Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagata, Hiroshi; Kochiyama, Mami; Chinone, Marina; Sugaya, Naoto; Nishimura, Arashi; Ishikawa, Joji; Sakai, Akihiro; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-016, 44 Pages, 2025/03
The elemental composition of the structural materials of nuclear reactor facilities is used as one of the important parameters in activation calculations that are evaluated when formulating decommissioning plans. Regarding the elemental composition of aluminum alloys and other materials used as structural materials for test and research reactors, sufficient data is not available regarding elements other than the major elements. For this reason, samples were collected from aluminum alloy, beryllium, hafnium, and other materials that have been used as the main structural materials of JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor), and their elemental compositions were analyzed. This report summarizes the elemental composition data of 78 elements obtained in FY2023.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Domae, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 32nd Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2024) (Internet), p.496 - 498, 2024/10
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Domae, Takeshi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(5), p.052008_1 - 052008_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Domae, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Radio-Frequency Superconductivity (SRF 2023), p.947 - 951, 2023/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been proposing an accelerator-driven system (ADS) as a future nuclear system to efficiently reduce the high-level radioactive waste generated at nuclear power plants. As the first step toward the full-scale CW proton linac for the JAEA-ADS, we are now prototyping a low-beta (around 0.2) single-spoke cavity. Because there is no experience in manufacturing super-conducting spoke cavities in Japan, prototyping and performance testing of the cavity are essential to ensure the feasibility of the JAEA-ADS. The dimensional parameters of the prototype spoke cavity were optimized to obtain higher cavity performance. The actual cavity fabrication started in 2020. Most of the cavity parts were fabricated in fiscal year 2020 by press-forming and machining. In 2021, we started welding the cavity parts together. After investigating the optimum welding conditions using mock-up test pieces, each cavity part was joined with smooth welding beads. Currently, the cavity's body section and the beam port sections have been assembled. This paper presents the current status of the JAEA-ADS and it's cavity prototyping.
 Rh
Rh Ga explored by
Ga explored by 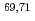 Ga nuclear quadrupole resonance
Ga nuclear quadrupole resonanceYamamoto, Shingo*; Fujii, Takuto*; Luther, S.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Hironori; B rtl, F.*; Ranjith, K. M.*; Rosner, H.*; Wosnitza, J.*; Strydom, A. M.*; et al.
rtl, F.*; Ranjith, K. M.*; Rosner, H.*; Wosnitza, J.*; Strydom, A. M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(11), p.115125_1 - 115125_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the microscopic magnetic properties, the nature of the 130 K phase transition, and the ground state in the recently synthesized compound Ce Rh
Rh Ga by use of
Ga by use of 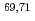 Ga nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR). The NQR spectra clearly show an unusual phase transition at
Ga nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR). The NQR spectra clearly show an unusual phase transition at 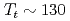 K, yielding a splitting of the high-temperature single NQR line into two well-resolved NQR lines, providing evidence for two crystallographically inequivalent Ga sites. The NQR frequencies are in good agreement with fully relativistic calculations of the band structure. Our NQR results indicate the absence of magnetic or charge order down to 0.3 K. The temperature dependence of the spin-lattice relaxation rate
K, yielding a splitting of the high-temperature single NQR line into two well-resolved NQR lines, providing evidence for two crystallographically inequivalent Ga sites. The NQR frequencies are in good agreement with fully relativistic calculations of the band structure. Our NQR results indicate the absence of magnetic or charge order down to 0.3 K. The temperature dependence of the spin-lattice relaxation rate  shows three distinct regimes, with onset temperatures at
shows three distinct regimes, with onset temperatures at 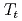 and 2 K. The temperature-independent
and 2 K. The temperature-independent  , observed between
, observed between 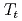 and 2 K, crosses over to a Korringa process,
and 2 K, crosses over to a Korringa process, 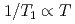 , below
, below  2 K, which evidences a rare two-ion Kondo scenario: The system evolves into a dense Kondo coherent state below 2.0 and 0.8 K probed by the two different Ga sites.
