Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
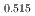 Gd
Gd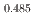 Mn
Mn O
O
Ishii, Yuta*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Lustikova, J.*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Wakabayashi, Yusuke*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*
Physical Review B, 110(18), p.184404_1 - 184404_7, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Yamamoto, Hajime*; Ikeda, Osamu*; Honda, Takashi*; Kimura, Kenta*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Suzuki, Akio*; Ishii, Kenji*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 8(9), p.094402_1 - 094402_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:51.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) I in riverbank sediment after the Fukushima accident
I in riverbank sediment after the Fukushima accidentNakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Oyama, Takuya; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Suzuki, Takashi
Environmental Pollution, 355, p.124213_1 - 124213_7, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.42(Environmental Sciences)This study investigated the transport behavior of  I by riverbank surveys conducted from 2013 to 2015 in a watershed where the
I by riverbank surveys conducted from 2013 to 2015 in a watershed where the  I/
I/ Cs activity ratio is low in the mountainous area and high in the plain as of 2011. Until 2015, the
Cs activity ratio is low in the mountainous area and high in the plain as of 2011. Until 2015, the  I/
I/ Cs activity ratio of the levee crown in the studied watershed was similar to that of the surrounding area in 2011. However, the
Cs activity ratio of the levee crown in the studied watershed was similar to that of the surrounding area in 2011. However, the  I/
I/ Cs ratios of the surface riverbank sediments were all low, indicating that radionuclides transported from the mountainous area were deposited on the riverbank in the plain. The vertical distribution of the
Cs ratios of the surface riverbank sediments were all low, indicating that radionuclides transported from the mountainous area were deposited on the riverbank in the plain. The vertical distribution of the  I/
I/ Cs ratio in the riverbank sediments indicated that some
Cs ratio in the riverbank sediments indicated that some  I and
I and  Cs deposited during the accident remained in the lower layers, but most were eroded immediately after the accident. Based on the
Cs deposited during the accident remained in the lower layers, but most were eroded immediately after the accident. Based on the  I/
I/ Cs ratios of sediments deposited on the riverbank, which remained constant until 2015 after the accident, the amount of
Cs ratios of sediments deposited on the riverbank, which remained constant until 2015 after the accident, the amount of  I discharged to the ocean was determined from the previously evaluated
I discharged to the ocean was determined from the previously evaluated  Cs discharge. It was calculated that 1.8
Cs discharge. It was calculated that 1.8 10
10 Bq and 1.2
Bq and 1.2 10
10 Bq of
Bq of  I were discharged with sediment from the studied watershed and the contaminated river watersheds (Abukuma River and Fukushima coastal rivers, including the study river), respectively. The results of this study indicate that the continuous
I were discharged with sediment from the studied watershed and the contaminated river watersheds (Abukuma River and Fukushima coastal rivers, including the study river), respectively. The results of this study indicate that the continuous  I discharge from the river contribute little to their amount in the seafloor sediments along the Fukushima coast.
I discharge from the river contribute little to their amount in the seafloor sediments along the Fukushima coast.
Koyama, Shinichi; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Tsai, T.-H.; Takano, Masahide; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Satoshi; et al.
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 216 Pages, 2023/11
In FY 2021 and 2022, JAEA perfomed the subsidy program for "the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy, Thermal Bahavior Estimation, and Simplified Analysis of Fuel Debris)" started in FY 2021. This presentation material summarized the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Nagae, Yuji; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Mizokami, Shinya; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Koyama, Shinichi
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 53 Pages, 2023/10
JAEA performed the subsidy program for the "Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technologies for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Estimation Technologies of RPV Damaged Condition, etc.) in 2022JFY. This presentation summarized briefly the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
Harada, Takuya*; Nagata, Mitsuhiro; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori
Chigaku Zasshi, 132(1), p.57 - 65, 2023/02
The Harachiyama Formation is Lower Cretaceous volcanic rocks, distributed in the eastern margin of the Kitakami Mountains in northeastern Japan. We performed whole-rock chemical analysis, zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotope analysis from the Harachiyama Formation to constrain the formation age and discuss the origin of magma. The lava and tuff samples of the Harachiyama Formation from the Omoto and Tsukue areas support island-arc rhyolitic rocks (SiO content
content  70%), and yielded the weighted mean U-Pb ages of 127.8
70%), and yielded the weighted mean U-Pb ages of 127.8  3.4 Ma and 129.2
3.4 Ma and 129.2  2.6 Ma (2
2.6 Ma (2 ), respectively. Eighteen zircon grains from two samples, dated between 141.6 Ma and 123.9 Ma, yielded positive
), respectively. Eighteen zircon grains from two samples, dated between 141.6 Ma and 123.9 Ma, yielded positive  Hf(t) values between +5.0 and +8.7. These ages and values are consistent with those of the Kitakami Granititods reported in previous studies. Therefore, it is suggested that the Harachiyama Formation have the same magmatic origin as the Kitakami Granitoid.
