Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Hayano, Akira; Ono, Hirokazu; Tachi, Yukio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
, 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency launched the Horonobe International Project (HIP) utilizing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The main objectives of this project are to develop and demonstrate advanced technologies to be used in repository design, operation and closure and a realistic safety assessment in deep geological disposal, and to encourage and train the next generation of engineers and researchers. In this review, an overview of the HIP is presented.
Ishii, Eiichi; Ozaki, Yusuke; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Sugawara, Kentaro*
Hydrogeology Journal, 33(1), p.63 - 85, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)This study performed virtual packer tests on modeled single fractures on computer and derived the relationship between flow dimension and mappable indicator, DI, which is defined by the mean stress, groundwater pressure, and rock tensile strength. The greater DI results in the smaller flow area in faults or fractures, subject to fracture-normal closure. Comparing the derived relationship with results from in situ hydraulic tests on natural faults in rock with few fracture-mineral-fillings revealed that flow-path connectivity is high (flow dimension 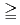 1.5) when DI was
1.5) when DI was  2.0 while was low (flow dimension
2.0 while was low (flow dimension  1.5) when DI was
1.5) when DI was 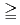 2.0. This relationship was valid even when DI was varied, or faults were sheared, during injection tests on faults, and even in rock with abundant fracture-mineral-fillings. However, flow-path connectivity in minor fractures far from faults could be also low even when DI was
2.0. This relationship was valid even when DI was varied, or faults were sheared, during injection tests on faults, and even in rock with abundant fracture-mineral-fillings. However, flow-path connectivity in minor fractures far from faults could be also low even when DI was  2.0 probably due to poor connection to the main fault network or sealing effects of fracture-mineral-fillings. When the permeability of intact rock is high, flow-path connectivity in fractures was high even when DI was
2.0 probably due to poor connection to the main fault network or sealing effects of fracture-mineral-fillings. When the permeability of intact rock is high, flow-path connectivity in fractures was high even when DI was 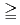 2.0. These findings can be helpful to map the spatial distribution of flow-path connectivity in faults or fractures from limited borehole data.
2.0. These findings can be helpful to map the spatial distribution of flow-path connectivity in faults or fractures from limited borehole data.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Ono, Hirokazu; Ishii, Eiichi
Dai-16-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.269 - 274, 2025/01
We investigated the development of the excavation damaged zone (EDZ) induced by the excavation of modeled disposal pit which was excavated as a part of the full-scale engineering barrier experiment at 350 m depth. Seismic and electric tomography surveys, observation of rock core samples, borehole televiewer surveys and three-dimensional excavation analysis were performed to evaluate the extent of the EDZ around the pit. It was clarified that the EDZ was developed 0.8 to 1.6 m from the wall of the pit at a relatively shallower depth caused by the effect of the EDZ induced around the floor of the gallery. The extent of the EDZ was gradually reduced along the depth, and the maximum extension was 0.3 m from the wall of the pit at the deeper section.
Ozaki, Yusuke
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 31(2), p.128 - 133, 2024/12
Task A of the Horonobe International Project (HIP) aims to investigate the characteristics of solute transport of the Koetoi Formation at 250 m stage of the Horonobe underground research laboratory (URL). The objective of this task is to develop a modeling approach of solute transport considering actual phenomena occurring in the rock based on in-situ tracer experiments along with the discussion on transferability of data and modeling approach from different geological environment. Phase 1 of task A is divided into four subtasks of planning of in situ experiments, laboratory experiments, field experiments, and modeling. These subtasks are tackled by participating organizations as collaborative research, and I present the current situation of each subtask and our cooperation.