2 K, which evidences a rare two-ion Kondo scenario: The system evolves into a dense Kondo coherent state below 2.0 and 0.8 K probed by the two different Ga sites.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Domae, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.180 - 183, 2022/09
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has proposed an accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS) to efficiently reduce high-level radioactive waste generated at nuclear power plants. One of the challenging R&D aspects of ADS is the reliability of the accelerator. In preparation for the full-scale design of the CW proton linac for the JAEA-ADS, we are now prototyping a low-beta (around 0.2) single spoke cavity. Since there is no experience in Japan in manufacturing a superconducting spoke cavity, prototyping and performance testing of the cavity is essential to ensure the feasibility of the JAEA-ADS linac. In the Japanese fiscal year 2021, we have started welding cavity parts together. By preliminarily examining the electron beam welding conditions, each press-formed niobium part was joined with a smooth welding bead. At present, we have fabricated the cavity's body part.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Junichiro; Matsuda, Makoto; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Kako, Eiji*; Domae, Takeshi*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.299 - 302, 2021/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) tandem booster is one of the pioneering superconducting heavy ion linac in the world. It consists of 40 QWRs with an operation frequency of 130 MHz and 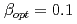 , and has potential to accelerate various ions up to Au to 10 MeV/u. The user operation was started in 1994, however, it has been suspended since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. Recently, in addition to the efforts to restart the tandem booster, activities to develop new lower-beta cavities to improve the acceleration efficiency of heavier ions such as Uranium has been launched. In this work, the current status of the design study of the QWRS for the JAEA tandem facility is presented. Electro-magnetic design using simulation code was performed and acceleration gradient of 5.7 MV/m and 6.6 MV/m was obtained for 130-MHz and 65-MHz QWRs, respectively.
, and has potential to accelerate various ions up to Au to 10 MeV/u. The user operation was started in 1994, however, it has been suspended since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. Recently, in addition to the efforts to restart the tandem booster, activities to develop new lower-beta cavities to improve the acceleration efficiency of heavier ions such as Uranium has been launched. In this work, the current status of the design study of the QWRS for the JAEA tandem facility is presented. Electro-magnetic design using simulation code was performed and acceleration gradient of 5.7 MV/m and 6.6 MV/m was obtained for 130-MHz and 65-MHz QWRs, respectively.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Domae, Takeshi*; Kako, Eiji*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Umemori, Kensei*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.612 - 615, 2021/06
Harada, Masahide; Sekijima, Mitsuaki*; Morikawa, Noriyuki*; Masuda, Shiho; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Sakai, Kenji; Kai, Tetsuya; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Muto, Giichi*; Suzuki, Akio*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011099_1 - 011099_6, 2021/03
In MLF at J-PARC, a unified mercury radioactivity monitor (UHAM) is installed to find an indication of failure of the mercury target and loop system by detecting radioactive materials leaked from the system with a  -ray energy analysis with Germanium semi-conductor detectors (Ge detectors). It is composed of three units of sampling port and radiation monitors: (1) HAM for interstitial helium gas layer between the mercury vessel and surrounding water shroud of the mercury target, (2) CAM for atmosphere in the hot cell where the target loop is operated and (3) VAM for helium gas in the helium vessel where the target vessel is installed. Once any leakages of radioactive materials are detected, an alarm signal is issued immediately to the accelerator control system to stop beam operation. Software and hardware have been upgraded yearly. For example, two Ge detectors are used for HAM for redundancy, NaI Scintillation detectors are also used as supplemental for the Ge detector to keep availability of the system for high counting rate event. In April 2015, the UHAM activated when a small water coolant leakage from the water shroud of the mercury target occurred. VAM detected an abnormal increase of the counting rate in the helium vessel. It was also indicated that the measured radioactive nuclides were generated from the activation of the coolant (water) in the water shroud and not from the mercury.
-ray energy analysis with Germanium semi-conductor detectors (Ge detectors). It is composed of three units of sampling port and radiation monitors: (1) HAM for interstitial helium gas layer between the mercury vessel and surrounding water shroud of the mercury target, (2) CAM for atmosphere in the hot cell where the target loop is operated and (3) VAM for helium gas in the helium vessel where the target vessel is installed. Once any leakages of radioactive materials are detected, an alarm signal is issued immediately to the accelerator control system to stop beam operation. Software and hardware have been upgraded yearly. For example, two Ge detectors are used for HAM for redundancy, NaI Scintillation detectors are also used as supplemental for the Ge detector to keep availability of the system for high counting rate event. In April 2015, the UHAM activated when a small water coolant leakage from the water shroud of the mercury target occurred. VAM detected an abnormal increase of the counting rate in the helium vessel. It was also indicated that the measured radioactive nuclides were generated from the activation of the coolant (water) in the water shroud and not from the mercury.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Konomi, Taro*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011049_1 - 011049_6, 2021/03
 -Al
-Al O
O (0001)
(0001)Entani, Shiro*; Honda, Mitsunori; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Li, S.*; Sakai, Seiji*
Surface Science, 704, p.121749_1 - 121749_6, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:37.71(Chemistry, Physical)Graphene is expected to be one of the most promising materials for nanoelectronics and spintronics. In most graphene-based devices, the graphene channel is placed on insulating substrates. Therefore, the study of inter-facial interactions between graphene and the insulator surface is of critical importance. In this study, the vertical arrangement of graphene which is transferred on  -Al
-Al O
O (0001) has been studied by normal incidence X-ray standing wave (NIXSW) technique. The analysis of the NIXSW profile reveals that the graphene layer is located at 3.57 (
(0001) has been studied by normal incidence X-ray standing wave (NIXSW) technique. The analysis of the NIXSW profile reveals that the graphene layer is located at 3.57 ( ) above the
) above the  -Al
-Al O
O (0001) surface, which is larger than the interlayer distance of graphite at 3.356 (
(0001) surface, which is larger than the interlayer distance of graphite at 3.356 ( ). Micro- Raman spectroscopy shows that the transferred graphene has a limited spatial distribution of hole concentration. The present study shows that transferred graphene on the sapphire substrate followed by vacuum-annealing has an atomically flat surface free from residual contaminations such as organic compounds and there occurs the hole-doping in graphene.