Hf(t) values between +5.0 and +8.7. These ages and values are consistent with those of the Kitakami Granititods reported in previous studies. Therefore, it is suggested that the Harachiyama Formation have the same magmatic origin as the Kitakami Granitoid.
Nakanishi, Takahiro; Oyama, Takuya; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Sakuma, Kazuyuki
Journal of Coastal Research, 114(SI), p.310 - 314, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.44(Environmental Sciences)The two huge typhoons in 2019, Hagibis and Bualoi, caused enormous flood damage to Fukushima. On the basis of field observations over 6 years in Ukedo River near the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant, sediment and  Cs discharges from the river catchment were quantitatively evaluated. Approximately 90% of annual sediment and
Cs discharges from the river catchment were quantitatively evaluated. Approximately 90% of annual sediment and  Cs discharges in 2019 was occupied during the typhoons Hagibis and Bualoi events. This sediment discharge was almost twice than the discharge during the largest ever flood event since the Fukushima nuclear accident, caused by typhoon Etau in September 2015. However,
Cs discharges in 2019 was occupied during the typhoons Hagibis and Bualoi events. This sediment discharge was almost twice than the discharge during the largest ever flood event since the Fukushima nuclear accident, caused by typhoon Etau in September 2015. However,  Cs discharge during Hagibis and Bualoi events was two-thirds that of Etau event, because the particulate
Cs discharge during Hagibis and Bualoi events was two-thirds that of Etau event, because the particulate  Cs concentration in river water decreased during the observation period. Moreover,
Cs concentration in river water decreased during the observation period. Moreover,  Cs discharge during two typhoon events in 2019 accounted for only 0.1% of the catchment
Cs discharge during two typhoon events in 2019 accounted for only 0.1% of the catchment  Cs deposition and the impact of radiocesium to the coastal area was extremely limited.
Cs deposition and the impact of radiocesium to the coastal area was extremely limited.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Yamada, Teppei*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Takeguchi, Masaki*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shimoyama, Iwao; Kozai, Naofumi; Morooka, Satoshi
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(2), p.105114_1 - 105114_12, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:43.75(Engineering, Environmental)Remediating toxic ion contamination is crucial for protecting human health and the environment. This study aimed to provide a powerful strategy for effectively utilizing bone waste from the food production and preparation industries for removal of toxic ions. Here, we show that immersing pig bone in NaHCO solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr
solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr , Cd
, Cd , Pb
, Pb , and Cu
, and Cu . The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
. The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
Tomiyasu, Keisuke*; Ito, Naoko*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Takahashi, Yuki*; Onodera, Mitsugi*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Nojima, Tsutomu*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; et al.
Advanced Quantum Technologies (Internet), 1(3), p.1800057_1 - 1800057_7, 2018/12
Spin-state transition, also known as spin crossover, plays a key role in diverse systems. In theory, the boundary range between the low- and high-spin states is expected to enrich the transition and give rise to unusual physical states. However, no compound that realizes a nearly degenerate critical range as the ground state without requiring special external conditions has yet been experimentally identified. This study reports that the Sc substitution in LaCoO3 destabilizes its nonmagnetic low-spin state and generates an anomalous paramagnetic state accompanied by the enhancement of transport gap and magneto-lattice-expansion as well as the contraction of Co-O distance with the increase of electron site transfer. These phenomena are not well described by the mixture of conventional low- and high-spin states, but by their quantum superposition occurring on the verge of a spin-state transition.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Nishihata, Yasuo; Kogure, Toshihiro*; Okochi, Takuo*; Yasui, Akira*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 112(2), p.021603_1 - 021603_5, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:29.91(Physics, Applied)A synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) was applied to demonstrate pinpoint analysis of micrometer-sized weathered biotite clay particles with artificially adsorbed cesium (Cs) atoms. Despite the insulating properties of the clay, we observed the spatial distributions of constituent elements (Si, Al, Cs, Mg, Fe) without charging issues. We found that Cs atoms were likely to be adsorbed evenly over the entire particle. Spatially-resolved X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) of the Cs M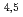 -edge region showed Cs to be present in a monocation state (Cs
-edge region showed Cs to be present in a monocation state (Cs ). Further pinpoint XAS measurements were also performed at the Fe L
). Further pinpoint XAS measurements were also performed at the Fe L -edge to determine the chemical valence of the Fe atoms. Our results demonstrate the utility of SR-PEEM as a tool for spatially-resolved chemical analyses of various environmental substances, which is not limited by the poor conductivity of samples.
