Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Tobita, Minoru*; Haraga, Tomoko; Endo, Tsubasa*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-013, 30 Pages, 2021/12
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JPDR facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 21 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2018-2019.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2018-2019.
Tsuchida, Daiki; Haraga, Tomoko; Tobita, Minoru*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Omori, Takeshi*; Murakami, Hideaki*; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-022, 34 Pages, 2021/03
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3 and JPDR. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 22 radionuclides( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Ba,
Ba,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Omori, Atsushi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Hata, Kuniki; Sato, Tomonori; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Tada, Eiji*; et al.
Zairyo To Kankyo, 69(4), p.107 - 111, 2020/04
To evaluate the effect of oxidants, which are formed by radiolysis of water under gamma ray irradiation, on the corrosion of a carbon steel in humid environment, ozone was introduced as a model oxidant in to humidity-controlled air at 50 C in a thermo-hygrostat chamber. Corrosion monitoring was performed by using an Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor-type (ACM) sensor consisting of a carbon steel anode and an Ag cathode. The output current of the ACM sensor was increased with the increase in relative humidity and it was obviously increased with the increase in the introduced ozone concentration at each relative humidity. The results indicate that ozone accelerates the corrosion of the carbon steel. The effect of ozone on the corrosion acceleration is attributed to the fast reduction reaction and fast dissolution reaction in to water compared to that of oxygen.
C in a thermo-hygrostat chamber. Corrosion monitoring was performed by using an Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor-type (ACM) sensor consisting of a carbon steel anode and an Ag cathode. The output current of the ACM sensor was increased with the increase in relative humidity and it was obviously increased with the increase in the introduced ozone concentration at each relative humidity. The results indicate that ozone accelerates the corrosion of the carbon steel. The effect of ozone on the corrosion acceleration is attributed to the fast reduction reaction and fast dissolution reaction in to water compared to that of oxygen.
Tobita, Minoru*; Haraga, Tomoko; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Seki, Kotaro*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Kochiyama, Mami; Shimomura, Yusuke; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-016, 72 Pages, 2020/02
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 25 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Mo,
Mo,  Tc,
Tc, 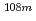 Ag,
Ag,  Sn,
Sn,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Yamada, Tomonori; Takebe, Toshihiko*; Ishizuka, Ippei*; Daido, Hiroyuki*; Hanari, Toshihide; Shibata, Takuya; Omori, Shinya*; Kurosawa, Koichi*; Sasaki, Go*; Nakada, Masahiro*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(12), p.1171 - 1179, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)We describe a new chipping technique combined with a water-jet technique as one of the candidate techniques for the retrieval of fuel debris and support structures as part of the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. We performed proof-of-principle experiments to demonstrate the removal capability of metal parts, where we focused on the observation of removal processes from a metallic sample using a 5.5-kW continuous wave fiber laser combined with continuous and pulsed water jets.
Kurihara, Momo*; Yasutaka, Tetsuo*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Ashikawa, Nobuo*; Ebina, Hiroyuki*; Iijima, Takeshi*; Ishimaru, Kei*; Kanai, Ramon*; Karube, Jinichi*; Konnai, Yae*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 322(2), p.477 - 485, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.76(Chemistry, Analytical)We assessed the repeatability and reproducibility of methods for determining low dissolved radiocesium concentrations in freshwater in Fukushima. Twenty-one laboratories pre-concentrated three of 10 L samples by five different pre-concentration methods (prussian-blue-impregnated filter cartridges, coprecipitation with ammonium phosphomolybdate, evaporation, solid-phase extraction disks, and ion-exchange resin columns), and activity of radiocesium was measured. The z-scores for all of the  Cs results were within
Cs results were within  2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
 Mo content in metal waste generated at the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor
Mo content in metal waste generated at the Japan Power Demonstration ReactorShimada, Asako; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Kameo, Yutaka
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 314(2), p.1361 - 1365, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.14(Chemistry, Analytical)A separation method of Mo from Nb, Zr, and the matrix elements of rubble waste was modified to determine the content of  Mo in metal waste. A separation scheme to treat 1 g of metal waste was established by optimizing the amount of ascorbic acid, the rinsing solution, and repeating of the procedure. A thin-layer source was prepared using direct drop deposition and evaporation to measure
Mo in metal waste. A separation scheme to treat 1 g of metal waste was established by optimizing the amount of ascorbic acid, the rinsing solution, and repeating of the procedure. A thin-layer source was prepared using direct drop deposition and evaporation to measure  Mo content. Finally,
Mo content. Finally,  Mo content in the metal waste generated at the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor was analyzed using the developed method.
Mo content in the metal waste generated at the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor was analyzed using the developed method.
