Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 gyrokinetic simulations of ohmic L-mode plasmas in linear and saturated ohmic confinement regimes
gyrokinetic simulations of ohmic L-mode plasmas in linear and saturated ohmic confinement regimesIdomura, Yasuhiro; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Garbet, X.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Tore Supra Teams*
Physics of Plasmas, 30(4), p.042508_1 - 042508_18, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.59(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Two time slices in linear and saturated ohmic confinement (LOC and SOC) regimes in a Tore Supra ohmic L-mode discharge are analyzed using nonlinear global full- gyrokinetic simulations, and qualitative features of the LOC-SOC transition are reproduced. The exhaust of carbon impurity ions is caused by fast ion mixing, which is driven by the toroidal field stress. The intrinsic rotation develops in the opposite direction between the LOC and SOC phases, which is characterized by the different features of the mode asymmetry between trapped electron modes in the LOC phase and ion temperature gradient driven modes in the SOC phase, leading to the change of the profile shear stress. The energy fluxes of electrons and deuterium ions are dominant in the LOC and SOC phases, respectively, and the ratio of the energy confinement time between two phases agree with the experimental value.
gyrokinetic simulations, and qualitative features of the LOC-SOC transition are reproduced. The exhaust of carbon impurity ions is caused by fast ion mixing, which is driven by the toroidal field stress. The intrinsic rotation develops in the opposite direction between the LOC and SOC phases, which is characterized by the different features of the mode asymmetry between trapped electron modes in the LOC phase and ion temperature gradient driven modes in the SOC phase, leading to the change of the profile shear stress. The energy fluxes of electrons and deuterium ions are dominant in the LOC and SOC phases, respectively, and the ratio of the energy confinement time between two phases agree with the experimental value.
Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*; Heim, D. M.*; Maeyama, Shinya*; Garbet, X.*; Grandgirard, V.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Masatoshi*
Physics of Plasmas, 28(1), p.012304_1 - 012304_21, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This article demonstrates a data compression technique for the time series of five dimensional distribution function data based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Phase space bases and corresponding coefficients are constructed by PCA in order to reduce the data size and the dimensionality. It is shown that about 83% of the variance of the original five dimensional distribution can be expressed with 64 components. This leads to the compression of the degrees of freedom from 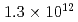 to
to 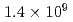 . One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
. One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
Asahi, Yuichi*; Grandgirard, V.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Donnel, P.*; Garbet, X.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Latu, G.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 61(6), p.065015_1 - 065015_15, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.41(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The role of poloidal convective cells on transport processes is studied with the full-F gyrokinetic code GYSELA. For this purpose, we apply a numerical filter to convective cells and compare the simulation results with and without the filter. The energy flux driven by the magnetic drifts turns out to be reduced by a factor of about 2 once the numerical filter is applied. A careful analysis reveals that the frequency spectrum of the convective cells is well-correlated with that of the turbulent Reynolds stress tensor, giving credit to their turbulence-driven origin. The impact of convective cells can be interpreted as a synergy between turbulence and neoclassical dynamics.
Donnel, P.*; Garbet, X.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Asahi, Yuichi; Wilczynski, F.*; Caschera, E.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Gillot, C.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 61(1), p.014003_1 - 014003_11, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:60.80(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Poloidal asymmetries of the 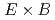 plasma flow are known to play a role in neoclassical transport. According to conventional neoclassical theory, the level of poloidal asymmetry of the electric potential is expected to be very small. In the present work, a general framework for the generation of axisymmetric structures of potential by turbulence is presented. Zonal flows, geodesic acoustic modes and convective cells are described by a single model. This is done by solving the gyrokinetic equation coupled to the quasi-neutrality equation. This calculation provides a predictive calculation of the frequency spectrum of flows given a specified forcing due to turbulence. It also shows that the dominant mechanism comes from zonal flow compression at intermediate frequencies, while ballooning of the turbulence Reynolds stress appears to be the main drive at low frequency.
plasma flow are known to play a role in neoclassical transport. According to conventional neoclassical theory, the level of poloidal asymmetry of the electric potential is expected to be very small. In the present work, a general framework for the generation of axisymmetric structures of potential by turbulence is presented. Zonal flows, geodesic acoustic modes and convective cells are described by a single model. This is done by solving the gyrokinetic equation coupled to the quasi-neutrality equation. This calculation provides a predictive calculation of the frequency spectrum of flows given a specified forcing due to turbulence. It also shows that the dominant mechanism comes from zonal flow compression at intermediate frequencies, while ballooning of the turbulence Reynolds stress appears to be the main drive at low frequency.
