Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Polevoi, A. R.*; Loarte, A.*; 林 伸彦; Kim, H. S.*; Kim, S. H.*; Koechl, F.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Medvedev, S. Yu.*; 村上 匡且*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(6), p.063019_1 - 063019_8, 2015/05
被引用回数:44 パーセンタイル:87.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The operational space (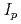 -
- ) for long pulse scenarios of ITER was assessed by 1.5D core transport modelling with pedestal parameters predicted by the EPED1 code. The analyses include the majority of transport models presently used for interpretation of experiments and ITER predictions. The EPED1 code was modified to take into account boundary conditions predicted by SOLPS for ITER. In contrast with standard EPED1 assumptions, EPED1 with the SOLPS boundary conditions predicts no degradation of the pedestal pressure as density is reduced. Lowering the plasma density to
) for long pulse scenarios of ITER was assessed by 1.5D core transport modelling with pedestal parameters predicted by the EPED1 code. The analyses include the majority of transport models presently used for interpretation of experiments and ITER predictions. The EPED1 code was modified to take into account boundary conditions predicted by SOLPS for ITER. In contrast with standard EPED1 assumptions, EPED1 with the SOLPS boundary conditions predicts no degradation of the pedestal pressure as density is reduced. Lowering the plasma density to 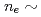 5-6
5-6  10
10 m
m leads to an increased plasma temperature (similar pedestal pressure), which reduces the loop voltage and increases the duration of the burn phase to
leads to an increased plasma temperature (similar pedestal pressure), which reduces the loop voltage and increases the duration of the burn phase to 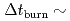 1000 s with Q
1000 s with Q 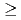 5 for
5 for 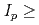 13 MA at moderate normalised pressure (
13 MA at moderate normalised pressure (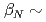 2). These ITER plasmas require the same level of additional heating power as the reference Q = 10 inductive scenario at 15 MA. However, unlike the "hybrid" scenarios considered previously, these H-mode plasmas do not require specially shaped q profiles nor improved confinement in the core for the transport models considered in this study. Thus, these medium density H-mode plasma scenarios with
2). These ITER plasmas require the same level of additional heating power as the reference Q = 10 inductive scenario at 15 MA. However, unlike the "hybrid" scenarios considered previously, these H-mode plasmas do not require specially shaped q profiles nor improved confinement in the core for the transport models considered in this study. Thus, these medium density H-mode plasma scenarios with 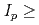 13 MA present an attractive alternative to hybrid scenarios to achieve ITER's long pulse Q
13 MA present an attractive alternative to hybrid scenarios to achieve ITER's long pulse Q 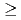 5 and deserve further analysis and experimental demonstration in present tokamaks.
5 and deserve further analysis and experimental demonstration in present tokamaks.
Luce, T. C.*; Challis, C. D.*; 井手 俊介; Joffrin, E.*; 鎌田 裕; Politzer, P. A.*; Schweinzer, J.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Stober, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013015_1 - 013015_15, 2013/12
被引用回数:45 パーセンタイル:87.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The ITPA IOS group has coordinated experimental and modeling activity on the development of advanced inductive scenarios for applications in the ITER tokamak. This report documents the present status of the physics basis and the prospects for applications in ITER. The key findings are: (1) inductive scenarios capable of higher 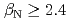 than the ITER baseline scenario (
than the ITER baseline scenario (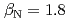 ) with normalized confinement at or above the standard H-mode scaling have been established under stationary conditions on the four largest diverted tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JET, JT-60U) in a broad range in
) with normalized confinement at or above the standard H-mode scaling have been established under stationary conditions on the four largest diverted tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JET, JT-60U) in a broad range in 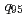 and density; (2) MHD modes can play a key role in reaching stationary high performance, but also define the stability and confinement limits; (3) the experiments have yielded clearer measurements of the normalized gyroradius scalin; and (4) coordinated modeling activity supports the present research by clarifying the most significant uncertainties in the projections to ITER.
and density; (2) MHD modes can play a key role in reaching stationary high performance, but also define the stability and confinement limits; (3) the experiments have yielded clearer measurements of the normalized gyroradius scalin; and (4) coordinated modeling activity supports the present research by clarifying the most significant uncertainties in the projections to ITER.