Hanari, Toshihide; Takebe, Toshihiko*; Yamada, Tomonori; Daido, Hiroyuki; Ishizuka, Ippei*; Omori, Shinya*; Kurosawa, Koichi*; Sasaki, Go*; Nakada, Masahiro*; Sakai, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2017/04
In decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, a retrieval process of fuel debris in the Primary Containment Vessel by a remote operation is one of the key issues. In this process, prevention of spreading radioactive materials is one of the important considerations. Furthermore, an applicable technique to the process requires keeping of reasonable processing-efficiency. We propose to use the combined technique including a laser light and a water jet as a retrieval technique of the fuel debris. The laser processing technique combined with a repetitive pulsed water jet could perform an efficient retrieval processing. Our experimental result encourages us to promote further development of the technique towards a real application at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Omori, Hiroyuki; Nebashi, Koji; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-029, 31 Pages, 2015/03
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required for the radioactive waste generated from research facilities in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to dispose of in a near-surface repository. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid waste generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid waste generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In this report, we reported the analytical data determined in fiscal 2014 ( Cs and
Cs and  Mo) and summarized them with the radioactivity concentrations obtained in the past as basic data to consider the evaluation method of radioactivity concentrations in the stored waste taken from JPDR.
Mo) and summarized them with the radioactivity concentrations obtained in the past as basic data to consider the evaluation method of radioactivity concentrations in the stored waste taken from JPDR.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-038, 137 Pages, 2014/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2013. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2013, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Watanabe, Koichi; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Sakamaki, Keiko; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 21(2), p.63 - 74, 2014/12
Static leach tests were conducted for simulated HLW glass in CaCl /Ca(OH)
/Ca(OH) solutions to investigate the corrosion behavior of HLW glass under calcium-rich environments induced by cement based materials in geological repositories. Another series of leach tests were conducted in deionized water in the presence of iron to investigate the effects of iron over-pack on the glass corrosion. In Ca solutions, corrosion of the glass was inhibited during the test period compared to that in deionized water, while the corrosion was enhanced at the presence of iron. The enhancement of the glass corrosion was assumed to be accompanied with transformation of silica, a glass network former, into iron silicates.
solutions to investigate the corrosion behavior of HLW glass under calcium-rich environments induced by cement based materials in geological repositories. Another series of leach tests were conducted in deionized water in the presence of iron to investigate the effects of iron over-pack on the glass corrosion. In Ca solutions, corrosion of the glass was inhibited during the test period compared to that in deionized water, while the corrosion was enhanced at the presence of iron. The enhancement of the glass corrosion was assumed to be accompanied with transformation of silica, a glass network former, into iron silicates.
Kato, Shinichi*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hotchi, Hideaki; Okabe, Kota; Omori, Chihiro*; Tamura, Fumihiko; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.444 - 447, 2014/06
The incoherent tune spread occurs by the space charge force and this becomes one of beam loss sources for the high intensity proton accelerator. This kind of beam loss was measured in the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) in J-PARC in the high intensity beam test. To measure the incoherent tune spread we have started to develop for a magnetic dipole exciter with magnetic alloy. It was found that it would be realized the exciter with several-kW electric power in the range of 3 MHz from our experimental results.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Onoe, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-050, 114 Pages, 2014/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2012. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2012, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-018, 169 Pages, 2013/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in 2011 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2011, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Bamba, Tsunetaka
International Journal of Corrosion, 2011(1), p.796457_1 - 796457_6, 2011/09
Static leach tests were conducted for simulated HLW glass in MgCl solution for up to 92 days to investigate the dissolution mechanism of HLW glass under coastal repository condition. Under the condition that magnesium ion exists in leachate, the dissolution rate of the glass did not decrease with time during leaching, while the rate decreased when the magnesium ion depleted in the leachate. In addition, precipitated layer consist of magnesium/silica was observed at the surface of the glass after the leach tests. The present results imply that dissolution of the glass is accompanied with formation of magnesium silicate consuming silica; a glass network former. As a consequence, the glass dissolved with an initial high dissolution rate.
solution for up to 92 days to investigate the dissolution mechanism of HLW glass under coastal repository condition. Under the condition that magnesium ion exists in leachate, the dissolution rate of the glass did not decrease with time during leaching, while the rate decreased when the magnesium ion depleted in the leachate. In addition, precipitated layer consist of magnesium/silica was observed at the surface of the glass after the leach tests. The present results imply that dissolution of the glass is accompanied with formation of magnesium silicate consuming silica; a glass network former. As a consequence, the glass dissolved with an initial high dissolution rate.
 Bh and
Bh and  Db produced in the
Db produced in the  Cm +
Cm +  Na reaction
Na reactionMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_6, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:77.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of an isotope  Bh and its daughter nucleus
Bh and its daughter nucleus  Db produced by the
Db produced by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 ) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.
) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
 113 produced by the
113 produced by the  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction
113 reactionMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We performed the experiment to synthesize an isotope of the element 113 produced by a  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope
113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope  113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of
113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of  Bh and
Bh and  Db via previously unknown decays of
Db via previously unknown decays of  113,
113, 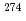 Rg, and
Rg, and 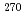 Mt. Although the
Mt. Although the  Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the
Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the  Bh, we performed the direct production of
Bh, we performed the direct production of  Bh by the
Bh by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5n)
Na,5n) Bh reaction. In this experiment, the
Bh reaction. In this experiment, the  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
Komori, Daisuke*; Yamashita, Masato*; Konishi, Hiroyuki; Hanaki, Satoshi*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Omori, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English