Ozaki, Yusuke; Ishii, Eiichi
Geoenergy (Internet), 2(1), p.geoenergy2023-056_1 - geoenergy2023-056_11, 2024/12
This study estimated the effective hydraulic conductivity around the Horonobe URL from the monitoring data of inflow into shaft and change in hydraulic pressure measured in HDB-6 for over ten years. The effective hydraulic conductivity was related to the fault transmissivities and flow dimension using Landau-Lifshitz-Matheron's formula. From the comparison of the estimated effective hydraulic conductivity with the calculated fault transmissivities, the effective hydraulic conductivity was compatible with the transmissivities considering the dependency on ductility index and flow dimension.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Tamura, Tomonori; Ishii, Eiichi
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Coupled Processes in Fractured Geological Media; Observation, Modeling, and Application (CouFrac2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/11
In high-level radioactive waste disposal, it is crucial to estimate the transmissivity of gallery excavation-induced fractures, i.e., excavation damaged zone (EDZ) fractures, because EDZ fractures can be a radionuclide migration pathway after the backfilling of the facility is completed. From previous research, the transmissivity of the fracture can be estimated through the empirical equation using the parameter ductility index (DI), which corresponds to the effective mean stress normalized to the tensile strength of the rock. In this research, we performed a hydromechanical coupling analysis of a gallery excavation at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory to estimate the transmissivity of the EDZ fracture before the excavation. At first, we simulated the gallery excavation at 350 m and showed that the measured transmissivity was within the range of the estimated transmissivity using the DI. After that, we also predicted the excavation of a gallery at 500 m by setting the hydromechanical parameters acquired from the laboratory tests before the excavation. The estimated transmissivity at 500 m was one order of magnitude less than that at 350 m. This result might be related to the closure of the fracture under high-stress conditions and low rock strength.
Ozaki, Yusuke; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Kimura, Shun
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Coupled Processes in Fractured Geological Media; Observation, Modeling, and Application (CouFrac2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/11
Electrical resistivity tomography was repeatedly carried out to investigate the changes of the electrical resistivity distribution around 350m Niche No. 2 and No. 4 in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The electrical resistivity around Niche No. 2 did not change so much after the high resistive zone appeared around the tunnel by the excavation under opened condition during the studied period. Around Niche No. 4, the electrical resistivity was investigated under closed condition by engineered barrier system (EBS) where the EBS and surrounding rocks were disturbed artificially by water injection and heating. Our results could capture the change in the distribution of electrical resistivity due to the artificial disturbances in and around of Niche No. 4. These results would help us to understand the time lapse behavior of excavation damaged zone and re-saturation process in and around the EBS from the construction to the closure.
Hirota, Akinari*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Sakuma, Keisuke; Ozaki, Yusuke; Ishii, Eiichi; Suzuki, Yohei*
Microbial Ecology, 87, p.132_1 - 132_15, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.84(Ecology)Deep underground galleries are used to access the deep biosphere in addition to mining and other engineering applications such as geological disposal of radioactive wastes. Fracture networks developed in the excavation damaged zone (EDZ) are concerned to accelerate mass transport, where microbial colonization might be possible due to the availability of space and nutrients. In this study, microbial biofilms at EDZ fractures were investigated by drilling from a 350-m deep gallery and subsequent borehole logging at the Horonobe underground research laboratory (URL). By using microscopic and spectroscopic techniques, the dense colonization of microbial cells was demonstrated at the surfaces of the EDZ fractures with high hydraulic conductivities. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis revealed the dominance of gammaproteobacterial lineages, the cultivated members of which are aerobic methanotrophs. Near-complete Horonobe groundwater genomes affiliated within the methanotrophic lineages were fully equipped with genes involved in aerobic methanotrophy. Although the mediation of aerobic methanotrophy remains to be demonstrated, microbial O production was supported by the presence of genes in the near-complete genomes, such as catalase and superoxide dismutase that produce O
production was supported by the presence of genes in the near-complete genomes, such as catalase and superoxide dismutase that produce O from reactive oxygen species and a nitric oxide reductase gene with the substitutions of amino acids in motifs. It is concluded that the EDZ fractures provide energetically favorable subsurface habitats to microorganisms.
