Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ta and
Ta and  Bi considering experimental double differential cross-section data
Bi considering experimental double differential cross-section dataNguyen, T. T. H.*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Sanami, Toshiya*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 322, p.10004_1 - 10004_3, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Bi at 13 and 17 MeV photon energies
Bi at 13 and 17 MeV photon energiesNguyen, T. T. H.*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Sanami, Toshiya*
JAEA-Conf 2024-002, p.139 - 143, 2024/11
Hirayama, Hideo*; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Okura, Takehisa; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Taki, Mitsumasa; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.295 - 307, 2021/10
Kirihara, Yoichi; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sanami, Toshiya*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Itoga, Toshiro*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Takemoto, Akinori*; Yamaguchi, Masashi*; Asano, Yoshihiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.444 - 456, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:62.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sanami, Toshiya*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nakamura, Shoji
JAEA-Conf 2017-001, 222 Pages, 2018/01
The 2016 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Kobayashi Hall of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, on November 17 and 18, 2016. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan in cooperation with Radiation Science Center, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency and North Kanto Branch of Atomic Energy Society of Japan. In the symposium, there were one tutorial, "Historical Evolution of Accelerators" and four oral sessions, "Overview of the ImPACT Program - Reduction and Resource Recycling of High Level Wastes through Nuclear Transmutation", "Facilities and experiments for nuclear data in Japan", "Nuclear data from measurement to application", and "Progress of neutron nuclear data measurement and research for its basics and application". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, evaluation, benchmark and application was presented in the poster session. Among 65 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 31 papers including 10 oral and 21 poster presentations.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kowatari, Munehiko; Nishino, Sho; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwase, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1188 - 1195, 2017/11
The equivalent doses to the lens of the eye and extremities for radiation workers should be assessed properly to ensure that the dose limits are not exceeded. Recently, the following two issues has pressed demand on more appropriate evaluation of the equivalent doses of the lens of the eye and extremity. One is the new occupational dose limit for the lens of the eye the ICRP recommended. The other is growing demand on handling of highly activated materials in the maintenance works of an accelerator and contaminated materials during the decommissioning works of nuclear facility, which increases the potential exposure risk to the extremities to a wider variety of radio-nuclides. Since the points to be assessed for the exposures to the lens of the eye and the extremities are apart from the trunk, the homogeneity of the radiation fields would be significantly impact on the assessment of these equivalent doses. However, there has been no sufficient and available method to identify the nonhomogeneous situations systematically in terms of the eye lens or extremity monitoring. The goal of this study is to provide the framework to identify the nonhomogeneous exposure situations. In order to fulfil this purpose, newly proposed indices to represent the homogeneity were calculated by Monte Carlo simulation incorporated with mathematical phantom, verifying the benchmark measurements. Important parameters that significantly impact on these indices were also shown from the various trials of calculations of homogeneity indices.
Itashiki, Yutaro*; Imabayashi, Yoichi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Satoh, Daiki; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 41(4), p.344 - 349, 2016/12
Carbon ion therapy has achieved satisfactory results because of high curability and minimally invasiveness. However, patients have a risk to get a secondary cancer. In order to estimate the risk, it is essential to understand particle transportation and nuclear reactions in the patient's body. The particle transport Monte Carlo simulation code is a useful tool to understand them. Since the code validation for heavy ion incident reactions is not enough, the experimental data of the elementary reaction processes is needed. We measured neutron production double-differential cross-sections (DDXs) on a carbon bombarded with 430 MeV/nucleon carbon beam which is a possible candidate of future therapy beam. The experiment was performed at PH2 beam line of the HIMAC of National Institute of Radiological Sciences. The 430 MeV/nucleon carbon beam was irradiated on a 5 cm 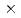 5 cm
5 cm 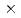 1 cm graphite target rotated 45
1 cm graphite target rotated 45 to the beam axis. The beam intensity was set to 10
to the beam axis. The beam intensity was set to 10 particles / spill. A 0.5 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillator was placed to monitor the beam intensity. Neutrons produced in the target were measured with two sizes of NE213 liquid organic scintillators located at six angles of 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90
particles / spill. A 0.5 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillator was placed to monitor the beam intensity. Neutrons produced in the target were measured with two sizes of NE213 liquid organic scintillators located at six angles of 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 . The 5.08 cm long one was used to obtain the neutron spectra from 1 MeV to 10 MeV and the 12.7 cm long one was used above 5 MeV. The 2 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillators to discriminate charged particles were set in front of the neutron detectors. The kinetic energies of neutrons were determined by the time-of-flight (TOF) method. Background neutrons were estimated by a measurement with iron shadow bars between the target and each neutron detector. An electronic circuit for data acquisition consisted of NIM and CAMAC modules. The experimental data was compared with calculated results obtained by Monte Carlo simulation codes as PHITS. The PHITS code reproduced the experimental data well.