-edge to determine the chemical valence of the Fe atoms. Our results demonstrate the utility of SR-PEEM as a tool for spatially-resolved chemical analyses of various environmental substances, which is not limited by the poor conductivity of samples.
Nakanishi, Takahiro; Oyama, Takuya; Hagiwara, Hiroki
KEK Proceedings 2017-6, p.107 - 111, 2017/11
At riverbanks in six rivers (Odaka, Ukedo, Takase, Kuma, Tomioka and Kido rivers) of eastern Fukushima, dose rate distribution in the cross section had been observed from January 2013 to December 2016. Dose rates in the flood plain which were flooded periodically were different from the surroundings. In rivers without reservoirs (Odaka, Takase and Kuma rivers), dose rates in the flood plain were affected by average radiocesium inventory in the whole catchments. By contrast, in rivers with reservoirs (Ukedo, Tomioka and Kido rivers), dose rates in the flood plain were affected by those in the downstream area of reservoirs and the erosion effect.
Watanabe, Takayoshi; Oyama, Takuya; Ishii, Yasuo; Niizato, Tadafumi; Abe, Hironobu; Mitachi, Katsuaki; Sasaki, Yoshito
KEK Proceedings 2017-6, p.122 - 126, 2017/11
no abstracts in English
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Dohi, Terumi; Nakama, Shigeo; Funaki, Hironori; Misono, Toshiharu; Oyama, Takuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Seiji*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-018, 86 Pages, 2017/10
Since the accidents at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant following the Tohoku Region Pacific Coast Earthquake on March 11th, 2011, Fukushima Environmental Safety Center has carried out research on natural mobilization of radionuclide (especially radiocesium) and future forecast from forest to water system and surrounding residential areas. The report summarizes the latest results that have been accumulated from each study field, of our agency together with the other related research organizations. The contents of the report is to be used as evidence-based information for the QA-styled pages in the website of JAEA Sector of Fukushima Research and Development at the time of next renewal.
Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Honda, Mitsunori; Shimoyama, Iwao; Ito, Kenichi*; Mampuku, Yuzo*; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 59(8), p.483 - 487, 2017/08
, 59(8), p.483 - 487, 2017/08
no abstracts in English
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; Iijima, Kazuki; Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Hagiwara, Hiroki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 164, p.36 - 46, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:35.05(Environmental Sciences)The environments of Fukushima have been contaminated due to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accidents caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011. Released radio-cesium mainly affects radiation dose in the environment of Fukushima. It is concerned that redistribution of the radiation dose due to water discharge will be occurred due to the transportation of radio-cesium. Especially, deposition of the transferred soil particle with radio-cesium at flood plain with downstream area is possible cause of increasing radiation dose. Therefore, it is important to understand the influence of deposition behavior of radio-cesium on radiation dose. The paper discusses the deposition behaviors of radio-cesium at river based on the data obtained from the river investigations.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeda, Masaki; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-014, 274 Pages, 2016/08
We synthesized the research results from the Mizunami/Horonobe Underground Research Laboratories (URLs) and geo-stability projects in the second midterm research phase. This report can be used as a technical basis for the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan/Regulator at each decision point from siting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase).
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Yokota, Hideharu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2015-007, 269 Pages, 2015/08
We have synthesised the research results from Mizunami/Horonobe URLs and geo-stability projects in the second mid-term research phase. It could be used as technical bases for NUMO/Regulator in each decision point from sitting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase). High quality construction techniques and field investigation methods have been developed and implemented and these will be directly applicable to the National Disposal Program (along with general assessments of hazardous natural events and processes). It will be crucial to acquire technical knowledge on decisions of partial backfilling and final closure by actual field experiments in Mizunami/Horonobe URLs as main themes for the next phases.
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.46(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of  Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
 Si
Si
Yamashita, Takuya*; Shimoyama, Yusuke*; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Onuki, Yoshichika; Sumiyoshi, Hiroaki*; Fujimoto, Satoshi*; Levchenko, A.*; Shibauchi, Takasada*; et al.
Nature Physics, 11(1), p.17 - 20, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:90.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi; Masud, R. S.*; Kawamura, Takuya*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Niibori, Yuichi*
Nihon Ion Kokan Gakkai-Shi, 25(4), p.220 - 227, 2014/11
no abstracts in English