Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakanishi, Takumi*; Hori, Yuta*; Shigeta, Yasuteru*; Sato, Hiroyasu*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Munakata, Koji*; Ohara, Takashi; Okazawa, Atsushi*; Shimada, Rintaro*; Sakamoto, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 145(35), p.19177 - 19181, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Okumura, Yoshikazu; Gobin, R.*; Knaster, J.*; Heidinger, R.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Cara, P.*; Chauvin, N.*; Chel, S.*; Gex, D.*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02A739_1 - 02A739_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)IFMIF is an accelerator based neutron facility having two set of linear accelerators each producing 125mA/CW deuterium ion beams (250mA in total) at 40MeV. The LIPAc (Linear IFMIF Prototype Accelerator) being developed in the IFMIF-EVEDA project consists of an injector, a RFQ accelerator, and a part of superconducting Linac, whose target is to demonstrate 125mA/CW deuterium ion beam acceleration up to 9MeV. The injector has been developed in CEA Saclay and already demonstrated 140mA/100keV deuterium beam. The injector was disassembled and delivered to the International Fusion Energy Research Center (IFERC) in Rokkasho, Japan, and the commissioning has started after its reassembly 2014; the first beam production has been achieved in November 2014. Up to now, 100keV/120mA/CW hydrogen ion beam has been produced with a low beam emittance of 0.2  .mm.mrad (rms, normalized).
.mm.mrad (rms, normalized).
Okumura, Yoshikazu; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Cara, P.*; Chauvin, N.*; Chel, S.*; Gex, D.*; Gobin, R.*; Harrault, F.*; Heidinger, R.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.203 - 205, 2015/09
Under the framework of Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and Euratom, IFMIF/EVEDA project was launched in 2007 to validate the key technologies to realize IFMIF. The most crucial technology to realize IFMIF is two set of linear accelerator each producing 125mA/CW deuterium ion beams up to 40MeV. The prototype accelerator, whose target is 125mA/CW deuterium ion beam acceleration up to 9MeV, is being developed in International Fusion Research Energy Center (IFERC) in Rokkasho, Japan. The injector developed in CEA Saclay was delivered in Rokkasho in 2014, and is under commissioning. Up to now, 100keV/120mA/CW hydrogen ion beams and 100keV/90mA/CW duty deuterium ion beams are successfully produced with a low beam emittance of 0.21  .mm.mrad (rms, normalized). Delivery of RFQ components will start in 2015, followed by the installation of RF power supplies in 2015.
.mm.mrad (rms, normalized). Delivery of RFQ components will start in 2015, followed by the installation of RF power supplies in 2015.
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Oki, Kensuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 463, p.537 - 540, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:83.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakamura, Makoto; Tobita, Kenji; Gulden, W.*; Watanabe, Kazuhito*; Someya, Yoji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Araki, Takao*; Matsumiya, Hisato*; Ishii, Kyoko*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(9-10), p.2028 - 2032, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear accident, a social need for assuring safety of fusion energy has grown gradually in the Japanese (JA) fusion research community. DEMO safety research has been launched as a part of BA DEMO Design Activities (BA-DDA). This paper reports progress in the fusion DEMO safety research conducted under BA-DDA. Safety requirements and evaluation guidelines have been, first of all, established based on those established in the Japanese ITER site invitation activities. The amounts of radioactive source terms and energies that can mobilize such source terms have been assessed for a reference DEMO, in which the blanket technology is based on the Japanese fusion technology R&D programme. Reference event sequences expected in DEMO have been analyzed based on the master logic diagram and functional FMEA techniques. Accident initiators of particular importance in DEMO have been selected based on the event sequence analysis.
Nakamura, Makoto; Tobita, Kenji; Someya, Yoji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Gulden, W.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Araki, Takao*; Watanabe, Kazuhito*; Matsumiya, Hisato*; Ishii, Kyoko*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9, p.1405139_1 - 1405139_11, 2014/10
Key aspects of the safety study of a water-cooled fusion DEMO reactor is reported. Safety requirements, dose target, DEMO plant model and confinement strategy of the safety study are briefly introduced. The internal hazard of a water-cooled DEMO, i.e. radioactive inventories, stored energies that can mobilize these inventories and accident initiators and scenarios, are evaluated. It is pointed out that the enthalpy in the first wall/blanket cooling loops, the decay heat and the energy potentially released by the Be-steam chemical reaction are of special concern for the water-cooled DEMO. An ex-vessel loss-of-coolant of the first wall/blanket cooling loop is also quantitatively analyzed. The integrity of the building against the ex-VV LOCA is discussed.