. The 5.08 cm long one was used to obtain the neutron spectra from 1 MeV to 10 MeV and the 12.7 cm long one was used above 5 MeV. The 2 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillators to discriminate charged particles were set in front of the neutron detectors. The kinetic energies of neutrons were determined by the time-of-flight (TOF) method. Background neutrons were estimated by a measurement with iron shadow bars between the target and each neutron detector. An electronic circuit for data acquisition consisted of NIM and CAMAC modules. The experimental data was compared with calculated results obtained by Monte Carlo simulation codes as PHITS. The PHITS code reproduced the experimental data well.
Satoh, Daiki; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Itashiki, Yutaro*; Imabayashi, Yoichi*; Koba, Yusuke*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Nakao, Noriaki*; Uozumi, Yusuke*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 387, p.10 - 19, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)Double-differential neutron yields from a water phantom bombarded with 290-MeV/nucleon and 430-MeV/nucleon carbon ions were measured at emission angles of 15 , 30
, 30 , 45
, 45 , 60
, 60 , 75
, 75 , and 90
, and 90 using the neutron-detection system constituting of liquid organic scintillators. The angular distributions of neutron yields and effective doses around the phantom were obtained by integrating the double-differential neutron yields and applying the fluence-to-effective dose conversion coefficients. The experimental data were compared with results of the Monte-Carlo simulation code PHITS. The PHITS results showed good agreement with the measured data. From the results, we concluded that the PHITS simulation is applicable to the dose estimation at carbon-therapy facilities.
using the neutron-detection system constituting of liquid organic scintillators. The angular distributions of neutron yields and effective doses around the phantom were obtained by integrating the double-differential neutron yields and applying the fluence-to-effective dose conversion coefficients. The experimental data were compared with results of the Monte-Carlo simulation code PHITS. The PHITS results showed good agreement with the measured data. From the results, we concluded that the PHITS simulation is applicable to the dose estimation at carbon-therapy facilities.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Sanami, Toshiya*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Koura, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Shoji
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, 247 Pages, 2016/09
The 2015 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Ibaraki Quantum Beam Research Center, on November 19 and 20, 2015. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency and North Kanto Branch of Atomic Energy Society of Japan. In the symposium, there were two tutorials, "Theory of Few-Body Systems and Recent Topics" and "Use of Covariance Data 2015" and four oral sessions, "Recent Research Topics", "Progress of AIMAC Project", "Present Status of JENDL Evaluated Files", and "Nuclear Data Applications". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, evaluation, benchmark and application was presented in a poster session. Among 99 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 46 papers including 13 oral and 33 poster presentations.
Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Imabayashi, Yoichi*; Itashiki, Yutaro*; Satoh, Daiki; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Takada, Masashi*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.81 - 87, 2015/02
Cancer therapy using heavy ion beam has been adopted as highly advanced medical treatment by reason of its clinical advantages. It has become more important to estimate the risk of secondary cancer from recent survey. During treatment, secondary particles such as neutrons and -rays are producedby heavy ion induced nuclear reactions in a patient body as well as beam delivery apparatuses. For the risk assessment of secondary cancer, it is essential to know contribution of secondary neutrons by extra dose to organs in the vicinity of the irradiated tumor because the secondary neutron has a long flight path length and gives undesired dose to normal tissues in a wide volume. The experimental data of neutron energy spectra are required for dose estimations with high accuracy. Especially, precise data around neutron energy of 1 MeV is required because neutron of the energy region has a large relative biological e ectiveness. Estimation of the secondary neutron yield data is important for estimation of radiation safety on both of workers and public in treatment facilities.
Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Lee, H. S.*; Soha, A.*; Ramberg, E.*; Coleman, R.*; Jensen, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 337, p.68 - 77, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)The energy spectra of neutrons were measured by a time-of-flight method for 120 GeV protons on thick graphite, aluminum, copper, and tungsten targets with an NE213 scintillator at the Fermilab Test Beam Facility. Neutron energy spectra were obtained between 25 and 3000 MeV at emission angles of 30, 45, 120, and 150 . The spectra were parameterized as neutron emissions from three moving sources and then compared with theoretical spectra calculated by PHITS and FLUKA codes. The yields of the theoretical spectra were substantially underestimated compared with the yields of measured spectra. The integrated neutron yields from 25 to 3000 MeV calculated with PHITS code were 16-36% of the experimental yields and those calculated with FLUKA code were 26-57% of the experimental yields for all targets and emission angles.
. The spectra were parameterized as neutron emissions from three moving sources and then compared with theoretical spectra calculated by PHITS and FLUKA codes. The yields of the theoretical spectra were substantially underestimated compared with the yields of measured spectra. The integrated neutron yields from 25 to 3000 MeV calculated with PHITS code were 16-36% of the experimental yields and those calculated with FLUKA code were 26-57% of the experimental yields for all targets and emission angles.
Hirayama, Hideo*; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Okura, Takehisa; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Taki, Mitsumasa; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(3), p.119 - 126, 2014/09
A method of deducing the I-131 concentration in a radioactive plume from the time history of peak count rates determined from pulse height spectra obtained from an NaI(Tl)scintillation detector employed as a detector of a monitoring post was presented. The concentrations of I-131 in the plumes were estimated from the count rates using the calculated response of the NaI(Tl) detector with egs5 for a model of a plume uniformly containing I-131. This method was applied to the data from the monitoring posts at Nuclear Science Research Institutes of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The estimated time history variation of I-131 concentrations in plumes was in fair agreement with those measured directly by an air sampling method. The difference was less than a factor of 4 for plumes that arrived on March 15 and March 21, indicating relatively high I-131 concentrations among the plumes studied in this work.
Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Uehara, Haruhiko*; Nishizawa, Tomoya*; Mizuno, Takafumi*; Takamiya, Masanori*; Hashiguchi, Taro*; Satoh, Daiki; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 119, p.303 - 306, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Heavy ion cancer therapy has been increased by reason of its clinical advantages. During the treatment, the secondary particles such as neutron and  -ray are produced by nuclear reactions of a heavy ion incidence on a nucleus in a patient body. Estimation of the secondary neutrons yields data is essential for assessment of radiation safety on both of workers and public in treatment facilities. We have measured the neutron yields from carbon ion incidence on carbon, nitrogen and oxygen targets in wide angular range from 15
-ray are produced by nuclear reactions of a heavy ion incidence on a nucleus in a patient body. Estimation of the secondary neutrons yields data is essential for assessment of radiation safety on both of workers and public in treatment facilities. We have measured the neutron yields from carbon ion incidence on carbon, nitrogen and oxygen targets in wide angular range from 15 to 90
to 90 with 100- and 290-MeV/u.
with 100- and 290-MeV/u.
Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Uehara, Haruhiko*; Nishizawa, Tomoya*; Hirabayashi, Keiichi*; Satoh, Daiki; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Takada, Masashi*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.709 - 712, 2014/04
Heavy ion cancer therapy has been increased by reason of its clinical advantages. During the treatment, the secondary particles such as neutron and  -ray are produced by nuclear reactions of a heavy ion incidence on a nucleus in a patient body. Estimation of the secondary neutrons yields data is essential for assessment of radiation safety on both of workers and public in treatment facilities. Neutron energy spectra from a water phantom simulating the patient body were obtained at GSI only for forward directions. We measured the neutron yields from carbon ion incident on a water phantom in wide angular range from 15
-ray are produced by nuclear reactions of a heavy ion incidence on a nucleus in a patient body. Estimation of the secondary neutrons yields data is essential for assessment of radiation safety on both of workers and public in treatment facilities. Neutron energy spectra from a water phantom simulating the patient body were obtained at GSI only for forward directions. We measured the neutron yields from carbon ion incident on a water phantom in wide angular range from 15 to 90
to 90 with the therapeutic ion energy.
with the therapeutic ion energy.
Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Uehara, Haruhiko*; Nishizawa, Tomoya*; Mizuno, Takafumi*; Satoh, Daiki; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Takada, Masashi*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*
JAEA-Conf 2013-002, p.137 - 142, 2013/10
Heavy ion cancer therapy has been increased by reason of its clinical advantages. During the treatment, the secondary particles such as neutron and  -ray are produced by nuclear reactions of a heavy ion incidence on a nucleus in a patient body. Estimation of double differential cross sections of secondary neutron is important to risk assessment of extra dose to organs in the vicinity of the irradiated tumor. Accurate data in neutron energy around 1 MeV is required because neutron in the energy region has large relative biological effectiveness. Neutron double differential cross sections by inducing 290 MeV/u carbon ion to bio-elements have been obtained experimentally. In order to have knowledge of neutron production by deceleration carbon in a human body, we measured the neutron yields from carbon ion incidence on a carbon target of neutron energy below 1 MeV in wide angular range from 15
-ray are produced by nuclear reactions of a heavy ion incidence on a nucleus in a patient body. Estimation of double differential cross sections of secondary neutron is important to risk assessment of extra dose to organs in the vicinity of the irradiated tumor. Accurate data in neutron energy around 1 MeV is required because neutron in the energy region has large relative biological effectiveness. Neutron double differential cross sections by inducing 290 MeV/u carbon ion to bio-elements have been obtained experimentally. In order to have knowledge of neutron production by deceleration carbon in a human body, we measured the neutron yields from carbon ion incidence on a carbon target of neutron energy below 1 MeV in wide angular range from 15 to 90
to 90 with 100 MeV/u.
with 100 MeV/u.
Uozumi, Yusuke*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uehara, Haruhiko*; Nishizawa, Tomoya*; Mizuno, Takafumi*; Satoh, Daiki; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Takada, Masashi*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*; et al.
HIMAC-140, p.234 - 235, 2013/08
In the heavy-ion radiotherapy, considerable discussion has been attracted regarding the potential for second cancer induction by secondary neutrons produced from the primary heavy-ion fragmentation. We have started new measurements at 100 MeV/u to investigate the neutron production by heavy ions decelerating in a patient body.
Hirayama, Hideo*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sanami, Toshiya*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Sato, Osamu*; Takagi, Shunji*; Suzuki, Toshikazu*; Iwai, Satoshi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 55(2), p.83 - 96, 2013/02
, 55(2), p.83 - 96, 2013/02
Since the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant, units of radiation doses such as Sv have been frequently reported by newspapers. However, it is not exactly understood even by experts on nuclear engineering that there are two different concepts which are the protection quantity such as the effective dose related to a radiation health risk and the practical quantity such as ambient dose equivalents related to measurements. In this special issue, Radiological Protection Quantity, and Operational Quantity and Radiological Protection Quantity, explain the radiation protection dose system including the protection and practical quantities established by ICRP and ICRU. Relation between Dosimeters used at Fukushima etc. and Radiological Protection Quantity describes a method and its problems to measure radiations from Cs on surface and underground using survey meters and personal dosimeters, and convert the measured values to effective doses.