Polevoi, A. R.*; 林 伸彦; Kim, H. S.*; Kim, S. H.*; Koechl, F.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Loarte, A.*; Medvedev, S. Yu.*; 村上 匡且*; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 37D, p.P2.135_1 - P2.135_4, 2013/07
Long-pulse operation 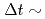 1000 s with
1000 s with 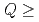 5 is foreseen in ITER to demonstrate high neutron fluence scenarios which can be of use for the nuclear technology and for the TBM. In this study we address the viability of achieving ITER's long-pulse scenario in plasma regimes with H-mode confinement level by characterizing the current-density operational space and the achievable Q with long pulse burning phases. The EPED1 model with boundary conditions from SOLPS predicts no degradation of pedestal pressure with decreasing density in ITER. Modelling of core transport with 1.5D transport models carried out with pedestal parameters predicted by EPED1+SOLPS indicate that there is a large operational space for long pulse plasma operation with high fusion gain
5 is foreseen in ITER to demonstrate high neutron fluence scenarios which can be of use for the nuclear technology and for the TBM. In this study we address the viability of achieving ITER's long-pulse scenario in plasma regimes with H-mode confinement level by characterizing the current-density operational space and the achievable Q with long pulse burning phases. The EPED1 model with boundary conditions from SOLPS predicts no degradation of pedestal pressure with decreasing density in ITER. Modelling of core transport with 1.5D transport models carried out with pedestal parameters predicted by EPED1+SOLPS indicate that there is a large operational space for long pulse plasma operation with high fusion gain 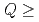 5. Reducing the plasma density to
5. Reducing the plasma density to 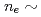 5-6 10
5-6 10 m
m leads to an increased plasma temperature (similar pedestal pressure) which reduces the loop voltage and increases the duration of the burn phase to
leads to an increased plasma temperature (similar pedestal pressure) which reduces the loop voltage and increases the duration of the burn phase to 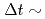 1000 s with
1000 s with 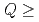 5 for
5 for 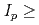 13 MA at moderate normalised pressure,
13 MA at moderate normalised pressure, 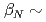 2. Unlike the "hybrid" scenarios, these H-mode plasmas do not require specially shaped q profiles nor improved confinement in the core for the majority of the transport models considered in this study. Thus, these medium density H-mode plasma scenarios present an attractive alternative to hybrid scenarios to achieve ITER's long pulse.
2. Unlike the "hybrid" scenarios, these H-mode plasmas do not require specially shaped q profiles nor improved confinement in the core for the majority of the transport models considered in this study. Thus, these medium density H-mode plasma scenarios present an attractive alternative to hybrid scenarios to achieve ITER's long pulse.
