Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kubota, Tomohiro; Kuroda, Hisao*; Watanabe, Mirai*; Takahashi, Akiko*; Nakazato, Ryoji*; Tarui, Mika*; Matsumoto, Shunichi*; Nakagawa, Keita*; Numata, Yasuko*; Ouchi, Takao*; et al.
Atmospheric Environment, 243, p.117856_1 - 117856_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:10.92(Environmental Sciences)The dry and wet depositions of atmospheric ammonia (NH ) is one of the important pathways of nitrogen loads to aquatic ecosystems. Crop and livestock agriculture, one of the largest emitters of NH
) is one of the important pathways of nitrogen loads to aquatic ecosystems. Crop and livestock agriculture, one of the largest emitters of NH in Asian countries, are known to cause high spatial and seasonal variation of NH
in Asian countries, are known to cause high spatial and seasonal variation of NH and influence the surrounding lake basin areas via its dry and wet deposition. However, the spatial characteristics of the NH
and influence the surrounding lake basin areas via its dry and wet deposition. However, the spatial characteristics of the NH concentration in basin scale are not completely understood for regulation in NH
concentration in basin scale are not completely understood for regulation in NH emission. Here we aim to clarify dominant factors of spatial and seasonal variations of the NH
emission. Here we aim to clarify dominant factors of spatial and seasonal variations of the NH concentration in a eutrophic lake basin surrounded by agricultural areas in Japan. Passive sampling over various land use categories in the basin was conducted at 36 sites in total from October 2018 to January 2020. Interestingly, the observed NH
concentration in a eutrophic lake basin surrounded by agricultural areas in Japan. Passive sampling over various land use categories in the basin was conducted at 36 sites in total from October 2018 to January 2020. Interestingly, the observed NH concentration near the livestock houses were higher in winter than summer, which was inconsistent with knowledge of seasonal changes of current NH
concentration near the livestock houses were higher in winter than summer, which was inconsistent with knowledge of seasonal changes of current NH emission inventory based on temperature-driven volatilization process. Comparing monthly NH
emission inventory based on temperature-driven volatilization process. Comparing monthly NH concentrations with various meteorological factors, we suggested the importance of seasonal advection of NH
concentrations with various meteorological factors, we suggested the importance of seasonal advection of NH from high emission sources to which has been rarely paid attention by the previous past studies. As for this, should be considered for lake ecosystem management since deposition of NH
from high emission sources to which has been rarely paid attention by the previous past studies. As for this, should be considered for lake ecosystem management since deposition of NH is known to be closely related to the ecological processes such as phytoplankton blooming.
is known to be closely related to the ecological processes such as phytoplankton blooming.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 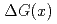 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:192 Percentile:99.39(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 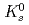 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Miyamoto, Yoichi; Ouchi, Jin
Glass Technology, 39(4), p.142 - 148, 2002/00
None
 /Fe
/Fe in a candidate glass for immobilisation of high level nuclear waste
in a candidate glass for immobilisation of high level nuclear wasteIwase, Masanori*; Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Miyamoto, Yoichi; Ouchi, Jin
Glass Technology, 39(4), p.142 - 146, 1998/08
None
Ouchi, Jin; ; Kawamura, Kazuhiro; ; ; Sasage, Kenichi; Odakura, Makoto
PNC TN8410 97-044, 53 Pages, 1997/03
The glass transition temperature of simulated waste glass was measured by DTA installed in CPF (Chemical Processing Facility) and HTS (High Level Waste Technology Section). This measurement was intended to confirm the agreement between hot and cold data as a part of characterization of high level waste glass. Glass transition temperature is an index of the temperature to keep thermal stability of high-level waste glass. Since devitrification deteriorates characteristics of waste glass above glass transition temperature, it is necessary to measure glass transition temperature and keep glass temperature below glass transition temperature. The conventional method to determine glass transition temperature is the measurement of thermal expansion, but DTA is adopted for radioactive sample because of easier preparation. We obtained following results by measuring glass transition temperature of simulated waste glasses after calibration with standard specimen : (1)The average glass transition temperature of TVF waste glass (P0798) measured by DTA in HTS and CPF was 494 C (standard deviation 3
C (standard deviation 3  : 8.2
: 8.2 C) and 495
C) and 495 C (3
C (3 : 1.8
: 1.8 C), respectively. The difference between two analyzer was 1
C), respectively. The difference between two analyzer was 1 C. It shows the good agreement between hot and cold DTA data. (2)Glass transition temperature of P0798 measured by thermal expansion method was 495
C. It shows the good agreement between hot and cold DTA data. (2)Glass transition temperature of P0798 measured by thermal expansion method was 495 C(3
C(3 : 8.1
: 8.1 C) and it agrees well with that measured by DTA. (3)The average glass transition temperature of simulated highly waste-loading glass (P1102) measured by DTA in HTS and CPF was 510.5
C) and it agrees well with that measured by DTA. (3)The average glass transition temperature of simulated highly waste-loading glass (P1102) measured by DTA in HTS and CPF was 510.5  2.5
2.5 C.
C.
Yoneya, Masayuki; Kawamura, Kazuhiro; ; Sasage, Kenichi; ; Ouchi, Jin
Donen Giho, (98), p.85 - 90, 1996/06
None
Kawamura, Kazuhiro; ; ; Ouchi, Jin;
PNC TN8100 96-003, 173 Pages, 1996/03
no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Ouchi, Jin; Iwase, Masanori*; Watanabe, H.*
Radioactive Waste Management and the Nuclear Fuel Cycle, 20(1), p.61 - 70, 1995/12
None
Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Ouchi, Jin
MRS '94, 0 Pages, 1995/00
None
Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Ouchi, Jin
Proceedings of 18th International Symposium on Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management (MRS '94), 0 Pages, 1995/00
None
Yoneya, Masayuki; Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Igarashi, Hiroshi; Ouchi, Jin
Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Radioactive Waste Management and Environmental Remediation (ICEM '95), p.389 - 393, 1995/00
None
Igarashi, Hiroshi; Masaki, Toshio; Ouchi, Jin
SPECTRUM '94, 0 Pages, 1994/08
None
Ouchi, Jin; Ayame, Yasuo; Terada, Akihiko; Masaki, Toshio; Kobayashi, Hiroaki; Igarashi, Hiroshi
PNC TN8410 94-219, 473 Pages, 1994/06
None