Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morita, Koji*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Sato, Ikkenn
JNC TY9400 2005-022, 119 Pages, 2005/08
It is one of important problems for more reliable reactor safety evaluation to improve numerical simulation techniques for involved thermal-hydraulic phenomena of multiphase, multicomponent flows in core disruptive accidents. In the present cooperative research, physical model development and experimental investigation were performed for transient condensation phenomena of a vapor bubble with noncondensable gas to improve applicability of a fast-reactor safety analysis code for the phase-transition phenomena in multicomponent systems. In addition, basic validity of the developed models was demonstrated through the experimental analysis, and then applicability of the fast-reactor safety analysis code was discussed for bubble condensation behaviors under rector conditions.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Onoda, Yuichi; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Sato, Ikkenn
JNC TN9400 2005-045, 123 Pages, 2005/06
During the course of core disruptive accidents in liquid-metal fast reactors, a boiling pool of molten fuel/steel mixture could be formed. The stability of this boiling-pool, for which in-pile experimental data with real reactor materials are very limited, plays an important role in the determination of the accident scenarios. In the TPA2 test of the CABRI-RAFT program (from 1996 to 2002), the fuel-to-steel heat transfer characteristic governing the pool behavior was investigated as a joint study with the French 'Institut de Radioprotection et de Surete Nucleaire' (IRSN). This test was performed in the CABRI reactor in 2001 using a test capsule that contains fresh 12.3% enriched UO pellets with embedded stainless steel balls. Following a pre-heating phase, the capsule was submitted to a transient overpower resulting in fuel melting and steel vaporization. The steel vapor-pressure build-up observed during the transient was quite weak, suggesting the presence of a strong mechanism to limit the fuel-to-steel heat transfer. The detailed experimental data evaluation suggested a phenomenon that the steel vaporization at the surface of steel ball blanketed the steel from molten fuel. This vapor blanketing seems to be a mechanism reducing the fuel-to-steel heat transfer. An analysis with the SIMMER-III code, a multi-component multi-phase thermal-hydraulics code, was performed in this study. This code simulation could well reproduce the pressure buildup and boiling pool behavior which occurred in the test by applying specifically reduced heat transfer coefficients.
pellets with embedded stainless steel balls. Following a pre-heating phase, the capsule was submitted to a transient overpower resulting in fuel melting and steel vaporization. The steel vapor-pressure build-up observed during the transient was quite weak, suggesting the presence of a strong mechanism to limit the fuel-to-steel heat transfer. The detailed experimental data evaluation suggested a phenomenon that the steel vaporization at the surface of steel ball blanketed the steel from molten fuel. This vapor blanketing seems to be a mechanism reducing the fuel-to-steel heat transfer. An analysis with the SIMMER-III code, a multi-component multi-phase thermal-hydraulics code, was performed in this study. This code simulation could well reproduce the pressure buildup and boiling pool behavior which occurred in the test by applying specifically reduced heat transfer coefficients.
Kamiyama, Kenji; Kubo, Shigenobu; Sato, Ikkenn
JNC TY9400 2004-030, 103 Pages, 2005/02
The objective of the EAGLE project is to confirm a possible scenario in the postulated core disruptive accident of sodium cooled fast reactors, in which the molten fuel discharging from the core region in the early stage of the accident with its inherent mechanisms would prevent energetic re-criticalities. In order to obtain necessary experimental data, in-pile and out-of-pile experiments utilizing facilities of National Nuclear Center in the Republic of Kazakhstan were planed and are currently carried out. This document reports progress and results of the out-of-pile experiments which consist of a part of the EAGLE program. In the out-of-pile program so far, a series of experiments has been carried out aiming at establishment of basic necessary technology which consists of melting of the fuel-simulating material using the induction heating, transferring it into the test section and measuring the related phenomena during the experiments. Following knowledge and results have been obtained so far: - Using uranium dioxide and alumina as candidate materials for fuel simulant, basic experimental technology has been established, and fundamental data of molten material discharge were obtained under the condition without sodium. - With uranium dioxide, certain efforts, such as providing carbonized metal coating on the crucible inner surface, have been made to prevent chemical reaction between uranium dioxide and the graphite crucible so as to obtain molten uranium dioxide without a great deal of unfavorable impurities which prevent reasonable simulation of the real fuel behavior. It was concluded, however, that present techniques did not allow molten uranium dioxide with sufficient grade. - Alumina, which has well-known thermophysical properties, was evaluated to have adequate characteristics in terms of simulating real molten fuel behavior. Through implementation of the experiments, it was confirmed that molten alumina with sufficient purity and characteristics could be g
Yamano, Hidemasa; Onoda, Yuichi; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Sato, Ikkenn
6th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor, 54 Pages, 2004/10
Focusing on the cover layer materials (as the Radon Barrier Materials), which could have the effect to restrain the radon from scattering into the air and the effect of the radiation shielding, we produced the radon barrier materials with crude bentonite on an experimental basis, using the rotary type comprehensive unit for grinding and mixing, through which we carried out the evaluation of the characteristics thereof.
