Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Morishita, Kazuki; Marufuji, Takato; Ishikawa, Takashi; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Nakano, Tomoyuki
JAEA-Technology 2023-016, 41 Pages, 2023/09
This report summarizes the results of the stabilization treatments of post-experiment nuclear materials in Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) from August 2018 to March 2021. Based on the management standards for nuclear materials enacted after the contamination accident that occurred at PFRF on June 6, 2017, the post-experiment nuclear materials containing plutonium (Pu): samples mixed with organic substances that cause an increase in internal pressure due to radiolysis (including X-ray diffraction samples mixed with epoxy resin and plutonium powder which caused contamination accidents), carbides and nitrides samples which is reactive in air, and chloride samples which may cause corrosion of storage containers, were selected as targets of the stabilization. The samples containing organic materials, carbides and nitrides were heated in an air flow at 650  C and 950
C and 950  C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500
C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500  C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(24), p.16321 - 16326, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.11(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We clarified the chemical state transformation of deposits following the reduction of uranyl ion (U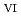 O
O
 ) from the results of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance, impedance spectra and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. We propose the following deposition mechanism: (1) U
) from the results of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance, impedance spectra and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. We propose the following deposition mechanism: (1) U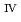 is formed by the disproportionation of U
is formed by the disproportionation of U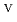 . (2) U
. (2) U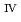 forms U
forms U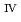 hydroxide deposits, and (3) finally, the hydroxide deposits transform into U
hydroxide deposits, and (3) finally, the hydroxide deposits transform into U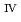 oxide, generally having a larger electrical resistance than the former.
oxide, generally having a larger electrical resistance than the former.
 (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd using cadmium chloride
using cadmium chlorideHayashi, Hirokazu; Shibata, Hiroki; Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(2), p.503 - 510, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)The formation of MPd (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu -type GdPd
-type GdPd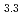 (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) and NpPd
0.0001 nm) and NpPd (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi
0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi -type NpPd
-type NpPd . Chlorination of the MPd
. Chlorination of the MPd (M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl
(M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl formation.
formation.
Komuro, Michiyasu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Kokusen, Junya; Shimizu, Osamu; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Inagawa, Jun
JAEA-Technology 2021-042, 197 Pages, 2022/03
Plutonium Research Building No.1 was constructed in 1960 for the purpose of establishing plutonium handling technology and studying its basic physical properties. Radiochemical research, physicochemical research and analytical chemistry regarding solutions and solid plutonium compounds had been doing for the research program in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In 1964, the laboratory building was expanded and started the researching plutonium-uranium mixed fuel and reprocessing of plutonium-based fuel, playing an advanced role in plutonium-related research in Japan. Since then, the research target has been expanded to include transplutonium elements, and it has functioned as a basic research facility for actinides. The laboratory is constructed by concrete structure and it has the second floor, equipped with 15 glove boxes and 4 chemical hoods. Plutonium Research Building No.1 was decided as one of the facilities to be decommissioned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform Plan in September 2014. So far, the contamination survey of the radioactive materials in the controlled area, the decontamination of glove boxes, and the consideration of the equipment dismantling procedure have been performed as planned. The radioisotope and nuclear fuel materials used in the facility have been transfer to the other facilities in JAEA. The decommissioning of the facility is proceeding with the goal of completing by decommissioning the radiation controlled area in 2026. In this report, the details of the decommissioning plan and the past achievements are reported with the several data.
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Takeda, Shino*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kobayashi, Taishi*
The Chemistry of Thorium, Plutonium and MA, 254 Pages, 2022/03
The chemistry of nuclear materials such as Thorium (Part 1) and Plutonium (Part 2) was described in relation from the fundamentals on solid chemistry and solution chemistry to the practicals on the experiment and evaluation method in detail. Minor actinides such as Neptunium, Americium, Curium and Protoactinium, was introduced the basics on the solid and solution chemistry.
