Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:74.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:80.70(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.
 Bh in the
Bh in the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 )
) Bh reaction and its decay properties
Bh reaction and its decay propertiesHaba, Hiromitsu*; Fan, F.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Kondo, Narumi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.024625_1 - 024625_12, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.65(Physics, Nuclear) acidic solutions
acidic solutionsYokoyama, Akihiko*; Kitayama, Yuta*; Fukuda, Yoshiki*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Murakami, Masashi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Yano, Shinya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi*
Radiochimica Acta, 107(1), p.27 - 32, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.85(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear) and Au surfaces in preparation for chemical investigations on Cn, Nh, and Fl at TASCA
and Au surfaces in preparation for chemical investigations on Cn, Nh, and Fl at TASCALens, L.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Ballof, J.*; Block, M.*; David, H. M.*; Despotopulos, J.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Ballof, J.*; Block, M.*; David, H. M.*; Despotopulos, J.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 106(12), p.949 - 962, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:68.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Online gas-solid adsorption studies with single atom quantities of Hg, Tl, and Pb on SiO and Au surfaces were carried out using short-lived radioisotopes with half-lives in the range of 4-49 s. This is a model study to measure adsorption enthalpies of superheavy elements Cn, Nh, and Fl. The short-lived isotopes were produced and separated by the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI. The products were stopped in He gas, and flushed into gas chromatography columns made of Si detectors whose surfaces were covered by SiO
and Au surfaces were carried out using short-lived radioisotopes with half-lives in the range of 4-49 s. This is a model study to measure adsorption enthalpies of superheavy elements Cn, Nh, and Fl. The short-lived isotopes were produced and separated by the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI. The products were stopped in He gas, and flushed into gas chromatography columns made of Si detectors whose surfaces were covered by SiO or Au. The short-lived Tl and Pb were successfully measured by the Si detectors with the SiO
or Au. The short-lived Tl and Pb were successfully measured by the Si detectors with the SiO surface at room temperature. On the other hand, the Hg did not adsorb on the SiO
surface at room temperature. On the other hand, the Hg did not adsorb on the SiO surface, but adsorbed on the Au surface. The results demonstrated that the adsorption properties of short-lived Hg, Tl, and Pb could be studied with this setup, and that this method is applicable to the experiment for Cn, Nh, and Fl.
surface, but adsorbed on the Au surface. The results demonstrated that the adsorption properties of short-lived Hg, Tl, and Pb could be studied with this setup, and that this method is applicable to the experiment for Cn, Nh, and Fl.
 SO
SO and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)
and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Komori, Yukiko*; Murakami, Masashi; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Daisuke*; Asai, Masato; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 317(1), p.421 - 430, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.74(Chemistry, Analytical)We have studied extraction behavior of group-6 elements Mo and W to search for suitable conditions for an on-line extraction experiment of their heavier homolog, seaborgium (Sg). Batch-wise extraction of carrier-free radiotracers  Mo and
Mo and 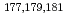 W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H
W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H SO
SO and 1.0
and 1.0 10
10 - 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H
- 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H SO
SO solutions with concentrations of [H
solutions with concentrations of [H SO
SO ]
]  2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
Eichler, R.*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Chiera, N. M.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Dressler, R.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.07005_1 - 07005_7, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:71.33(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In recent years gas-phase chemical studies assisted by physical pre-separation allowed for the productions and investigations of fragile single molecular species of superheavy elements. The latest highlight is the formation of very volatile hexacarbonyl compound of element 106, Sg(CO) . Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO)
. Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO) , W(CO)
, W(CO) , and Sg(CO)
, and Sg(CO) .
.
Munemoto, Takashi; Omori, Kazuaki*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Chemical Geology, 417, p.58 - 67, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:73.10(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Rare earth elements (REEs) combined with yttrium (YREE) in deep groundwater from granite and fracture-filling calcite are being studied at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU, Tono area, central Japan).
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Omori, Kazuaki; Munemoto, Takashi; Onoe, Hironori
Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(4), p.3041 - 3057, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:54.68(Environmental Sciences)Changes of hydrochemical condition resulting from large-scale underground facility construction to 500 m depth in sedimentary and granitic rock were evaluated at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU), Japan. The investigation of hydrochemical impact around the facility suggests that an understanding of hydrogeological structures, including hydrogeological compartments prior to facility construction and the locating of shafts/galleries in low permeability rock area is essential to minimize hydrochemical disturbances.
 13MI44 Boreholes)
13MI44 Boreholes)Hasegawa, Takashi; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Onuki, Kenji; Omori, Kazuaki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Technology 2015-011, 135 Pages, 2015/07
The geological, hydraulic and geochemical data such as rock mass classification, groundwater inflow points and the volume, water pressure, and hydraulic conductivity were obtained from boreholes (13MI38 13MI44) in the -500m Access/Research Gallery-North of Mizunami Underground Research laboratory (MIU). In addition to data acquisition, monitoring systems were installed to observe hydrochemical changes in the groundwater, and rock strain during and after the groundwater recovery experiment.