Morita, Koji*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Sato, Ikkenn
JNC TY9400 2004-013, 45 Pages, 2004/07
It is one of important problems for more reliable reactor safety evaluation to improve numerical simulation techniques for involved therma-hydraulic phenomena of multiphase, multicomponent flows in core disruptive accidents. In the present cooperative research, physical model development and experimental investigation were conducted for transient condensation phenomena of a vapor bubble with noncondensable gases to improve applicability of a fast-reactor safety analysis code for the phase-transition phenomena in multicomponent systems. This fiscal year experiments using steam mixed with nitrogen gas were performed for the transient bubble condensation phenomena, and then experimental data were obtained for relatively large-scale bubble behavior. In addition, experimental analyses was performed by the fast-reactor safety analysis code and its validity was discussed.
Kubo, Shigenobu; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kawada, Kenichi; Onoda, Yuichi; Sato, Ikkenn; Kamiyama, Kenji; Ueda, Nobuyuki*; Fujita, Satoshi; Niwa, Hajime
JNC TN9400 2004-041, 135 Pages, 2004/07
This report shows the results of the study on countermeasures for the elimination of re-criticality issue for the sodium cooled reactors, which was conducted in 2003 as a part of the feasibility study phase II for the commercialization of fast reactors. A sort of analytical studies related to the in-vessel retention capability under the unprotected loss of flow condition was conducted for the large scale and medium scale sodium cooled reactors, aiming at establishing some promising concepts to resolve the re-criticality issue keeping consistency with the basic concept of the core and plant design. Major conclusions are as follows. ABLE concept, which is proposed as a measure to enhance the fuel discharge capability in the early transition phase, needs much time to initiate fuel discharge than wrapper tube failure. Therefore it is currently concluded that it is difficult to show clear perspective. A modified version of FAIDUS which has less drawbacks on the core and cycle performance and related R&Ds than original FAIDUS was proposed for further study. In-place retention and cooling in the core region is important from view point of reduction of R&D loads conceming post accident material relocation and cooling at the bottom of the reactor vessel. A possibility of which the in-vessel retention can be achieved by quantitatively clarifying the effect of the superior cooling potential of sodium was shown. Based on the currently available information related to FAIDUS and ABLE, possible candidates of experimental studies were shown. An initiating phase analysis for the metallic fuel core with 550 C of core outlet temperature and 8
C of core outlet temperature and 8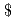 of sodium void worth resulted in mild consequence without prompt criticality. Although there is still large uncertainty in the early transition phase, it might be possible to avoid severe re-criticality. And it was shown that power excursion due to molten fuel sloshing might be milder than that of MOX fuel case.
of sodium void worth resulted in mild consequence without prompt criticality. Although there is still large uncertainty in the early transition phase, it might be possible to avoid severe re-criticality. And it was shown that power excursion due to molten fuel sloshing might be milder than that of MOX fuel case.
Sato, Ikkenn; Lemoine, F.*; Struwe, D.*
Nuclear Technology, 145(1), p.115 - 137, 2004/00
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:84.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the CABRI-2 program, 12 tests were performed under various transient conditions covering a wide range of accident scenarios using two types of pre-irradiated Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) fuel pins with different smear densities and burn-ups. For each fuel, a non-failure-transient test was performed and it provided basic information such as fuel thermal condition, fuel swelling and gas release. From the failure tests, information on failure mode, failure time and axial location was obtained. Based on this information, failure conditions such as fuel enthalpy and cladding temperature were evaluated. These failure conditions were compared with the CABRI-1 tests in which different fuels as well as different transient conditions were used. This comparison, together with supporting information available from existing in-pile and out-of-pile experiments, allowed an effective understanding on failure mechanisms depending on fuel and transient conditions. It is concluded that Pellet Cladding
Morita, Koji*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Konishi, Kensuke; Sato, Ikkenn
JNC TY9400 2003-011, 56 Pages, 2003/04
It is one of the important problems for more reliable reactor safety evaluation to improve numerical simulation techniques for involved thermal-hydraulic phenomena of multiphase, multicomponent flows in core disruptive accidents.In the present joint research, physical model development and experimental investigation were conducted for transient condensation phenomena of a vapor bubble with noncondensable gases to improve applicability of a fast-reactor safety analysis code for the phase-transition phenomena in multicomponent systems.In this fiscal year, preliminary experiments using noncondensable gas were performed for the transient bubble condensation phenomena, and then basic data were obtained for large-scale bubble behavior without condensation.In addition, a multiple-scale flow-regime model treating large-scale bubbles was newly proposed for the fast-reactor safety analysis code and applied to the analysis of the preliminary experiments successfully.
; Sato, Ikkenn
Nuclear Technology, 98(1), p.54 - 69, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:86.34(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Sato, Ikkenn; ;
Evaluation of Material Coolant Interaction and Material Movement and Relocation in Liquid Metal Reac, ,
None