Inagawa, Jun; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Takano, Masahide; Akie, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Osamu; Komuro, Michiyasu; Oura, Hirofumi*; Nagai, Isao*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-001, 144 Pages, 2021/08
Plutonium Research Building No.1 (Pu1) was qualified as a facility to decommission, and preparatory operations for decommission were worked by the research groups users and the facility managers of Pu1. The operation of transportation of whole nuclear materials in Pu1 to Back-end Cycle Key Element Research Facility (BECKY) completed at Dec. 2020. In the operation included evaluation of criticality safety for changing permission of the license for use nuclear fuel materials in BECKY, cask of the transportation, the registration request of the cask at the institute, the test transportation, formulation of plan for whole nuclear materials transportation, and the main transportation. This report circumstantially shows all of those process to help prospective decommission.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2020-001, 142 Pages, 2020/03
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) method is an attractive technique because real-time, in-situ and remote elemental analysis is possible without any sample preparation. The LIBS technique can be applied for analyzing elemental composition of samples under severe environments such as the estimation of impurities in the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the detection of fuel debris in the post-accident nuclear core reactor of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. For applying LIBS to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is indispensable to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). In the present study, an echelle spectrometer with a resolving power of 50,000 was employed to identify spectra of plutonium of wavelength ranging from 350 to 670nm. The 465 atomic spectra and 341 ionic spectra can be identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength of spectra is consistent with published values.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Khumaeni, A.*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 134, p.42 - 51, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:91.69(Spectroscopy)Spectroscopic properties of atomic species of plutonium were investigated by combining laser ablation and resonance absorption techniques for the analysis of a plutonium oxide sample. For 17 transitions of Pu atoms and ions, the absorbance, isotope shift, and hyperfine splitting were determined via Voigt profile fitting of the recorded absorption spectra. Three transitions were selected as candidates for analytical use. Using these transitions, we investigated the analytical performance that was attainable and determined a correlation coefficient R2 between the absorbance and plutonium concentration of 0.9999, a limit of detection of 30-130 ppm, and a relative standard deviation of approximately 6% for an abundance of  Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Segawa, Yukari; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kumagai, Yuta; Aoyagi, Noboru; Nakada, Masami; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Tamura, Yukito*; Okamoto, Hisato; Otomo, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2016-039, 64 Pages, 2017/03
The laboratory building No.1 for the plutonium research program (Bldg. Pu1) was chosen as one of the facilities to decommission by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform in September, 2013. The research groups, users of Bldg. Pu1, were driven by necessity to remove used equipment and transport nuclear fuel to other facilities from Bldg. Pu1. Research Group for Radiochemistry proactively established the Used Equipment Removal Team for the smooth operation of the removal in April, 2015. The team classified six types of work into the nature of the operation, removal of used equipment, disposal of chemicals, stabilization of mercury, stabilization of nuclear fuel, transportation of nuclear fuel and radioisotope, and survey of contamination status inside the glove boxes. These works were completed in December, 2015. This report circumstantially shows six works process, with the exception of the approval of the changes on the usage of nuclear fuel in Bldg. Pu1 to help prospective decommission.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yamamoto, Masahiro
ECS Transactions, 75(27), p.51 - 57, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:36.09(Electrochemistry)We investigated the deposition of U(IV) following a valence change of U as electrodeposition using an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM). When measurements of the reduction of U(VI) in a weak acid solution were performed, deposits of U(IV) were observed on the electrode surface. From deposition rates, pH dependence of them, and oxidation potentials of deposits, we proposed the following deposition mechanism. The deposition is divided into the three phases; First, in the induction phase, U(IV) produced by the disproportionation forms U(IV) hydroxide nucleus. Next, in the growth phase, U(IV) deposits begin to grow. In this phase, the deposits catalyze the reduction of U(V) to U(IV), resulting an increase of the reduction current. Finally, in the transformation phase, U(IV) hydroxide species transform into U dioxide having more stable state.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2016-005, 40 Pages, 2016/05
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) method is an attractive technique because real-time, in-situ and remote elemental analysis is possible without any sample preparation. The LIBS technique can be applied for analyzing elemental composition of samples under severe environments such as the estimation of impurities in the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the detection of fuel debris in the post-accident nuclear core reactor of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For applying LIBS to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is indispensable to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). In the present study, an echelle spectrometer with a resolving power of 50,000 was employed to identify spectra of natural uranium of wavelength ranging from 470 to 670 nm. The 173 atomic spectra and 119 ionic spectra can be identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2015-012, 48 Pages, 2015/10
It is important to analyze the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the fuel debris generated at the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Therefore, the remote analysis for nuclear fuel materials using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) is studied. For applying Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is very important to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). Then, the high resolution spectra of natural uranium of wavelength region of 350-470 nm are measured using LIBS, 247 atomic spectra and 294 single ion spectra were identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
Reza Kenkyu, 42(12), p.918 - 922, 2014/12
For the remote analysis of the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA), Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) was applied to uranium oxide (U O
O ) including a small amount of neodymium oxide (Nd
) including a small amount of neodymium oxide (Nd O
O ) as a simulated sample of MA. By using deconvolution technique for the spectra of Nd in U, the complex, overlapped and confused spectra were separated and their actual intensities were determined. As a result, the calibration curve with good linearity and the detection limit of less than 700 ppm were demonstrated.