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Yoshikawa, Masayuki*; Oki, Kensuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; et al.
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
Satoh, Daiki; Kojima, Kensuke; Oizumi, Akito; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kugo, Teruhiko; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Endo, Akira; Okajima, Shigeaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(5), p.656 - 670, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)A calculation system for the estimation of decontamination effect (CDE) has been developed to support planning a rational and effective decontamination. The method calculates the dose-rate distribution before and after decontamination, according to the distribution of radioactivity and the decontamination factor (DF), and uses a dose rate reduction factor (DRRF) to estimate the decontamination effect. The results that were calculated by using the CDE were compared with the results of measurements as well as with the results of calculations that were performed using a Monte Carlo particle transport code PHITS. It was found that the CDE successfully reproduced the measured as well as the calculated dose-rate distributions, requiring less than several seconds of calculation time.
 adsorption
adsorption  lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water molecules
lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water moleculesIshizaki, Manabu*; Akiba, Sae*; Otani, Asako*; Hoshi, Yuji*; Ono, Kenta*; Matsuba, Mayu*; Togashi, Takanari*; Kanaizuka, Katsuhiko*; Sakamoto, Masatomi*; Takahashi, Akira*; et al.
Dalton Transactions, 42(45), p.16049 - 16055, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:179 Percentile:99.58(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We have revealed the fundamental mechanism of specific Cs adsorption into Prussian blue (PB) in order to develop high-performance PB-based Cs
adsorption into Prussian blue (PB) in order to develop high-performance PB-based Cs adsorbents in the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident. We compared two types of PB nanoparticles with formulae of Fe
adsorbents in the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident. We compared two types of PB nanoparticles with formulae of Fe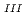
 [Fe
[Fe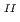 (CN)
(CN) ]3
]3 xH
xH O (x = 10-15) (PB-1) and (NH
O (x = 10-15) (PB-1) and (NH )0.70Fe
)0.70Fe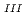 1.10[Fe
1.10[Fe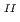 (CN)
(CN) ]
] 1.7H
1.7H O (PB-2) with respect to the Cs
O (PB-2) with respect to the Cs adsorption ability. The synthesised PB-1, by a common stoichiometric aqueous reaction between 4Fe
adsorption ability. The synthesised PB-1, by a common stoichiometric aqueous reaction between 4Fe and 3[Fe
and 3[Fe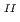 (CN)
(CN) ]
]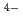 , showed much more efficient Cs
, showed much more efficient Cs adsorption ability than did the commercially available PB-2.
adsorption ability than did the commercially available PB-2.
Satoh, Daiki; Kojima, Kensuke; Oizumi, Akito; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kugo, Teruhiko; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Endo, Akira; Okajima, Shigeaki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 109(1), p.1261 - 1263, 2013/11
A computer software, named CDE (Calculation system for Decontamination Effect), has been developed to support planning the decontamination. CDE is programed with VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), and runs on Microsoft Excel with a user friendly graphical interface. It calculates dose rate distributions in a target area before and after the decontamination from a radioactivity distribution and DF (Decontamination Factor), which is a ratio of original radioactivity to remaining one after the decontamination. DRRF (Dose Rate Reduction Factor) is also derived to express the decontamination effect. All the calculation results are visualized on an image of the target area with color map. Owing to its quick calculation speed, CDE is able to investigate the decontamination effect in various cases for a short period. This is very useful to establish a rational decontamination plan before an action.
Satoh, Daiki; Oizumi, Akito; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kojima, Kensuke; Kugo, Teruhiko; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Endo, Akira; Okajima, Shigeaki
RIST News, (53), p.12 - 23, 2012/09
Decontamination planning based on a computer simulation code CDE is discussed in this paper. Large amount of radionuclides had been discharged to environment in the accident of the Tokyo Electronic Power Corporation Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant. CDE has been developed to support planning the decontamination. From the present study, it is validated that the computer simulation is very useful to predict the effect of the scenario before actions, and to plan the decontamination.