Imbeaux, F.*; Citrin, J.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; K chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; 宮本 斉児; 中村 幸治*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; 宮本 斉児; 中村 幸治*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083026_1 - 083026_11, 2011/08
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:80.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from various tokamaks have been analysed by means of integrated modelling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. A set of empirical heat transport models for L-mode has been validated on a multi-machine experimental dataset for predicting the 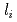 dynamics within
dynamics within  0.15 accuracy during current ramp-up and ramp-down phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of
0.15 accuracy during current ramp-up and ramp-down phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of 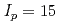 MA). These projections include a sensitivity study to various assumptions of the simulation. While the heat transport model is at the heart of such simulations, more comprehensive simulations are required to test all operational aspects of the current ramp-up and ramp-down phases of ITER scenarios. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free-boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are also described, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
MA). These projections include a sensitivity study to various assumptions of the simulation. While the heat transport model is at the heart of such simulations, more comprehensive simulations are required to test all operational aspects of the current ramp-up and ramp-down phases of ITER scenarios. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free-boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are also described, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
村上 和功*; Park, J. M.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Garcia, J.*; Bonoli, P.*; Budny, R. V.*; Doyle, E. J.*; 福山 淳*; 林 伸彦; 本多 充; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Recent progress on ITER steady-state scenario modeling by the ITPA-IOS group is reviewed. Code-to-code benchmarks as the IOS group's common activities for the two steady-state scenarios (weak shear scenario and internal transport barrier scenario) are reviewed. These are discussed in terms of transport and kinetic profiles, heating and CD sources using various transport codes.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; 福山 淳*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; 林 伸彦; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from various tokamaks have been analysed by means of integrated modelling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of Ip = 15 MA). These projections include a sensitivity studies to various assumptions of the simulation. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are described in the second part of the paper, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; 福山 淳*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; 林 伸彦; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