Asahi, Yuichi*; Grandgirard, V.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Garbet, X.*; Latu, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Donnel, P.*; Ehrlacher, C.*
Physics of Plasmas, 24(10), p.102515_1 - 102515_17, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:44.32(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Two full-F global gyrokinetic codes are benchmarked to compute flux-driven ion temperature gradient turbulence in tokamak plasmas. For this purpose, the Semi-Lagrangian code GYSELA and the Eulerian code GT5D are employed, which solve the full-F gyrokinetic equation with a realistic fixed flux condition. Using the appropriate settings for the boundary and initial conditions, flux-driven ITG turbulence simulations are carried out. The avalanche-like transport is assessed with a focus on spatio-temporal properties. A statistical analysis is performed to discuss this self-organized criticality (SOC) like behaviors, where we found 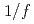 spectra and a transition to
spectra and a transition to 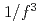 spectra at high-frequency side in both codes. Based on these benchmarks, it is verified that the SOC-like behavior is robust and not dependent on numerics.
spectra at high-frequency side in both codes. Based on these benchmarks, it is verified that the SOC-like behavior is robust and not dependent on numerics.
Villard, L.*; Bottino, A.*; Brunner, S.*; Casati, A.*; Chowdhury, J.*; Dannert, T.*; Ganesh, R.*; Garbet, X.*; G rler, T.*; Grandgirard, V.*; et al.
rler, T.*; Grandgirard, V.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 52(12), p.124038_1 - 124038_18, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:60.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)B coulet, M.*; Huysmans, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Garbet, X.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Rimini, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Litaudon, X.*; Monier-Garbet, P.*; An
coulet, M.*; Huysmans, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Garbet, X.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Rimini, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Litaudon, X.*; Monier-Garbet, P.*; An , J.-M.*; et al.
, J.-M.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 45(12A), p.A93 - A113, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:86 Percentile:90.65(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Asahi, Yuichi*; Garbet, X.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Grandgirard, V.*; Latu, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Donnel, P.*; Ehrlacher, C.*; Passeron, Ch.*
no journal, ,
Two global full-f gyrokinetic codes, which have been developed at CEA and JAEA, are benchmarked. Quantitative agreements between two codes are obtained regarding linear processes such as the linear stability of ion temperature gradient driven modes, the linear damping of zonal flows, and the collisional transport. Preliminary benchmarks on nonlinear turbulence simulations show some differences of calculation results, which arise due to differences in calculation models such as boundary conditions and heat source models, and the remaining issues towards quantitative nonlinear benchmarks are clarified.
Asahi, Yuichi*; Grandgirard, V.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Sarazin, Y.*; Latu, G.*; Garbet, X.*
no journal, ,
This talk reviews outcomes from BMTFF projects, which was conducted for FY2015-2016. In this project, in order to establish a firm basis of full-f gyrokinetic models, two major full-f gyrokinetic codes in EU and Japan, GYSELA and GT5D, were benchmarked. In FY2015, all the numerical implementations were examined, and boundary conditions were fixed to be the same. With this correction, collisional transport, linear zonal flow damping, and linear stability of the ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) mode were successfully benchmarked. In FY2016, the same source and sink models were implemented in both codes, and nonlinear turbulence simulations were benchmarked. Decaying ITG turbulence simulations without heat sources showed similar profile relaxation processes, and nonlinear critical temperature gradients agreed quantitatively with each other. On the other hand, driven ITG turbulence simulations with heat sources showed intermittent bursts of avalanche like transport, which indicate similar 1/f type frequency spectra.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Garbet, X.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Tore Supra Teams*
no journal, ,
LOC-SOC (linear and saturated ohmic confinement) transition phenomena in ohmic plasmas on ToreSupra tokamak were analyzed using full-f gyrokinetic simulations on Fugaku, and transition from trapped electron mode turbulence to ion temperature gradient driven turbulence was confirmed between LOC phase (low density, high Zeff) and SOC phase (high density, low Zeff). Numerical experiments qualitatively recovered experimental observations such as changes in energy confinement times and intrinsic rotation profiles, and exhaust of carbon impurity ions.