) as a simulated sample of MA. By using deconvolution technique for the spectra of Nd in U, the complex, overlapped and confused spectra were separated and their actual intensities were determined. As a result, the calibration curve with good linearity and the detection limit of less than 700 ppm were demonstrated.
Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kurata, Masaki; Takano, Masahide
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2014/10
The chemical and transport behaviors of Pu and U in the corroded debris must be understood for the criticality safety control of Pu and U in the debris, especially for the removal operations and storage. Therefore, the chemical changes of UO and PuO
and PuO powders, disks and U and Pu metal disks in H
powders, disks and U and Pu metal disks in H O
O aqueous solution have been checked, where H
aqueous solution have been checked, where H O
O is formed by the radiolysis of H
is formed by the radiolysis of H O. As a result, UO
O. As a result, UO changed to hydrated uranium peroxide, whereas the PuO
changed to hydrated uranium peroxide, whereas the PuO remained unchanged. U metal was more reactive with H
remained unchanged. U metal was more reactive with H O
O aqueous solution than Pu metal. The chemical changes of the mixed UO
aqueous solution than Pu metal. The chemical changes of the mixed UO /PuO
/PuO powders in H
powders in H O
O aqueous solution have been investigated. The dried slurry of the middle zone of H
aqueous solution have been investigated. The dried slurry of the middle zone of H O
O aqueous solution was mainly composed of hydrated uranium peroxide, whereas the dried powder of the bottom zone was mainly composed of PuO
aqueous solution was mainly composed of hydrated uranium peroxide, whereas the dried powder of the bottom zone was mainly composed of PuO .
.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kimura, Takaumi; Kihara, Sorin*
Electrochimica Acta, 141, p.6 - 12, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:9.00(Electrochemistry)Reduction processes of U(VI) in weakly acidic solutions were investigated based on electrochemical and spectrophotometric measurements. A reversible one-electron reduction of U(VI) to U(V) and a further irreversible reduction of U(V) were observed voltammetrically at a gold microdisk electrode in solutions of pH from 2.0 to 3.5. Aggregates of U(IV) were formed as a deposit on the electrode and a colloid in the bulk solution, when the electrolysis was carried out at a gold gauze electrode, even though the potential applied was that available for the first one-electron reduction wave of U(VI) observed. It was elucidated that the aggregate was produced by the combination of the one-electron reduction to U(V) and the disproportionation of U(V) producing U(IV) and U(VI). The aggregate enhanced the rate of the disproportionation of U(V), and hence the reduction current of U(VI) increased abruptly when a definite amount of aggregate was formed on the electrode, in the solution, or both.
Otobe, Haruyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 442(1-3), p.394 - 399, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The chemical properties (ex. atomic diffusion), the thermal properties (ex. melting point and thermal diffusivity) and the mechanical properties of oxide fuels are significantly dependent on the oxygen defects of the oxide fuels. For the first step to specify the oxygen defects of oxide fuels, we have tried the thermodynamic approaches to the oxygen defects by comparing the relations between the molar ratio of oxygen to metal (O/M) and the oxygen potentials of Pu, Am, Cm, Ce oxides and several solid solutions including Zr and Np dioxides. Consequently, we have found the consistent properties in the relations between O/M and the oxygen potentials of actinide, lanthanide oxides and their solid solutions, in addition to the dependence of the relations on the crystal structures.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Takano, Masahide; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Koyama, Tadafumi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 297(1), p.139 - 144, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.42(Chemistry, Analytical)Curium trichloride was synthesized by the solid state reaction of curium nitride with cadmium chloride heated from room temperature to 748K in a dynamic vacuum. The product was hexagonal  CmCl
CmCl , of which lattice parameters were determined to be a= 0.7385
, of which lattice parameters were determined to be a= 0.7385 0.0005 and c= 0.4201
0.0005 and c= 0.4201 0.0005 nm. The melting temperature of the
0.0005 nm. The melting temperature of the  CmCl
CmCl sample was determined to be 970
sample was determined to be 970 3 K by differential thermal analyses using a gold crucible. These values are close to those reported in literatures. The results show that mg-scale CmCl
3 K by differential thermal analyses using a gold crucible. These values are close to those reported in literatures. The results show that mg-scale CmCl samples for thermochemical measurements were prepared from the purified oxide sample without the use of corrosive reagents.