from reactive oxygen species and a nitric oxide reductase gene with the substitutions of amino acids in motifs. It is concluded that the EDZ fractures provide energetically favorable subsurface habitats to microorganisms.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Sasao, Eiji; Hibara, Ryoko*; Murakami, Hiroaki; Ozaki, Yusuke
Heliyon (Internet), 10(17), p.e37417_1 - e37417_17, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Understanding the mass transfer characteristics of matrix diffusion and sorption is important in geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in crystalline rock. We present a comparative discussion of the effective diffusion coefficient (De), porosity, and petrological data for rock samples collected from the Toki Granite in central Japan, to evaluate the role of micropores within minerals in retardation by matrix diffusion and sorption in granitic rocks. De was derived from the through-diffusion experiments. Petrological data consist of the fracture frequency, the extent of hydrothermal alteration in the minerals, the micropore volume in the minerals, and the three-dimensional modal mineralogy for the target rock samples. The relationship between the De, porosity, and petrological data has the following implications: 1) Micropores act as storage pores that contribute to retardation; 2) Once the uranine, cations, and anion penetrate the micropores in the minerals through matrix diffusion, the cations are sorbed on the micropore surfaces; 3) Regions with a high fracture frequency are associated with not only active advection-dispersion through fractures, but also retardation due to matrix diffusion and sorption.
Rapp, L.*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Firestein, K. L.*; Sagae, Daisuke*; Habara, Hideaki*; Mukai, Keiichiro*; Tanaka, Kazuo*; Gamaly, E. G.*; Kodama, Ryosuke*; Seto, Yusuke*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(2), p.023101_1 - 023101_18, 2024/04
It is generally known that irradiating a solid surface with a laser pulse of ultra-relativistic intensity generates a plasma on the surface, which in turn creates an ultrahigh pressure inside. In this study, the crystal structure analysis of high-pressure phases generated inside silicon single-crystals irradiated by this laser was performed using the diffraction system at the Stress and Imaging apparatus of BL22XU, which is a JAEA-BL. The results obtained confirm the existence of high-pressure phases that silicon is said to possess: body-centered, rhombohedral, hexagonal, and tetragonal phases in the interior. We can get the results that the crystal structure of silicon polymorphs of being include body-centered, rhombohedral, hexagonal-diamond, tetragonal exists. In the future, we will accumulate data and apply them to control the internal structure, strength, and functionality of materials.
Maeda, Masaki*; Tanabe, Tadao*; Nishiwaki, Tomoya*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Dozaki, Koji*; Nishimura, Koshiro*; Fujii, Sho*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tanaka, Akio*; Suzuki, Yusuke*; et al.
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Oketani, Kazuki*; Fujii, Hirokazu*; Zhao, Y.*; Kato, Masaji*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Matsui, Hiroya; Kono, Masanori*
Zairyo, 73(3), p.220 - 225, 2024/03
The fractures in the rock are the main pass of groundwater flow and solute transport. The filling of fine-grained particle, such as clay minerals, was confirmed to decrease the permeability of rock by laboratory experiment. This research aimed to verify the occurrence of the phenomena in the field. The water containing the clay minerals was injected into the rock at the 200m stage of the Mizunami Underground research laboratory. The hydraulic conductivity decreased two order before and after the injection. This result suggested that the decrease of hydraulic conductivity by the filling of fine-grained particle in the fractures occurred in the real field.
Ozaki, Yusuke; Ono, Hirokazu; Aoyagi, Kazuhei
Shigen, Sozai Koenshu (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/09
In the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, the in-situ experiment for performance confirmation of engineered barrier system was performed at the 350 m stage to develop the technology for geological disposal. Several measurements have been conducted in and around the test drift to investigate the time dependent impact of the experiment on the rock and backfilled tunnel. Some measurement results are introduced in this presentation.
Ozaki, Yusuke
Rock Mechanics Bulletin (Internet), 2(3), p.100057_1 - 100057_12, 2023/07
In this study, a series of data repeatedly acquired by first arrival traveltime tomography for seven years was analyzed to investigate the time-lapse behavior of excavation damaged zone (EDZ) at 350 m stage in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The data was highly affected by the shotcrete on the drift wall, and a priori information on the structure of shotcrete was incorporated into the inversion process to alleviate the effect. In addition, time-lapse inversion was applied to trace the change in P-wave velocity in time. Our inversion results indicated that time dependent change of EDZ was not recognized under open-drift condition during the period in the site.
Ozaki, Yusuke; Ishii, Eiichi
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/05
This study aims to verify the estimated hydrogeological model by simulating the monitoring data of pore pressure for longer than 14 years around Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL). A previous study estimated hydrogeological structure around the URL by simulating the monitoring data for 1 year. The subsequent monitoring data of hydraulic head at the same location enabled to validate the hydrogeological structure.
