Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kinase, Akari; Goto, Katsunori*; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-004, 60 Pages, 2024/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3 and stored at the waste storage facility L. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc, 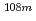 Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
 C
CMohamad, A. B.; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Furumoto, Kenichiro*; Okada, Yuji*; Sato, Daiki*
Corrosion Science, 224, p.111540_1 - 111540_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:55.06(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:94.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.46(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Yamashita, Takuya; Honda, Takeshi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Nozaki, Kenichiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Sato, Ikken; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 209(6), p.902 - 927, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:80.64(Nuclear Science & Technology) 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:88.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:74.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:95.97(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,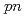 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Honda, Takeshi*; Nozaki, Kenichiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 206(10), p.1517 - 1537, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:91.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Yoshiyuki; Aono, Ryuji; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Testing 2019-003, 20 Pages, 2019/12
In the Radioactive Waste Management Technology Section, the radioactive liquid waste generated in the test using natural uranium in the past has been stored based on the contents of permission. Although we decided to perform solidification treatment in order to reduce the risk in storage, no rational treatment method has been established so far. Therefore, we examined adsorption treatment of natural uranium using uranium adsorbent (Tannix), and finally stabilized treatment by cement solidification. The treatment methods and findings obtained for a series of operations in waste liquid treatment are summarized in this report for reference when treating similar liquid waste.
Pham, V. H.; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki; Furumoto, Kenichiro*; Sato, Hisaki*; Ishibashi, Ryo*; Yamashita, Shinichiro
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.670 - 674, 2019/09
Haraga, Tomoko; Ouchi, Kazuki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Hoshino, Hitoshi*; Tanana, Rei*; Fujihara, Takashi*; Kurokawa, Hideki*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1032, p.188 - 196, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:46.22(Chemistry, Analytical)The development of safe, rapid and highly sensitive analytical methods for radioactive samples, especially actinide (An) ions, represents an important challenge. Here we propose a methodology for selecting appropriate emissive probes for An ions with very low consumption and emission of radioactivity by capillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence detection (CE-LIF), using a small chemical library of probes with eight different chelating moieties. It was found that the emissive probe, which possesses the tetradentate chelating moiety, was suitable for detecting uranyl ions. The detection limit for the uranyl-probe complex using CE-LIF combined with dynamic ternary complexation and on-capillary concentration techniques was determined to be 0.7 ppt. This method was successfully applied to real radioactive liquid samples collected from nuclear facilities.
Kamikubota, Norihiko*; Yamada, Shuei*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Yamamoto, Noboru*; Yoshida, Susumu*; Nemoto, Hiroyuki*
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Accelerator and Large Experimental Physics Control Systems (ICALEPCS 2017) (Internet), p.1470 - 1473, 2018/01
no abstracts in English
 Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationAono, Ryuji; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2017-025, 32 Pages, 2017/11
We have developed analytical methods for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for
Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Okafuji, Takashi*; Miura, Kazuhiro*; Sago, Hiromi*; Murakami, Hisatomo*; Kubo, Koji*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Wakai, Takashi; Shimomura, Kenta
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2017 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.591 - 595, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2017/00
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Hoken Butsuri, 51(4), p.209 - 217, 2016/12
A large amount of contaminated rubbles were generated by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS). For safe decommissioning of F1NPS, it is important to evaluate the composition and concentration of radionuclides in the rubbles. In this paper, to characterize the rubbles collected at F1NPS in Unit-1, Unit-2 and Unit-3, radiochemical analysis was operated. As a result of radiochemical analysis,  -ray-emitting nuclides
-ray-emitting nuclides  Co,
Co,  Cs and
Cs and 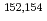 Eu,
Eu,  -ray-emitting nuclides
-ray-emitting nuclides  H,
H,  C,
C,  Sr and
Sr and  Tc, and
Tc, and  -particle-emitting nuclides
-particle-emitting nuclides 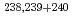 Pu,
Pu,  Am and
Am and  Cm were detected. In contrast,
Cm were detected. In contrast,  Nb and
Nb and  Eu concentrations were below the detection limit. Measured radioactive concentrations implied that
Eu concentrations were below the detection limit. Measured radioactive concentrations implied that  H,
H,  C,
C,  Co and
Co and  Sr concentrations depended on
Sr concentrations depended on  Cs concentration respectively. This analysis was characterized the radioactivity concentrations of the rubbles.
Cs concentration respectively. This analysis was characterized the radioactivity concentrations of the rubbles.
Yamashita, Takuya; Wakai, Takashi; Onizawa, Takashi; Sato, Kenichiro*; Yamamoto, Kenji*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 138(6), p.061407_1 - 061407_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)Yamashita, Takuya; Nagae, Yuji; Sato, Kenichiro*; Yamamoto, Kenji*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 138(2), p.024501_1 - 024501_7, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)Wakai, Takashi; Machida, Hideo*; Sato, Kenichiro*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2015 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2015/11
This paper describes a through-wall crack length evaluation procedure applicable to Leak Before Break (LBB) assessment of Japan Sodium cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR) pipes made of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. In LBB assessment of JSFR pipes, it is required to calculate virtual through-wall crack length, though the crack growth is quite small under design condition. Generally, it is known that the through-wall crack length depends on loading condition, namely the load ratio between tensile and bending and that the length under pure bending load condition is largest. This study proposes a simplified method to evaluate the through-wall crack length both for axial and circumferential cracks as a function of load ratio and fatigue crack growth characteristics. Using the method, through-wall crack length can be predicted as far as we know the loading condition and material properties.