ITERでの電流立ち上げ・立ち下げシナリオの準備に向けて、これら運転状態においてどの熱輸送モデルが適切であるかを決定するために、代表的なトカマクでの現在の実験結果を統合モデルシミュレーションにより解析した。本研究では、トカマク実験の解析結果をもとに、ITER標準誘導運転(プラズマ電流15MA)の電流立ち上げ・立ち下げシナリオでの予測を行った。統合モデルシミュレーション結果を、ASDEX Upgrade, C-Mod, DIII-D, JET, Tore Supraのオーミック加熱プラズマ及び外部加熱・電流駆動プラズマ実験データと比較することにより、さまざまな輸送モデルの検証を行った。最も実験結果の再現性の良かった幾つかのモデルを用いて、ITERの電流立ち上げ・立ち下げ段階での電子密度・電流密度プロファイルの予測を行った。電子温度プロファイルには輸送モデルによって大きな差が見られたが、最終的な電流密度プロファイルはモデル間でよく一致することがわかった。
Roach, C. M.*; Walters, M.*; Budny, R. V.*; Imbeaux, F.*; Fredian, T. W.*; Greenwald, M.*; Stillerman, J. A.*; Alexander, D. A.*; Carlsson, J.*; Cary, J. R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 48(12), p.125001_1 - 125001_19, 2008/12
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:25.40(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)本論文では、国際トカマク物理活動において構築し2008年に一般公開した分布データベースについて述べる。分布データベースは、プラズマ輸送特性を記述するモデルの検証に活用される。1998年に一般公開した分布データベースに加えて、世界のトカマク装置(11台)で得られた代表的な分布データ(約100放電)を新たに登録している。例えば、JETとTFTRで実施されたDT放電、各装置で得られた内部輸送障壁を持つ放電やハイブリッド運転シナリオの放電などが含まれており、新規登録されたすべての放電の目的や特徴を装置ごとに記述している。また、分布データベースはftp, http, MDSplusを通して読み出しが可能である。
Giruzzi, G.*; Park, J. M.*; Murakami, M.*; Kessel, C. E.*; Polevoi, A.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Bonoli, P.*; Budny, R. V.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
The modeling of the steady-state ITER scenarios is reviewed, as a subject of common work of the ITPA-SSO group. Focus is made not only on the basic physics issues, resulting from theory and experiments, but also on the difficulties and the needs of integrated modeling. Specific issues connected with high bootstrap fraction in the long pulse operation are addressed. Bootstrap current can be enhanced either by large pedestal temperatures, or by Internal Transport Barriers (ITB). Recent simulations for both high-pedestal scenarios and ITB scenarios are compared. Results of code benchmarking for typical parameters of ITER scenarios are also analyzed, and prospects for improvement of the integrated modeling capability will be discussed.
Gormezano, C.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Luce, T. C.*; 井手 俊介; Becoulet, A.*; Litaudon, X.*; 諫山 明彦; Hobirk, J.*; Wade, M. R.*; 及川 聡洋; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S285 - S336, 2007/06
被引用回数:349 パーセンタイル:75.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)国際熱核融合実験炉(ITER)におけるプラズマ開発に向けた物理的基盤について最近の研究の国際的な進展についてまとめたものである。この章ではITERにおける定常運転に関して、以下の点に重点を置いて記述する。統合運転シナリオ, 運転シナリオの最近の開発状況について、定常運転のための加熱/電流駆動装置、定常運転へ向けた制御の課題について、ITERにおける定常運転とハイブリッド運転のシミュレーション。
Doyle, E. J.*; Houlberg, W. A.*; 鎌田 裕; Mukhovatov, V.*; Osborne, T. H.*; Polevoi, A.*; Bateman, G.*; Connor, J. W.*; Cordey, J. G.*; 藤田 隆明; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S18 - S127, 2007/06
本稿は、国際熱核融合実験炉(ITER)の物理基盤に関し、プラズマ閉じ込めと輸送に関する最近7年間(1999年に発刊されたITER Physics Basis後)の世界の研究の進展をまとめたものである。輸送物理一般、プラズマ中心部での閉じ込めと輸送,Hモード周辺ペデスタル部の輸送とダイナミクス及び周辺局在化モード(ELM)、そして、これらに基づいたITERの予測について、実験及び理論・モデリングの両面から体系的に取りまとめる。
鎌田 裕; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
周辺ペデスタル研究の進展とITERへ向けた予測について、最近の世界の研究をレビューする。周辺ペデスタル構造を決めるパラメータリンケージを明らかにするとともに、プラズマ過程と原子分子過程の両方がペデスタル幅を決定すること,周辺圧力勾配がピーリングバルーニング理論で系統的に説明できること,計測機器の進展によってELMの発展が明らかとなり非線形理論で説明可能であること,小振幅ELMの系統的同定がすすんだことなど、大きな発展があった。これらに基づいて、ITERのプラズマ性能の予測,ELMの小規模化等の検討が大きく進んだ。
及川 聡洋; 嶋田 道也; Polevoi, A. R.*; 内藤 磨; Bonoli, P. T.*; 林 伸彦; Kessel, C. E.*; 小関 隆久
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2007/03