Miyagawa, Reina*; Kamibayashi, Daisuke*; Nakamura, Hirotaka*; Hashida, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Somekawa, Toshihiro*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Ogura, Hiroyuki*; Sagae, Daisuke*; Seto, Yusuke*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.20955_1 - 20955_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.68(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We evaluated Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structure (LIPSS) crystal structures using the stress imaging station at BL22XU of JAEA-BL on SPring-8. Crystallization of LIPPS was used different two types laser these are Ti:Sapphire laser (wavelength: 800 nm) and MIR-FEL (mid-infrared free electron laser, wavelength 11.4  m). These lasers are different in the laser pulse structure and the wavelength. We investigated on the effects of formed LIPSS crystallization using different kind of laser. Measured synchrotron X-ray energy is 30 keV and beam size is 20
m). These lasers are different in the laser pulse structure and the wavelength. We investigated on the effects of formed LIPSS crystallization using different kind of laser. Measured synchrotron X-ray energy is 30 keV and beam size is 20  m. Detector of diffracted X-ray is two-dimensional detector (PILATUS300K, DECTRIS). LIPSS formed using Ti:Sapphire laser has deformed structure with good crystallinity. LIPSS formed using MIR-FEL has dislocation or fault without structural stress. These results show depending on select of laser forming LIPPS structure. These information becomes important a point of the functional application of LIPSS.
m. Detector of diffracted X-ray is two-dimensional detector (PILATUS300K, DECTRIS). LIPSS formed using Ti:Sapphire laser has deformed structure with good crystallinity. LIPSS formed using MIR-FEL has dislocation or fault without structural stress. These results show depending on select of laser forming LIPPS structure. These information becomes important a point of the functional application of LIPSS.
Ozaki, Yusuke; Ishii, Eiichi; Sugawara, Kentaro*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 31, p.100311_1 - 100311_13, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.79(Energy & Fuels)This study analyzed the long-term hydraulic pressure data during the excavation of Horonobe URL to estimate the variation of effective-hydraulic-conductivity. We performed the numerical simulation with the poroelastic effect for the estimation because the observed hydraulic pressure is highly affected by the Mandel-Cryer effect. The evaluation of the observed data based on our simulation results showed that the effective-hydraulic-conductivity gradually decreases from 400 m to 500 m in depth and is as low as the intact rock at depths greater than 500 m. Not only the analysis based on our simulation results but also the analysis based on analytical solution indicate the domain with different hydraulic properties in the Wakkanai Formation. These results suggest that the fracture-hydraulic-connectivity changes not abruptly but gradually over several tens of meters around the predicted boundary.
Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Takamatsu, Misao; Sakamoto, Naoki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Onishi, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-020, 42 Pages, 2021/10
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculate from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2020 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
Ozaki, Yusuke; Miyara, Nobukatsu
Proceedings of 14th SEGJ International Symposium (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/10
The drift excavation damages the intact rock around the drift wall and changes the physical properties there. The damaged domain is called excavation damaged zone (EDZ). The correct estimation of depth and the understanding of time lapse behavior of EDZ is required for the technology of drift closure. In Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL), we repeatedly performed the travel time tomography to investigate the time lapse behavior of EDZ generated in soft sedimentary rock over time. For the analysis of the acquired data for the travel time tomography, we performed numerical simulation and estimated the conceivable change in the arrival time. The results of numerical simulation indicate that the shotcrete on the drift wall has the great impact on the travel time because of its high stiffness whereas the effect of shotcrete fixing the ray path might be the advantage for the monitoring purpose. The analysis of the data acquired at 350 m suggest that the significant change in EDZ that surpasses the observation limit was not recognized.
Onoe, Hironori; Ishibashi, Masayuki*; Ozaki, Yusuke; Iwatsuki, Teruki
International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 144, p.104737_1 - 104737_14, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:59.61(Engineering, Geological)In this study, we investigated the methodology of modeling for fractured granite around the drift at a depth of 500 m in the Mizunami Underground Laboratory, Japan as a case study. As a result, we developed the fracture modeling method to estimate not only geological parameters of fractures but also hydraulic parameters based on the reproducibility of trace length distribution of fractures. By applying this modeling method, it was possible to construct a Discrete Fracture Network (DFN) model that can accurately reproduce the statistical characteristics of fractures.