Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1The crystal and magnetic structures of antiferromagnetic Mn deuterides formed by hydrogenating Mn metal at high temperature and high pressure, fcc  -MnDx and hcp
-MnDx and hcp  -MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from
-MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from  700 to
700 to  450 K and remained down to 300 K. N
450 K and remained down to 300 K. N el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for
el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for  -MnD
-MnD . For
. For  -MnD
-MnD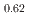 , saturation magnetic moment and N
, saturation magnetic moment and N el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1)
el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1) 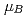 and 347(3) K, respectively. The N
and 347(3) K, respectively. The N el temperatures determined for
el temperatures determined for  -MnD
-MnD and
and  -MnD
-MnD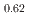 are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N
are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.13_1 - 13_8, 2024/11
The latest updates on PHITS, a versatile radiation transport code, focusing specifically on track-structure models are presented. Track structure calculations are methods used to simulate the movement of charged particles while explicitly considering each atomic reaction. Initially developed for radiation biology, these calculation methods aimed to analyze the radiation-induced damage to DNA and chromosomes. Several track-structure calculation models, including PHITS-ETS, PHITS-ETS for Si, PHITS-KURBUC, ETSART, and ITSART, have been developed and implemented to PHITS. These models allow users to study the behavior of various particles at the nano-scale across a wide range of materials. Furthermore, potential applications of track-structure calculations have also been proposed so far. This collection of track-structure calculation models, which encompasses diverse conditions, opens up new avenues for research in the field of radiation effects.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.8861_1 - 8861_2, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In our previous article (Nature Commun. 5, 5063 (2014)), the site occupancies of D atoms dissolved in an fcc Fe metal lattice were investigated via Rietveld refinement of neutron powder diffraction patterns collected at 988 K and 6.3 GPa. The fcc metal lattice has two interstitial sites available for accommodating D atoms: octahedral and tetrahedral sites. The Rietveld refinement revealed that D atoms occupied mainly the octahedral sites with occupancy of 0.532 and slightly the tetrahedral sites with occupancy of 0.056. Subsequent density-functional-theory (DFT) calculations by Antonov (Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019)) showed that the occupation energy on the tetrahedral site was significantly higher than that on the octahedral site; the tetrahedral site occupation was unlikely to occur even at temperatures as high as 988 K. We reexamined the site occupancies of D-atom by Rietveld refinement including extinction correction. As a result, the octahedral occupancy was increased to 0.60 and the tetrahedral occupancy was reduced to zero. The occupation of only the octahedral site for D atom is consistent with the DFT calculation, although in contrast to the previous results.
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kameo, Yutaka; Sato, Soichi; Kumagai, Yuta; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Nagai, Takayuki; Niibori, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masayuki; et al.
Introduction to Dismantling and Decommissioning Chemistry, 251 Pages, 2024/09
This book focuses on the dismantling and decommissioning of nuclear facilities and reactors that have suffered severe accidents. In Part 1, we introduce basic aspects ranging from fuel chemistry, analytical chemistry, radiation chemistry, corrosion, and decontamination chemistry to waste treatment and disposal. Then, Part 2 covers the chemistry involved in the decommissioning of various nuclear facilities, and discusses what chemical approaches are necessary and possible for the decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, how decommissioning should be carried out, and what kind of research and development and also human resource development are required for this.
 Be and
Be and  Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxes
Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxesSakurai, Hirohisa*; Kurebayashi, Yutaka*; Suzuki, Soichiro*; Horiuchi, Kazuho*; Takahashi, Yui*; Doshita, Norihiro*; Kikuchi, Satoshi*; Tokanai, Fuyuki*; Iwata, Naoyoshi*; Tajima, Yasushi*; et al.