13MI44) in the -500m Access/Research Gallery-North of Mizunami Underground Research laboratory (MIU). In addition to data acquisition, monitoring systems were installed to observe hydrochemical changes in the groundwater, and rock strain during and after the groundwater recovery experiment.
 Nb and
Nb and  Ta for chemical studies of element 105, Db, using the GARIS gas-jet system
Ta for chemical studies of element 105, Db, using the GARIS gas-jet systemHuang, M.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Murakami, Masashi*; Asai, Masato; Kaji, Daiya*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Kikutani, Yuki*; Komori, Yukiko*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 304(2), p.845 - 849, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.54(Chemistry, Analytical)A technique to utilize radioisotopes of Nb and Ta was developed for chemical studies of element 105, Db, by coupling a gas-jet transport system to the RIKEN gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS). The short-lived  Nb and
Nb and  Ta were produced with nuclear reactions using a
Ta were produced with nuclear reactions using a  F beam whose energy was the same as that to produce
F beam whose energy was the same as that to produce  Db. Then, they were separated with GARIS and extracted to a chemistry laboratory with the gas-jet transport system. By changing only magnetic field of GARIS and inserting an energy degrader and a shutter for recoil ions, we could deliver the
Db. Then, they were separated with GARIS and extracted to a chemistry laboratory with the gas-jet transport system. By changing only magnetic field of GARIS and inserting an energy degrader and a shutter for recoil ions, we could deliver the  Nb and
Nb and  Ta to a chemistry device for
Ta to a chemistry device for  Db without changing other experimental conditions.
Db without changing other experimental conditions.
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.68(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 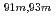 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-038, 137 Pages, 2014/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2013. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2013, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Omori, Kazuaki; Hasegawa, Takashi; Munemoto, Takashi; Masuda, Kaoru*; Aosai, Daisuke*; Inui, Michiharu*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-019, 121 Pages, 2014/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating the groundwater chemistry on excavating the underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground research Laboratory (MIU) Project at Mizunami City, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. In this report, we compiled data obtained by geochemical research for groundwater at the MIU in the fiscal year 2013.
Omori, Kazuaki; Munemoto, Takashi; Hasegawa, Takashi; Shingu, Shinya*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Research 2014-013, 29 Pages, 2014/08
We summarized investigation method of colloid in groundwater. We examined the ultrafiltration of groundwater by using in-situ water monitoring system and batch type airtight container. Additionally, we examined the cross flow filtration method replaced by ultrafiltration. The knowledge of investigating methods is obtained.
Kawamoto, Koji; Kuroiwa, Hiroshi; Yamada, Nobuto; Onuki, Kenji; Omori, Kazuaki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Omori, Masaki; Watanabe, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2014-011, 92 Pages, 2014/07
This document summarizes the data of pilot boreholes (12MI32) in the -500m Access/Research Gallery-South. The geological, hydraulic and geochemical data were obtained. In addition, groundwater monitoring system was installed to observe the groundwater pressure in initial condition and change during the excavation of gallery. The results of investigation, biotite granite with medium to coarse-grained equigranular texture are characterized. Rock mass classification is B from CM class. Minor fault with fault breccia are observed around 48.90mabh. However, S200_13 fault and IF_SB3_13_3 fault (that were presumed by an original model) were not observed. Density of fracture is large in the section of 40.00 to 80.00mabh. Water inflow was a maximum of 600 L/min in 78.83mabh. Permeability ranges from 2.0E-9 to 1.5E-08m/sec at the zone with low inflow, from 1.1E-05 to 1.6E-05m/sec at the zone with high inflow, respectively. Groundwater chemistry is rich in Na and Cl ion.
Omori, Kazuaki; Shingu, Shinya*; Masuda, Kaoru*; Aosai, Daisuke*; Inui, Michiharu*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2013-024, 284 Pages, 2014/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating the groundwater chemistry on excavating the underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground research Laboratory (MIU) Project at Mizunami City, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2012.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Onoe, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-050, 114 Pages, 2014/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2012. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2012, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
 Db in the
Db in the  Cm(
Cm( F,5
F,5 )
) Db reaction and decay properties of
Db reaction and decay properties of  Db and
Db and  Lr
LrHaba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Murakami, Masashi*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Sakai, Ryutaro*; et al.
Physical Review C, 89(2), p.024618_1 - 024618_11, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:81.97(Physics, Nuclear)Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yuguchi, Takashi; Omori, Kazuaki; Hasegawa, Takashi; Munemoto, Takashi
JAEA-Research 2013-021, 63 Pages, 2013/12
We evaluated the Phase I - hydrogeochemical model constructed by Surface-based investigation phase (Phase I), and observed hydrogeochemical change resulting from facility construction in Phase II research. Additionally we developed investigation technique on redox condition, colloid/organics, etc. at gallery in Phase III research. Hydrogeochemical changes in sedimentary rocks and granite resulting from facility construction have been caused by the change of mixing ratio among salinity-distinct groundwaters. Multivariate numerical analysis shows that the groundwater chemistry around drifts would change to that of shallow groundwater in the future. The know-hows on hydrochemical monitoring at the hydrogeological structures and numerical analysis were summarized to infer the hydrochemical changing processes during the facility construction.