 and 90
and 90 bombarded with 120-GeV protons
bombarded with 120-GeV protonsIwamoto, Yosuke; Sanami, Toshiya*; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Lee, H. S.*; Soha, A.*; Ramberg, E.*; Coleman, R.*; Jensen, D.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 3, p.65 - 68, 2012/10
Neutron energy spectra at 15 and 90
and 90 produced from carbon, aluminum, copper and tungsten targets bombarded with 120-GeV protons were measured at Fermilab Test Beam Facility (FTBF) for the validation of simulation codes. The target thicknesses were 60 cm for graphite, 50 cm for aluminum, 20, 40, and 60 cm for copper and 10 cm for tungsten, respectively. The neutron time-of-flight measurements were performed using an NE213 organic liquid scintillator at 5.2 m for 90
produced from carbon, aluminum, copper and tungsten targets bombarded with 120-GeV protons were measured at Fermilab Test Beam Facility (FTBF) for the validation of simulation codes. The target thicknesses were 60 cm for graphite, 50 cm for aluminum, 20, 40, and 60 cm for copper and 10 cm for tungsten, respectively. The neutron time-of-flight measurements were performed using an NE213 organic liquid scintillator at 5.2 m for 90 and 8.0 m for 15
and 8.0 m for 15 measuring from the center of the target to the surface of the detector. The raw signals (waveforms) obtained from photomultiplier tubes were recorded using the 10 bit digitizer (Agilent-acqiris DC282) with 0.5 ns sampling and 500 ns duration. To compare the experimental results, Monte Carlo calculations with the PHITS, MARS and FLUKA codes were performed. It was found that these calculated results underestimate the experimental results in the whole energy range.
measuring from the center of the target to the surface of the detector. The raw signals (waveforms) obtained from photomultiplier tubes were recorded using the 10 bit digitizer (Agilent-acqiris DC282) with 0.5 ns sampling and 500 ns duration. To compare the experimental results, Monte Carlo calculations with the PHITS, MARS and FLUKA codes were performed. It was found that these calculated results underestimate the experimental results in the whole energy range.
Uozumi, Yusuke*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Hirabayashi, Keiichi*; Uehara, Haruhiko*; Nishizawa, Tomoya*; Satoh, Daiki; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Takada, Masashi*; et al.
HIMAC-138, p.237 - 238, 2012/08
In the heavy-ion radiotherapy, considerable discussion has been attracted regarding the potential for second cancer induction by secondary neutrons produced from the primary heavy-ion fragmentation. It is important to measure energy-angle double-differential cross sections (DDXs) of neutron- and photon-productions in heavy-ion nuclear reactions. Since it is notoriously hard to measure the spectral cross sections of neutrons in an energy range of around 1 MeV where the RBE value reaches at its maximum. In the project by last year, experiments were carried out at the synchrotron HIMAC of NIRS, Japan. The beams were  C and
C and  O of 290 MeV/u and bombarded a carbon target. In measurements of neutrons and photons were used liquid scintillator detectors of 5" and 2". We have succeeded to lower the neutron energy threshold down to 0.6 MeV. The present results for neutron productions are in reasonable agreements with PHITS. Since our goal in technical aspects has been fulfilled, measurements will be continued for other reactions.
O of 290 MeV/u and bombarded a carbon target. In measurements of neutrons and photons were used liquid scintillator detectors of 5" and 2". We have succeeded to lower the neutron energy threshold down to 0.6 MeV. The present results for neutron productions are in reasonable agreements with PHITS. Since our goal in technical aspects has been fulfilled, measurements will be continued for other reactions.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
HIMAC-136, p.219 - 220, 2011/11
Measurements of lineal energy distribution were employed using 160 MeV proton and 490 MeV/u Si. The calculated 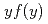 by PHITS and
by PHITS and 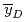 agree fairly well with those measured. The LET dependence of
agree fairly well with those measured. The LET dependence of 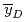 was obtained from 3 to 300 keV/um in this project.
was obtained from 3 to 300 keV/um in this project.