Satoh, Daiki; Kojima, Kensuke; Oizumi, Akito; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kugo, Teruhiko; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Endo, Akira; Okajima, Shigeaki
JAEA-Research 2012-020, 97 Pages, 2012/08
A computer software, named CDE (Calculation system for Decontamination Effect), has been developed to support planning the decontamination. CDE calculates the dose rates before the decontamination by using a database of dose contributions by radioactive cesium. The decontamination factor is utilized in the prediction of the dose rates after the decontamination, and dose rate reduction factor is evaluated to express the decontamination effect. The results are visualized on the image of a target zone with color map. In this paper, the overview of the software and the dose calculation method are reported. The comparison with the calculation results by a three-dimensional radiation transport code PHITS is also presented. In addition, the source code of the dose calculation program and user's manual of CDE are attached as appendices.
Seki, Yohji; Yoshikawa, Akira; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Hirose, Takanori; Ezato, Koichiro; Enoeda, Mikio; Sakamoto, Kensaku
Dai-17-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.265 - 266, 2012/06
In the case of a water cooled ceramic breeder in a blanket, pebbles of a ceramic tritium breeder are packed in a container constituted by a partition plate. Helium purge gas is applied as a transport fluid in a tritium recovery system. It is of importance to build database of a pressure drop as part of a design of the tritium recovery system. In this experimental study, the pressure drops of He gas through pebble bed were measured within the wide range of a flow rate up to 100 L/min. The results indicate that a laminar flow is dominant and the pressure drop was correctly predicted by the empirical equation within a part of flow rate. Reliability of prediction ability of pressure drop was established by this experiment within the flow rate which is less than 60 L/min. Moreover, this paper describes that slight difference between the experimental result and the empirical equation within a range of flow rate from 60 L/min to 100 L/min.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sakamoto, Yukio; Kureta, Masatoshi; Kugo, Teruhiko
JAEA-Technology 2011-026, 18 Pages, 2011/09
The present report discusses the effect of dose rate reduction by soil decontamination in order to make a remediation strategy for contaminated environment by radionuclides discharged by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The relation between area of soil decontamination and dose rate reduction for lands considered to be typical residences, public facilities and schools has been analyzed using the particle and heavy ion transport code PHITS, and an analytical model to assess the dose reduction rate with a simple equation was also suggested from the calculation results of PHITS. In the case of DF (Decontamination Factor) = 10 and decontamination radius = 100 m for the soil uniformly contaminated by Cs-137, the dose rate at the center of decontamination area is decreased by a factor of about five compared with the dose rate before decontamination.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Shurshakov, V. A.*; Yarmanova, E. N.*; Nikolaev, I. V.*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Sihver, L.*; Mancusi, D.*; Endo, Akira; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
Cosmic Research, 49(4), p.319 - 324, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.27(Engineering, Aerospace)HZE particle transport codes are the indispensable tool in the shielding design of spacecrafts. We are therefore developing a general-purpose Monte Carlo code PHITS, which can deal with the transports of all kinds of hadrons and heavy ions with energies up to 200 GeV/n in 3-dimensional phase spaces. The applicability of PHITS to space researches has been well verified by comparing the neutron spectra in spacecrafts calculated by the code with the corresponding experimental data. Recently, PHITS was employed in the estimation of radiation fields in the Russian Service Module in ISS. The results of the estimation indicate that PHITS can reproduce experimental data of the dose reduction rates due to water shielding attached on the wall of the Russian crew cabin fairly well. The details of the calculation procedures will be given in the presentation, together with the results of other applications of PHITS to the space exploration.
 from 140 MeV proton incident reactions
from 140 MeV proton incident reactionsIwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Endo, Akira; Sakamoto, Yukio; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Tamii, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.1753 - 1756, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.1(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutron production cross sections of carbon and iron targets for 140 MeV proton at 180 were measured at the RCNP cyclotron facility. The neutron energy spectra were obtained by using the time-of-flight technique in the energy range above 1 MeV. The results of carbon and iron targets were compared with experimental data for 113 MeV (p,xn) reactions at 150 deg by Meier et al. Our data gave good agreements with them in spite of different incident energies and angles. Calculations were performed with different intranuclear cascade models (Bertini, ISOBAR, and JQMD) implemented in the PHITS code. Calculated results with the ISOBAR and JQMD models roughly agreed with the experimental data for iron targets, although Bertini could not reproduce the high energy neutrons above 10 MeV.
were measured at the RCNP cyclotron facility. The neutron energy spectra were obtained by using the time-of-flight technique in the energy range above 1 MeV. The results of carbon and iron targets were compared with experimental data for 113 MeV (p,xn) reactions at 150 deg by Meier et al. Our data gave good agreements with them in spite of different incident energies and angles. Calculations were performed with different intranuclear cascade models (Bertini, ISOBAR, and JQMD) implemented in the PHITS code. Calculated results with the ISOBAR and JQMD models roughly agreed with the experimental data for iron targets, although Bertini could not reproduce the high energy neutrons above 10 MeV.
Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakane, Yoshihiro; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.20 - 23, 2011/02
An experimental method and data processing procedure have been developed for the measurement of neutron elastic scattering cross sections in intermediate energy region above 100 MeV. The data were obtained at Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) in Osaka University by utilizing a  Li(p,n) quasi-monoenergetic neutron source and Time-of-Flight (TOF) technique.
Li(p,n) quasi-monoenergetic neutron source and Time-of-Flight (TOF) technique.
Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 45(10), p.1159 - 1162, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Elastic neutron-scattering cross sections for carbon nucleus have been measured by using 134-MeV monoenergetic neutron beam in Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP), Osaka University. The measured angles were set at 6 , 8
, 8 , and 15
, and 15 in laboratory system. The liquid organic scintillators, whose size is 12.7 cm in diameter and 12.7 cm in thickness, were mounted at each angle as neutron detector. In the off-line analysis, the events of elastic-neutron scattering were extracted on basis of the Time-of-Flight (TOF) information. The results were compared with the data measured by the groupe of U.C. Davis with a recoil proton spectrometer and the evaluations of the nuclear data libraries, JENDL/HE-2007 and ENDF/B-VII.0. Our results show a good agreement with the data of U.C. Davis. This indicates that our experimental method based on the TOF teqnique is appropriate to the measurement of elastic neutron-scattering cross section in this energy region. In addition, we exhibit that the data of ENDF/B-VII.0 represent the experimental data, but JENDL/HE-2007 underestimates about 30
in laboratory system. The liquid organic scintillators, whose size is 12.7 cm in diameter and 12.7 cm in thickness, were mounted at each angle as neutron detector. In the off-line analysis, the events of elastic-neutron scattering were extracted on basis of the Time-of-Flight (TOF) information. The results were compared with the data measured by the groupe of U.C. Davis with a recoil proton spectrometer and the evaluations of the nuclear data libraries, JENDL/HE-2007 and ENDF/B-VII.0. Our results show a good agreement with the data of U.C. Davis. This indicates that our experimental method based on the TOF teqnique is appropriate to the measurement of elastic neutron-scattering cross section in this energy region. In addition, we exhibit that the data of ENDF/B-VII.0 represent the experimental data, but JENDL/HE-2007 underestimates about 30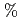 in the forward angle region.
in the forward angle region.
 for the 140 MeV proton incident reactions on carbon, iron, and gold
for the 140 MeV proton incident reactions on carbon, iron, and goldIwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Tamii, Atsushi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Endo, Akira; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 620(2-3), p.484 - 489, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:51.53(Instruments & Instrumentation)The neutron production cross sections of carbon, iron, and gold targets with 140 MeV protons at 180 were measured at the RCNP cyclotron facility. The time-of-flight technique was used to obtain the neutron energy spectra in the energy range above 1 MeV. The carbon and iron target results were compared with the experimental data from 113 MeV (p,xn) reactions at 150
were measured at the RCNP cyclotron facility. The time-of-flight technique was used to obtain the neutron energy spectra in the energy range above 1 MeV. The carbon and iron target results were compared with the experimental data from 113 MeV (p,xn) reactions at 150 reported by Meier et al. Our data agreed well with them in spite of different incident energies and angles. Calculations were then performed using different intra-nuclear cascade models (Bertini, ISOBAR, and JQMD) implemented with PHITS code. The results calculated using the ISOBAR and JQMD models roughly agreed with the experimental iron and gold target data, but the Bertini could not reproduce the high energy neutrons above 10 MeV.
reported by Meier et al. Our data agreed well with them in spite of different incident energies and angles. Calculations were then performed using different intra-nuclear cascade models (Bertini, ISOBAR, and JQMD) implemented with PHITS code. The results calculated using the ISOBAR and JQMD models roughly agreed with the experimental iron and gold target data, but the Bertini could not reproduce the high energy neutrons above 10 MeV.
Kobayashi, Nobuo*; Tasaki, Keisuke*; Kano, Sayaka*; Sakamoto, Sakiko*; Nakatsuka, Akira*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 70, 2008/11
no abstracts in English