samples for thermochemical measurements were prepared from the purified oxide sample without the use of corrosive reagents.
 Zr
Zr O
O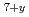
Otobe, Haruyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 94(10), p.3596 - 3599, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:25.57(Materials Science, Ceramics)The relations between the oxygen potentials and the oxygen-nonstoichiometry (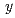 ) of the pyrochlore-type Am
) of the pyrochlore-type Am Zr
Zr O
O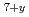 for 1333 K were measured by the electrochemical method using a zirconia solid electrolyte and the mass changes by the oxidation and reduction. It was found that the oxygen potential of Am
for 1333 K were measured by the electrochemical method using a zirconia solid electrolyte and the mass changes by the oxidation and reduction. It was found that the oxygen potential of Am Zr
Zr O
O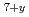 smoothly increased from -516.52 to 0 kJ/mol with increasing
smoothly increased from -516.52 to 0 kJ/mol with increasing 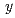 from 0.0 to 0.56 at 1333K. The oxygen potentials of Am
from 0.0 to 0.56 at 1333K. The oxygen potentials of Am Zr
Zr O
O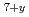 were higher than those of AmO
were higher than those of AmO at the corresponding O/M by approximately 130 kJ/mol. The difference of the oxygen potentials between Am
at the corresponding O/M by approximately 130 kJ/mol. The difference of the oxygen potentials between Am Zr
Zr O
O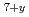 and AmO
and AmO was consistent with that between Pu
was consistent with that between Pu Zr
Zr O
O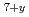 and PuO
and PuO considering the difference of the ionic radii between Am and Pu. This leads to the systematical understanding of the thermodynamic properties of the transuraniumm oxides.
considering the difference of the ionic radii between Am and Pu. This leads to the systematical understanding of the thermodynamic properties of the transuraniumm oxides.
Tagami, Susumu; Sano, Naruto; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Akabori, Mitsuo; Kurobane, Shiro
JAEA-Technology 2010-034, 65 Pages, 2010/10
An experimental facility called the Module for TRU High Temperature Chemistry (TRU-HITEC) was installed in the Back-end Cycle Key Elements Research Facility (BECKY) of the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility (NUCEF) in February, 2003. The main purpose of this facility is to perform the basic studies of the behavior the transuranium elements (TRU) in pyrochemical reprocessing and oxide fuels. Hot-experiment started in December, 2004. TRU-HITEC consists of three  /
/ cells and a glove box. This is the only facility in the country as large-scale facilities maintained a high purity argon gas atmosphere. The experience gained through the maintenance and improvement is useful also for the maintenance of similar designed facility. This report describes the maintenance method and improvement for the purpose of keeping the performance of TRU-HITEC.
cells and a glove box. This is the only facility in the country as large-scale facilities maintained a high purity argon gas atmosphere. The experience gained through the maintenance and improvement is useful also for the maintenance of similar designed facility. This report describes the maintenance method and improvement for the purpose of keeping the performance of TRU-HITEC.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2010-036, 14 Pages, 2010/10
For the remote analysis of low DF TRU (Decontamination Factor Transuranic) fuel, Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) was applied to uranium oxide including a small amount of calcium oxide (3306ppm(weight)) as a sample, and the spectrum emitted from laser-breakdown plasma was examined. The characteristics, such as spectrum intensity and plasma excitation temperature as a function of laser power, were measured using time-resolved spectroscopy. As a result, the laser power of around 5 mJ was found optimum to obtain the stable intensity and narrow line width of spectrum.