ITER定常運転シナリオにおける低域混成波(LH)による電流駆動性能を相対論的1次元フォッカープランクコードとトロイダル光線追跡コードを用いて評価した。現在のLHランチャー設計では電流駆動効率1.8 10
10 AW
AW m
m を実現し、LH駆動電流分布は周辺分布となり負磁気シア配位の形成に有利である。LHパワースペクトルのさらなる最適化についても検討した。また、中性粒子電流駆動(NBCD)について異なる計算手法を採る理論コードを使って検討した。バウンス平均したフォッカープランク方程式に基づくNBCD理論コードはトロイダル系での粒子の軌道効果を含むので、粒子軌道追跡モンテカルロコードによる結果と良い一致を示した。
を実現し、LH駆動電流分布は周辺分布となり負磁気シア配位の形成に有利である。LHパワースペクトルのさらなる最適化についても検討した。また、中性粒子電流駆動(NBCD)について異なる計算手法を採る理論コードを使って検討した。バウンス平均したフォッカープランク方程式に基づくNBCD理論コードはトロイダル系での粒子の軌道効果を含むので、粒子軌道追跡モンテカルロコードによる結果と良い一致を示した。
竹永 秀信; 大山 直幸; 浦野 創; 神谷 健作; 三代 康彦; 西山 友和; 笹島 唯之; 正木 圭; 平塚 一; 市毛 尚志; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (CD-ROM), 30I, 4 Pages, 2006/00
核融合炉では、高密度にて高閉じ込め状態を実現することが必要であり、そのためには高効率・高信頼性の粒子供給システムの確立が重要である。本発表では、ペレット入射及びガスパフによる粒子供給時のプラズマ閉じ込めとペデスタル特性、及び新粒子供給装置(改良ペレット入射装置,ガスジェット装置)の開発について報告する。高磁場側ペレット入射では、ペレットの侵入長は、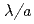 =0.1-0.3と評価された。この侵入距離は、中性ガス遮蔽モデルによるペレット溶発の計算結果より長く、ペレット溶発雲のドリフトを考慮したSMARTモデルの計算と一致した。高
=0.1-0.3と評価された。この侵入距離は、中性ガス遮蔽モデルによるペレット溶発の計算結果より長く、ペレット溶発雲のドリフトを考慮したSMARTモデルの計算と一致した。高
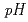 モードプラズマに高磁場側からペレットを入射した結果、
モードプラズマに高磁場側からペレットを入射した結果、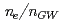
 0.7で
0.7で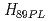
 2を得た。一方、ガスパフを使用した場合は、
2を得た。一方、ガスパフを使用した場合は、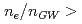 0.6で
0.6で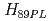 は1.6以下に低下した。ペデスタル圧力もペレット入射時の方が高い。ガスパフの有無に対しては、ペレット入射によるコールドパルスの伝搬にも違いが見られた。ガスパフ無しの場合は、内部輸送障壁で温度低下量の増加が観測されたが、その内側にはコールドパルスが伝搬しなかった。ガスパフ有りの場合は、中心部までコールドパルスの伝搬が観測され、温度分布の硬直性が強い。さらに、ペレット入射装置の長時間化,カダラッシュ研究所との研究協力にて設置したガスジェット装置の開発について報告する。
は1.6以下に低下した。ペデスタル圧力もペレット入射時の方が高い。ガスパフの有無に対しては、ペレット入射によるコールドパルスの伝搬にも違いが見られた。ガスパフ無しの場合は、内部輸送障壁で温度低下量の増加が観測されたが、その内側にはコールドパルスが伝搬しなかった。ガスパフ有りの場合は、中心部までコールドパルスの伝搬が観測され、温度分布の硬直性が強い。さらに、ペレット入射装置の長時間化,カダラッシュ研究所との研究協力にて設置したガスジェット装置の開発について報告する。
Polevoi, A. R.*; 嶋田 道也; 杉原 正芳; Igitkhanov, Y. L.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Medvedev, S. Y.*; Zvonkov, A. V.*; Ivanov, A. A.*
Nuclear Fusion, 45(11), p.1451 - 1456, 2005/11
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:69.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)粒子閉じ込めが改善された種々の閉じ込めシナリオにおいてペレット入射が満足すべき条件を検討した。その結果ペレット入射に必要な粒子補給量は100Pam /sで十分であることを明らかにした。この検討にはペデスタル輸送モデル,ヘリウム輸送モデル,SOL及びダイバータ輸送と整合性のある境界条件を用いた。誘導運転のHモード(HH98(y,2)=1)におけるペレット条件は衝突度が小さい領域における粒子閉じ込め改善を考慮した。ハイブリッド及び定常運転におけるペレット条件は改善閉じ込め(HH98(y,2)
/sで十分であることを明らかにした。この検討にはペデスタル輸送モデル,ヘリウム輸送モデル,SOL及びダイバータ輸送と整合性のある境界条件を用いた。誘導運転のHモード(HH98(y,2)=1)におけるペレット条件は衝突度が小さい領域における粒子閉じ込め改善を考慮した。ハイブリッド及び定常運転におけるペレット条件は改善閉じ込め(HH98(y,2) 1)を考慮した。粒子輸送条件が広範囲に変化してもプラズマ性能はそれほど変化しないことを示した。中性粒子電流駆動及び電子サイクロトロン電流駆動のみを用いた新しい定常運転シナリオを開発した。この運転シナリオは低域混成波電流駆動を必要としないためペレット入射による電流駆動効率の低下の問題を回避することが可能である。
1)を考慮した。粒子輸送条件が広範囲に変化してもプラズマ性能はそれほど変化しないことを示した。中性粒子電流駆動及び電子サイクロトロン電流駆動のみを用いた新しい定常運転シナリオを開発した。この運転シナリオは低域混成波電流駆動を必要としないためペレット入射による電流駆動効率の低下の問題を回避することが可能である。
嶋田 道也; Costley, A. E.*; Federici, G.*; 伊尾木 公裕*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Polevoi, A. R.*; 杉原 正芳
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 337-339, p.808 - 815, 2005/03
被引用回数:70 パーセンタイル:96.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ITERは燃焼プラズマの研究と実現を目的とした核融合実験炉である。その特徴は、加熱パワーのほとんどがアルファ加熱によって供給されるということである。ITERは現在運転中の装置からの顕著なステップであり、かつ核融合炉開発において不可欠のステップである。ITERの成功は、プラズマ壁相互作用の制御のいかんにかかっていると言っても過言ではない。ITERは熱束,粒子束及び時間スケールにおいて現在の装置を一桁ないし二桁上回るからである。ITERにおけるプラズマ壁相互作用の制御の戦略として、セミクローズ・ダイバータ,強力な燃料補給と排気,ディスラプション及びELM制御,交換可能なプラズマ対向材料、及び段階を追った運転などを計画している。