). Micro- Raman spectroscopy shows that the transferred graphene has a limited spatial distribution of hole concentration. The present study shows that transferred graphene on the sapphire substrate followed by vacuum-annealing has an atomically flat surface free from residual contaminations such as organic compounds and there occurs the hole-doping in graphene.
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCOkudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Kenji; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahashi, Shingo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 977, p.164301_1 - 164301_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:88.75(Instruments & Instrumentation) F from
F from  O
O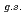 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:72.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 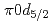 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O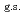 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Konomi, Taro*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2019) (Internet), p.399 - 402, 2019/11
Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Takada, Hiroshi; Kai, Tetsuya; Nakatani, Takeshi; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; Watanabe, Akihiko*
JAEA-Technology 2018-011, 57 Pages, 2019/01
For safely and efficiently operating a spallation neutron source and a muon target, a general control system (GCS) operates within Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF). GCS administers operation processes and interlocks of many instruments. It consists of several subsystems such as an integral control system (ICS), interlock systems (ILS), shared servers, network system, and timing distribution system (TDS). Although GCS is an independent system that controls the target stations, it works closely with the control systems of the accelerators and other facilities in J-PARC. Since the first beam injection, GCS has operated stably without any serious troubles after modification based on commissioning for operation and control. Then, significant improvements in GCS such as upgrade of ICS by changing its framework software and function enhancement of ILS were proceeded until 2015. In this way, many modifications have been proceeded in the entire GCS during a period of approximately ten years after start of beam operation. Under these situation, it is important to comprehend upgrade history and present status of GCS in order to decide its upgrade plan. This report summarizes outline, structure, roles and functions of GCS in 2017.
 Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Dioguardi, A. P.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Thomas, S. M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Cary, S. K.*; Kozimor, S. A.*; Albrecht-Schmitt, T. E.*; Choi, H. C.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Thompson, J. D.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(3), p.035104_1 - 035104_6, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a detailed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of  Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB
Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB ), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The
), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The  Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that
Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that  Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the
Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the  Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time (
Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time ( ), indicate that PuB
), indicate that PuB adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and
adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and 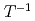 imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB
imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB is a good candidate topological insulator.
is a good candidate topological insulator.
Torigoe, Shuhei*; Hattori, Takayuki*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Honda, Takashi*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Abe, Hitoshi*; Murakawa, Hiroshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(13), p.134443_1 - 134443_7, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Entani, Shiro*; Honda, Mitsunori; Shimoyama, Iwao; Li, S.*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Sakai, Seiji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(4S), p.04FP04_1 - 04FP04_4, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.48(Physics, Applied)Sakai, Takuro; Iikura, Hiroshi; Yamada, Naoto*; Sato, Takahiro*; Ishii, Yasuyuki*; Uchida, Masaya*
QST-M-8; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2016, P. 140, 2018/03
Kawamura, Seiko; Oku, Takayuki; Watanabe, Masao; Takahashi, Ryuta; Munakata, Koji*; Takata, Shinichi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Journal of Neutron Research, 19(1-2), p.15 - 22, 2017/11
Sample environment (SE) team at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC has worked on development and operation of SE equipment and devices. All the members belong to one sub-team at least, such as Cryogenic and magnet, High temperature, High pressure, Soft matter and special environment including Pulse magnet, Hydrogen environment, Light irradiation and  He spin filter. Cryostats, a magnet, furnaces, a VX-6-type Paris-Edinburgh press and a prototype of a Spin-Exchange Optical Pumping (SEOP) based
He spin filter. Cryostats, a magnet, furnaces, a VX-6-type Paris-Edinburgh press and a prototype of a Spin-Exchange Optical Pumping (SEOP) based  He spin filter for polarized neutron beam experiments are in operation. Furthermore, a prototype of compact power supply for a pulsed magnet system is currently developed. In the J-PARC Research Building, several pieces of equipment for softmatter research such as a rheometer and a gas and vapor adsorption measurement instrument have been prepared.
He spin filter for polarized neutron beam experiments are in operation. Furthermore, a prototype of compact power supply for a pulsed magnet system is currently developed. In the J-PARC Research Building, several pieces of equipment for softmatter research such as a rheometer and a gas and vapor adsorption measurement instrument have been prepared.