Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
和田 有希*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 中村 佳敬*; 森本 健志*; 佐藤 光輝*; 牛尾 知雄*; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; 米徳 大輔*; 澤野 達也*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 125(4), p.e2019JD031730_1 - e2019JD031730_11, 2020/02
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:78.78(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)During 2017-2018 winter operation of the Gamma-Ray Observation of Winter Thunderclouds experiment in Japan, two downward terrestrial gamma-ray flashes (TGFs) that triggered atmospheric photonuclear reactions were detected. They took place during winter thunderstorms on 5 December 2017 and 9 January 2018 at Kanazawa, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. Each event coincided with an intracloud/intercloud discharge, which had a negative-polarity peak current higher than 150 kA. Their radio waveforms in the low-frequency band are categorized as a distinct lightning type called energetic in-cloud pulse (EIP). Negative-polarity EIPs have been previously suggested to be highly associated with downward TGFs, and the present observations provide evidence of the correlation between them for the first time. Furthermore, both of the downward TGFs followed gamma-ray glows, minute-lasting high-energy emissions from thunderclouds. It is suggested that the negative EIPs took place with downward propagating negative leaders or upward positive ones developed in highly electrified regions responsible for the gamma-ray glows.
和田 有希*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 中村 佳敬*; 古田 禄大; 湯浅 孝行*; 中澤 知洋*; 森本 健志*; 佐藤 光輝*; 松元 崇弘*; 米徳 大輔*; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.67_1 - 67_9, 2019/06
被引用回数:60 パーセンタイル:92.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two types of high-energy events have been detected from thunderstorms. One is "terrestrial gamma-ray flashes" (TGFs), sub-millisecond emissions coinciding with lightning discharges. The other is minute-lasting "gamma-ray glows". Although both phenomena are thought to originate from relativistic runaway electron avalanches in strong electric fields, the connection between them is not well understood. Here we report unequivocal simultaneous detection of a gamma-ray glow termination and a downward TGF, observed from the ground. During a winter thunderstorm in Japan on 9 January 2018, our detectors caught a gamma-ray glow, which moved for 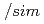 100 s with ambient wind, and then abruptly ceased with a lightning discharge. Simultaneously, the detectors observed photonuclear reactions triggered by a downward TGF, whose radio pulse was located within
100 s with ambient wind, and then abruptly ceased with a lightning discharge. Simultaneously, the detectors observed photonuclear reactions triggered by a downward TGF, whose radio pulse was located within  1 km from where the glow ceased. It is suggested that the highly-electrified region producing the glow was related to the initiation of the downward TGF.
1 km from where the glow ceased. It is suggested that the highly-electrified region producing the glow was related to the initiation of the downward TGF.
榎戸 輝揚*; 和田 有希*; 古田 禄大*; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; 奥田 和史*; 牧島 一夫*; 佐藤 光輝*; 佐藤 陽祐*; 中野 俊男*; et al.
Nature, 551(7681), p.481 - 484, 2017/11
被引用回数:132 パーセンタイル:97.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Relativistic electrons accelerated by electric fields of lightnings and thunderclouds emit bremsstrahlung  rays, which have been detected at ground observations. The energy of the
rays, which have been detected at ground observations. The energy of the  rays is sufficiently high to potentially invoke atmospheric photonuclear reactions
rays is sufficiently high to potentially invoke atmospheric photonuclear reactions  N(
N( , n)
, n) N, which would produce neutrons and eventually positrons via
N, which would produce neutrons and eventually positrons via 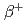 decay of generated unstable radioactive isotopes, especially
decay of generated unstable radioactive isotopes, especially  N. However, no clear observational evidence for the reaction has been reported to date. Here we report the first detection of neutron and positron signals from lightning with a ground observation. During a thunderstorm on 6 February 2017 in Japan, an intense
N. However, no clear observational evidence for the reaction has been reported to date. Here we report the first detection of neutron and positron signals from lightning with a ground observation. During a thunderstorm on 6 February 2017 in Japan, an intense  -ray flash (
-ray flash ( 1 ms) was detected at our monitoring sites. The subsequent initial burst quickly subsided with an exponential decay constant of 40-60 ms, followed by a prolonged line emission at
1 ms) was detected at our monitoring sites. The subsequent initial burst quickly subsided with an exponential decay constant of 40-60 ms, followed by a prolonged line emission at  0.511MeV, lasting for a minute. The observed decay timescale and spectral cutoff at
0.511MeV, lasting for a minute. The observed decay timescale and spectral cutoff at  10 MeV of the initial emission are well explained with de-excitation
10 MeV of the initial emission are well explained with de-excitation  rays from the nuclei excited by neutron capture. The centre energy of the prolonged line emission corresponds to the electron-positron annihilation, and hence is the conclusive indication of positrons produced after the lightning. Our detection of neutrons and positrons is unequivocal evidence that natural lightning triggers photonuclear reactions.
rays from the nuclei excited by neutron capture. The centre energy of the prolonged line emission corresponds to the electron-positron annihilation, and hence is the conclusive indication of positrons produced after the lightning. Our detection of neutrons and positrons is unequivocal evidence that natural lightning triggers photonuclear reactions.
