abstracts in English
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Anayama, Yoshimasa*; Onishi, Seiki; Sakurai, Shinji; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Okuno, Koichi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(4), p.585 - 590, 2011/04
Soft-type neutron shielding resin has been developed by improving an existing hard-type neutron shielding material by the epoxy-based resin as the additional shielding material. A flexible heat resistant neutron shielding material has been developed, which consists of newly polymer-based resin with boron. The neutron shielding performance of the developed flexible heat resistant resin by the  Cf neutron source is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The outgas of H, H
Cf neutron source is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The outgas of H, H , NH
, NH , H
, H O, CO, O
O, CO, O , C
, C H
H and CO
and CO from the developed resin have been measured at high temperature environment (250
from the developed resin have been measured at high temperature environment (250 C) by thermal desorption spectroscopy methods. The soft-type resin and the newly developed heat resistant resin will be applied to prevent the effects of the neutron streaming and to control the movement of vibrated pipe as the seal material around the plumbing in the future fast reactor and the innovative fission reactor.
C) by thermal desorption spectroscopy methods. The soft-type resin and the newly developed heat resistant resin will be applied to prevent the effects of the neutron streaming and to control the movement of vibrated pipe as the seal material around the plumbing in the future fast reactor and the innovative fission reactor.
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Takiyoshi, Koji*; Amano, Toshio*; Kawasaki, Hiromitsu*; Okuno, Koichi*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.36 - 39, 2011/02
A complete 3D radiation shielding analysis by PHITS has been performed for the JT-60U and JT-60 superconducting tokamak device (JT-60SA) in the present study. The PHITS has been developed for high energy particles physics in Japan. The neutron and photon transport analysis less than 20 MeV with the general cross section library is the same algorism of MCNP-4C code. The monoenergetic neutron (E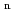 = 2.45 MeV) of the DD fusion devices are used for the neutron source in the analysis. The neutron source distribution are available a toroidally symmetric source for the analysis. The toroidal source has a poloidal distribution, so that a source routine in the PHITS has been replaced a newly developed source routine. The visual nuclear responses such as the neutron flux distribution, the photon flux distribution, the nuclear heating of the coils and the dose rate around the devices has been calculated by the PHITS for the fusion tokamak devices. Initial results by the PHITS have been demonstrated.
= 2.45 MeV) of the DD fusion devices are used for the neutron source in the analysis. The neutron source distribution are available a toroidally symmetric source for the analysis. The toroidal source has a poloidal distribution, so that a source routine in the PHITS has been replaced a newly developed source routine. The visual nuclear responses such as the neutron flux distribution, the photon flux distribution, the nuclear heating of the coils and the dose rate around the devices has been calculated by the PHITS for the fusion tokamak devices. Initial results by the PHITS have been demonstrated.
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Okuno, Koichi*; Sakurai, Shinji
Nuclear Technology, 168(2), p.553 - 558, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The resin as a neutron shielding material with flexibility in shape and lightness is expected to be set up near the fusion tokamak devices and as the collimator of the diagnostics. KRAFTON-HB4 is epoxy-based resin that contains boron. It has been developed for future FBR shielding materials. The heat resistant temperature is  150
150 C. EPONITE is neutron shielding material based on Colemanite and epoxy-based resin that contains boric acid. It has been developed for a PET shielding materials. The heat resistant temperature is
C. EPONITE is neutron shielding material based on Colemanite and epoxy-based resin that contains boric acid. It has been developed for a PET shielding materials. The heat resistant temperature is  200
200 C. The boron-loaded resin with the heat resistance applicable to 300
C. The boron-loaded resin with the heat resistance applicable to 300 C has been newly developed. The developed resin is made of phenol-based resin that has improved heatproof. The weight percent of hydrogen and boron are the developed resin (H: 1.94, B: 6.1), KRAFTON-HB4 (H: 10.5, B: 2.0), and EPONITE (H: 3.8, B: 30.4). Neutron attenuation experiments of these resins were carried out using
C has been newly developed. The developed resin is made of phenol-based resin that has improved heatproof. The weight percent of hydrogen and boron are the developed resin (H: 1.94, B: 6.1), KRAFTON-HB4 (H: 10.5, B: 2.0), and EPONITE (H: 3.8, B: 30.4). Neutron attenuation experiments of these resins were carried out using  Cf neutron source. In the experiments, neutron dose attenuation were measured by a REM counter. The tenth layer of Polyethylene, the developed resin, KRAFTON-HB4 and EPONITE are 0.14 m, 0.14 m, 0.15 m and 0.09 m, respectively.
Cf neutron source. In the experiments, neutron dose attenuation were measured by a REM counter. The tenth layer of Polyethylene, the developed resin, KRAFTON-HB4 and EPONITE are 0.14 m, 0.14 m, 0.15 m and 0.09 m, respectively.