嶋田 道也; Campbell, D.*; Stambaugh, R.*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; 朝倉 伸幸; Costley, A. E.*; Donn , A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
, A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
この論文では、物理基盤の最近の進展によって、ITERの性能予測がどのように影響されるかを要約する。これまで懸案であった課題についての進展、及びハイブリッド及び定常運転シナリオが新たに開発されたことによってITERの目標達成はより確実となった。安全係数が4付近において電流分布を調整することにより、標準のHモードよりも閉じ込めを改善し、壁無し条件でのベータ限界にまでベータを上昇させることが可能であることが実験で明らかになった。この結果をITERに適用すると、12MA程度の低いプラズマ電流で、ELMが小さく、Qが10以上で1000秒以上の長パルス運転が可能である。電流減衰時間及びハロー電流に関する指針を実験データベースから導出してディスラプションの解析を行った。保守的な仮定を用いても真空容器内機器の電磁力は設計目標を下回り、ITERの設計がディスラプションに伴う力に対して十分な耐性を持つことを明らかにした。
嶋田 道也; Mukhovatov, V.*; Federici, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Kukushkin, A.*; 村上 好樹*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Pustovitov, V. D.*; 仙石 盛夫; 杉原 正芳
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.350 - 356, 2004/02
ITERの誘導運転において10以上のQを達成することの確実性をさらに向上させた。経験則による解析によると、ITERでは十分な裕度をもって10以上のQを達成できる。理論モデルを用いた解析によれば、10以上のQを達成するためには2-4keV以上の周辺ペデスタル温度が必要であるが、ペデスタルの比例則によると、この程度のペデスタル温度は達成可能である。タイプIのELMに伴う熱負荷は高密度運転によって許容範囲に低減できる可能性がある。もし必要であればダイバータ板をさらに傾斜させ、さらに熱流束密度を低減させることもできる。高密度側からペレット入射によってQを増加させELM熱負荷を低減できる可能性がある。また閉じ込め性能とベータ値への要求度がより少ない定常運転シナリオを開発した。このような運転領域で必要となる抵抗性壁モードの安定化は、真空容器が二重構造を持つことを考慮しても現有のコイル及び電源で実現可能であることを明らかにした。
嶋田 道也; Mukhovatov, V.*; Federici, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; 村上 好樹*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Pustovitov, V. D.*; 仙石 盛夫; 杉原 正芳
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.350 - 356, 2004/02
被引用回数:40 パーセンタイル:75.28(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)ITERの誘導運転において10以上のQを達成することの確実性をさらに向上させた。経験則による解析によると、ITERでは十分な裕度をもって10以上のQを達成できる。理論モデルを用いた解析によれば、10以上のQを達成するためには3.2-5.3keV以上の周辺ペデスタル温度が必要であるが、ペデスタルの比例則によると、この程度のペデスタル温度は達成可能である。タイプIのELMに伴う熱負荷は高密度運転によって許容範囲に低減できる可能性がある。もし必要であればダイバータ板をさらに傾斜させ、さらに熱流束密度を低減させることもできる。高磁場側からペレット入射によってQを増加させELM熱負荷を低減できる可能性がある。また閉じ込め性能とベータ値への要求度がより少ない定常運転シナリオを開発した。このような運転領域で必要となる抵抗性壁モードの安定化は、真空容器が二重構造を持つことを考慮しても現有のコイル及び電源で実現可能であることを明らかにした。
Mukhovatov, V.*; 嶋田 道也; Chudnovskiy, A. N.*; Costley, A. E.*; Gribov, Y.*; Federici, G.*; Kardaun, O. J. F.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Pustovitov, V. D.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 45(12), p.235 - 252, 2003/12
被引用回数:64 パーセンタイル:85.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)ITERはDT燃焼によって約0.5GWの核融合エネルギーを発生する最初の磁場閉じ込め装置である。最近の2, 3年の間に得られた研究成果によって、ITERのHモード運転においてQ 10を達成できることがほぼ確実となった。それらには、三角形度を高くすることによって得られたグリーンワルド密度付近における良好なHモード閉じ込め,理論モデルに基づく炉心プラズマ閉じ込めの予測の改良,D/Tイオンとヘリウム中性粒子との弾性衝突を考慮したダイバータモデル計算によるヘリウム灰除去効率の改善,NTM(新古典テアリング・モード)のフィードバック制御による
10を達成できることがほぼ確実となった。それらには、三角形度を高くすることによって得られたグリーンワルド密度付近における良好なHモード閉じ込め,理論モデルに基づく炉心プラズマ閉じ込めの予測の改良,D/Tイオンとヘリウム中性粒子との弾性衝突を考慮したダイバータモデル計算によるヘリウム灰除去効率の改善,NTM(新古典テアリング・モード)のフィードバック制御による 値の改善,ELM物理の理解の進展とELM緩和法の開発,ディスラプション緩和法の検証などがある。ITERはその機動性を用いて定常及び中間領域(ハイブリッド)運転を行うことも可能である。この論文においては、おもに誘導運転のプラズマ性能、及び定常運転のために要請される性能について議論を行う。
値の改善,ELM物理の理解の進展とELM緩和法の開発,ディスラプション緩和法の検証などがある。ITERはその機動性を用いて定常及び中間領域(ハイブリッド)運転を行うことも可能である。この論文においては、おもに誘導運転のプラズマ性能、及び定常運転のために要請される性能について議論を行う。