川村 真人*; 千代 悦司; 堀 利彦; 篠崎 信一; 佐藤 文明; 福井 佑治*; 二ツ川 健太*; 山崎 正義*; 佐川 隆*; 宮嶋 教至*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.605 - 607, 2014/06
J-PARCリニアック用クライストロン電源システムについて、過去1年間の運転状況等を報告する。181MeVリニアック運転対応として、2012年9月下旬より2013年5月下旬まで、年末年始の中断や、スケジュール化されたメンテナンス等を除き連続運転を行った。その間、AVR盤内制御線等のノイズ対策不備、アノード変調器内の電極部接触不良等の不具合による運転の中断があり、不具合の考察と対策などを行った。運転と並行して、2012年7月初めまで運転していたアノード変調器のうち、未改修分15台を改修して放電対策を施した。エネルギー増強対応として、震災により中断していた972MHzテストスタンドの再立上げ、HVDCPS#10とACS#16ステーション、HVDCPS#11とACS#17ステーションの立上げを行った。エネルギー増強対応の機器については、972MHzテストスタンドを6月18日に運転再開し、ACS#16, #17の両ステーションも近日運転を再開する予定である。
川村 真人*; 千代 悦司; 堀 利彦; 篠崎 信一; 佐藤 文明; 福井 佑治*; 二ツ川 健太*; 山崎 正義*; 佐川 隆*; 雪竹 光輝*; et al.
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.1243 - 1247, 2013/08
過去1年間のJ-PARCリニアック用クライストロン電源システムの運転状況について、東日本大震災による被災からの復旧、長期に渡る加速器運転停止を招いた高圧直流電源の故障を中心に述べる。また、エネルギー増強に向けた作業の状況を報告する。震災後、本電源システムは2011年10月中旬に試運転、11月上旬に181MeV用全機器の終夜連続運転の再開を果たし、2012年5月末までの当電源システムのHVオン時間は4,900時間である。2012年3月下旬、高圧直流電源(HVDCPS)1号機の変圧整流器が故障した。絶縁油タンクを開けて内部を確認した結果、整流用ダイオードスタックの破損が見られたので予備品と交換し、試運転を行ったところ再度故障し、別のダイオードスタックが破損した。結局当該変圧整流器は破棄し、代わりに予備機器を設置して運転を再開した。この影響で当電源システムは11日間停止、リニアックのビーム加速は15日間中断、ユーザーへの供給運転は18日間中断となった。
山崎 千里*; 村上 勝彦*; 藤井 康之*; 佐藤 慶治*; 原田 えりみ*; 武田 淳一*; 谷家 貴之*; 坂手 龍一*; 喜久川 真吾*; 嶋田 誠*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
被引用回数:52 パーセンタイル:70.47(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)ヒトゲノム解析のために、転写産物データベースを構築した。34057個のタンパク質コード領域と、642個のタンパク質をコードしていないRNAを見いだすことができた。
土屋 晴文; 榎戸 輝揚*; 和田 有希*; 古田 禄大*; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; 奥田 和史*; 牧島 一夫*; 佐藤 光輝*; 佐藤 陽祐*; et al.
no journal, ,
日本海沿岸地域にある原子力発電所や自治体が持つモニタリングポストにより、冬の雷の発生や雷雲の通過に伴った3MeV以上の高エネルギー放射線量の増大が観測されていた。こうした放射線は、雷や雷雲がもつ電場によって加速された電子の制動放射 線であると考えられている。また、近年、雷や雷雲に付随して中性子や陽電子の信号を捉えたという報告もあった。これは、制動放射だけではなく様々な高エネルギー反応が雷や雷雲の中で起こっている可能性を示唆しており、活発な議論がなされている。本発表では、現在までに原子力センシング研究グループが観測したロングバーストと呼ばれる雷雲の通過に伴って放射線量が数分ほど増大する事象と、雷に同期して発生する継続時間が1秒以下のショートバーストの観測結果について報告する。特に、2017年2月の落雷に伴って発生したショートバーストでは、雷が光核反応を誘発し、中性子, 陽電子および酸素や炭素の放射性同位体を生成した実験的な証拠を初めて確認することに成功した。本発表では、それらの生成メカニズムについても議論する。
線であると考えられている。また、近年、雷や雷雲に付随して中性子や陽電子の信号を捉えたという報告もあった。これは、制動放射だけではなく様々な高エネルギー反応が雷や雷雲の中で起こっている可能性を示唆しており、活発な議論がなされている。本発表では、現在までに原子力センシング研究グループが観測したロングバーストと呼ばれる雷雲の通過に伴って放射線量が数分ほど増大する事象と、雷に同期して発生する継続時間が1秒以下のショートバーストの観測結果について報告する。特に、2017年2月の落雷に伴って発生したショートバーストでは、雷が光核反応を誘発し、中性子, 陽電子および酸素や炭素の放射性同位体を生成した実験的な証拠を初めて確認することに成功した。本発表では、それらの生成メカニズムについても議論する。