Hayashi, Kimio; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Onose, Shoji; Ishida, Takuya; Nakamichi, Masaru; Katsuyama, Kozo; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Hasegawa, Teiji; Kodaka, Hideo; Takatsu, Hideyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-007, 168 Pages, 2009/03
In-pile functional tests of breeding blankets have been planned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), using a test blanket module (TBM) which will be loaded in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER). In preparation for the in-pile functional tests, JAEA has been being performed irradiation experiments of lithium titanate (Li TiO
TiO ), which is the first candidate of solid breeder materials for the blanket of the demonstration reactor (DEMO) under designing in Japan. The present report describes (1) results of a detailed design and trial fabrication tests of a dismantling apparatus for irradiation capsules which were used in irradiation experiments by the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of JAEA, and (2) results of a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility for post-irradiation examinations (PIEs). In the detailed design of the dismantling apparatus, datailed specifications and the installation methods were examined, based on results of a conceptual design and basic design. In the trial fabrication, cutting tests were curried out by making a mockup of a cutting component. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility was carried out in order to secure a facility for PIE work after the capsule dismantling, which revealed a technical feasibility.
), which is the first candidate of solid breeder materials for the blanket of the demonstration reactor (DEMO) under designing in Japan. The present report describes (1) results of a detailed design and trial fabrication tests of a dismantling apparatus for irradiation capsules which were used in irradiation experiments by the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of JAEA, and (2) results of a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility for post-irradiation examinations (PIEs). In the detailed design of the dismantling apparatus, datailed specifications and the installation methods were examined, based on results of a conceptual design and basic design. In the trial fabrication, cutting tests were curried out by making a mockup of a cutting component. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility was carried out in order to secure a facility for PIE work after the capsule dismantling, which revealed a technical feasibility.
 C heat resistant boron-loaded resin for neutron shielding
C heat resistant boron-loaded resin for neutron shieldingMorioka, Atsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Okuno, Koichi*; Sato, Satoshi; Verzirov, Y. M.; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Nishitani, Takeo; Tamai, Hiroshi; Shibama, Yusuke; Yoshida, Shigeru*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1085 - 1089, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:83.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A 300 C heat-resistant neutron shielding material is newly developed, which consists of phenol-based resin with 6 weight-% boron. The neutron shielding performance of the developed resin, examined by the
C heat-resistant neutron shielding material is newly developed, which consists of phenol-based resin with 6 weight-% boron. The neutron shielding performance of the developed resin, examined by the  Cf neutron source, is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The neutron shielding characteristic was also estimated by 3D Monte Carlo Code MCNP-4C2 using the continuous energy cross section data sets based on the JENDL-3.2. The calculation result agrees well with the experimental result. To understand the kinds of the outgas from the developed resin in the high temperature region, the mass spectrum of the outgas was measured until
Cf neutron source, is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The neutron shielding characteristic was also estimated by 3D Monte Carlo Code MCNP-4C2 using the continuous energy cross section data sets based on the JENDL-3.2. The calculation result agrees well with the experimental result. To understand the kinds of the outgas from the developed resin in the high temperature region, the mass spectrum of the outgas was measured until  300
300 C by Thermal Desorption Specroscopy (TDS). The observed mass number was 2, 17, 18, 28, 32, and 44. The number corresponds to hydrogen (H
C by Thermal Desorption Specroscopy (TDS). The observed mass number was 2, 17, 18, 28, 32, and 44. The number corresponds to hydrogen (H ), ammonia (NH
), ammonia (NH ), water (H
), water (H O), carbon monoxide (CO), oxygen (O
O), carbon monoxide (CO), oxygen (O ), carbon dioxide (CO
), carbon dioxide (CO ), respectively. The main outgas component from the resin at 100
), respectively. The main outgas component from the resin at 100 150
150 C was NH
C was NH  and H
and H O. The outgas of NH
O. The outgas of NH and H
and H O from the resin have been measured, however, the neutron shielding performance of the resin after 200
O from the resin have been measured, however, the neutron shielding performance of the resin after 200 C baking was almost the same as that before baking. The quantitative analysis of the outgas from the resin in the high temperature region was done by the Temperature Programmed Desorption (TPD) / Gas Chromatography and Mass spectrometry (GC/MS). The 13 kinds of organic gases have been observed by the amount of
C baking was almost the same as that before baking. The quantitative analysis of the outgas from the resin in the high temperature region was done by the Temperature Programmed Desorption (TPD) / Gas Chromatography and Mass spectrometry (GC/MS). The 13 kinds of organic gases have been observed by the amount of  g/g at 300
g/g at 300 C. The neutron shielding performance of the developed resin at 300
C. The neutron shielding performance of the developed resin at 300 C was simulated by the 3D analysis. The resonance cross section of the nucleus is broad at the high temperature region by the Doppler effect. The calculation results using 327
C was simulated by the 3D analysis. The resonance cross section of the nucleus is broad at the high temperature region by the Doppler effect. The calculation results using 327 C library and 20
C library and 20 C library are almost same.
C library are almost same.
Morioka, Atsuhiko; Okuno, Koichi*
Purasuchikkusu, 57(1), p.148 - 152, 2006/01
no abstracts in English
Morioka, Atsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Okuno, Koichi*; Tamai, Hiroshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(9), p.645 - 646, 2005/09
A 300  C heat-resistant neutron shielding material is newly developed, which consists of phenol-based resin with 5 weight-% boron. The neutron shielding performance of the developed resin, examined by the
C heat-resistant neutron shielding material is newly developed, which consists of phenol-based resin with 5 weight-% boron. The neutron shielding performance of the developed resin, examined by the  Cf neutron source, is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The resin is applicable to the port section of vacuum vessel of the DD plasma device to suppress the streaming neutrons and to reduce the nuclear heating of the superconducting coils.
Cf neutron source, is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The resin is applicable to the port section of vacuum vessel of the DD plasma device to suppress the streaming neutrons and to reduce the nuclear heating of the superconducting coils.
 Al conductor developed for JT-60SC
Al conductor developed for JT-60SCKizu, Kaname; Miura, Yushi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Matsui, Kunihiro; Ando, Toshinari*; Hamada, Kazuya; Hara, Eiji*; Imahashi, Koichi*; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1535 - 1538, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.57(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 Al D-shaped coil fabricated by react-and-wind method for JT-60 superconducting Tokamak
Al D-shaped coil fabricated by react-and-wind method for JT-60 superconducting TokamakKizu, Kaname; Miura, Yushi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Matsui, Kunihiro; Ando, Toshinari*; Hamada, Kazuya; Hara, Eiji*; Imahashi, Koichi*; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Proceedings of 6th European Conference on Applied Superconductivity (EUCAS 2003), p.400 - 407, 2003/00
Toroidal field coils (TFC) of the JT-60SC consist of 18 D-shape coils. The maximum magnetic field is 7.4 T at an operational current of 19.4 kA. An advanced Nb Al superconductor was developed for the TFC conductor material in JAERI. The Nb
Al superconductor was developed for the TFC conductor material in JAERI. The Nb Al has lower strain sensitivity on superconducting performances, and allows us to fabricate the TFC by react-and-wind (R&W) method that makes that the coil fabrication with high reliability becomes easier and the fabrication cost becomes lower. To demonstrate the coil fabrication by R&W method, a two-turn D-shape coil was developed. The D-shape coil was tested at 4.3-4.4K and 7-12T. Measured critical current (Ic) was 30 kA at 7.3 T and 4.4 K. Using the measured conductor and strand Ic values, the strain of the conductor was estimated to be -0.6%. The Ic-B-T characteristic expected by an empirical equation substituting this strain shows that the required temperature margin for TFC is satisfied. Thus, the R&W method was demonstrated to be the applicable fabrication method of the TFC.
Al has lower strain sensitivity on superconducting performances, and allows us to fabricate the TFC by react-and-wind (R&W) method that makes that the coil fabrication with high reliability becomes easier and the fabrication cost becomes lower. To demonstrate the coil fabrication by R&W method, a two-turn D-shape coil was developed. The D-shape coil was tested at 4.3-4.4K and 7-12T. Measured critical current (Ic) was 30 kA at 7.3 T and 4.4 K. Using the measured conductor and strand Ic values, the strain of the conductor was estimated to be -0.6%. The Ic-B-T characteristic expected by an empirical equation substituting this strain shows that the required temperature margin for TFC is satisfied. Thus, the R&W method was demonstrated to be the applicable fabrication method of the TFC.
Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Seki, Masahiro; Tsuji, Hiroshi; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Kato, Takashi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Hanada, Masaya; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 42(1), p.75 - 93, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japanese contributions to ITER Engineering Design Activity are presented, together with an introduction of the objectives and design of the ITER whose program have been carried out through the international collaboration by EU, Japan, Russian Federation and the USA. New technologies have been produced through the development, fabrication and testing of scalable models in the fields of superconducting magnet, reactor structure with vacuum vessel, high-heat-flux plasma facing component, neutral beam injector, high-power mm-wave generator and so on. As major contributions from Japan, development and testing results of a 13-T, 640-MJ, Nb Sn pulsed magnet, a 18-degree sector of vacuum vessel with a height of 15 m and a width of 9 m, CFC armors to CuCrZr cooling tube that withstood 20 MW/m
Sn pulsed magnet, a 18-degree sector of vacuum vessel with a height of 15 m and a width of 9 m, CFC armors to CuCrZr cooling tube that withstood 20 MW/m , a 31 mA/cm
, a 31 mA/cm negative ion beam source, a 1-MeV beam-accelerator, a 1-MW 170-GHz gyrotron were described.
negative ion beam source, a 1-MeV beam-accelerator, a 1-MW 170-GHz gyrotron were described.
Kato, Takashi; Tsuji, Hiroshi; Ando, Toshinari; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nakajima, Hideo; Sugimoto, Makoto; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Kawano, Katsumi; Oshikiri, Masayuki*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 56-57, p.59 - 70, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English