Physical Review D, 109(10), p.102005_1 - 102005_18, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Secular variations of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are inseparably associated with the galactic activities and should reflect the environments of the local galactic magnetic field, interstellar clouds, and nearby supernova remnants. The high-energy muons produced in the atmosphere by high-energy GCRs can penetrate deep underground and generate radioisotopes in the rock. As long lived radionuclides such as  Be and
Be and  Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of
Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of  Be and
Be and  Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced
Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced  Be and
Be and  Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.127 - 135, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:144 Percentile:99.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
 states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
Fujimori, Shinichi; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Sasabe, Norimasa*; Sato, Yoshiki*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Nakamura, Ai*; Maruya, A.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Electronic Structure (Internet), 5(4), p.045009_1 - 045009_7, 2023/11
Abe, Shinichiro; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Liao, W.*; Kato, Takashi*; Asai, Hiroaki*; Shimbo, Kenichi*; Matsuyama, Hideya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kobayashi, Kazutoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 70(8, Part 1), p.1652 - 1657, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Single event upsets (SEUs) caused by neutrons is a reliability problem for microelectronic devices in the terrestrial environment. Acceleration tests using white neutron beam provide realistic soft error rates (SERs), but only a few facilities can provide white neutron beam in the world. If single-source irradiation applicable to diverse neutron source can be utilized for the evaluation of the SER in the terrestrial environment, it contributes to solve the shortage of beam time. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of the SER estimation in the terrestrial environment by any one of these measured data with the SEU cross sections obtained by PHITS simulation. It was found that the SERs estimated by our proposed method are within a factor of 2.7 of that estimated by the Weibull function. We also investigated the effect of simplification which reduce the computational cost in simulation to the SER estimation.
Entani, Shiro*; Sato, Shinichiro*; Honda, Mitsunori; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Oshima, Takeshi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 199, p.110369_1 - 110369_7, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.04(Chemistry, Physical)Ni silicide synthesis by Ni ion beam irradiation into Si attracts attention due to its advantages including the ability of formation of local structures, the controllability of ion beams, the formability of silicide without heat treatment and the high reproducibility of the resulting specimen. In this work, we investigate the local atomic structure of Si implanted with 3.0 MeV Ni ions. Analysis of Ni K-edge fluorescent-yield extended X-ray absorption fine structure reveals that Ni atoms have mixed structure of metallic-like face-centered cubic Ni and NiSi
ions. Analysis of Ni K-edge fluorescent-yield extended X-ray absorption fine structure reveals that Ni atoms have mixed structure of metallic-like face-centered cubic Ni and NiSi phases at the initial stage of the irradiation and the formation of NiSi
phases at the initial stage of the irradiation and the formation of NiSi promotes significantly with the ion fluence above 10
promotes significantly with the ion fluence above 10  ions cm
ions cm . With consideration of the agreement between the ion fluence threshold for the structural transition and the critical Si-amorphization fluence, it is concluded that the amorphization of Si plays an important role in the synthesis of the NiSi
. With consideration of the agreement between the ion fluence threshold for the structural transition and the critical Si-amorphization fluence, it is concluded that the amorphization of Si plays an important role in the synthesis of the NiSi phase in Ni
phase in Ni -irradiated Si.
-irradiated Si.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Senzaki, Tatsuya; Arai, Yoichi; Yano, Kimihiko; Sato, Daisuke; Tada, Kohei; Ogi, Hiromichi*; Kawanobe, Takayuki*; Ono, Shimpei; Nakamura, Masahiro; Kitawaki, Shinichi; et al.
JAEA-Testing 2022-001, 28 Pages, 2022/05
In preparation for the decommissioning of Laboratory B of the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratory, the nuclear fuel material that had been stored in the glove box for a long time was moved to the Chemical Processing Facility (CPF). This nuclear fuel material was stored with sealed by a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) bag in the storage. Since it was confirmed that the PVC bag swelled during storage, it seems that any gas was generated by radiolysis of the some components contained in the nuclear fuel material. In order to avoid breakage of the PVC bag and keep it safety for long time, we began the study on the stabilization treatment of the nuclear fuel material. First, in order to clarify the properties of nuclear fuel material, radioactivity analysis, component analysis, and thermal analysis were carried out. From the results of thermal analysis, the existence of organic matter was clarified. Then, ion exchange resin with similar thermal characteristics was selected and the thermal decomposition conditions were investigated. From the results of these analyzes and examinations, the conditions for thermal decomposition of the nuclear fuel material contained with organic matter was established. Performing a heat treatment of a small amount of nuclear fuel material in order to confirm the safety, after which the treatment amount was scaled up. It was confirmed by the weight change after the heat treatment that the nuclear fuel material contained with organic matter was completely decomposed.
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.33(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
Furuta, Hiroshige*; Sato, Kaoru; Nishide, Akemi*; Kudo, Shinichi*; Saigusa, Shin*
Health Physics, 121(5), p.471 - 483, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.71(Environmental Sciences)Low dose radiation induced "health effects" containing cancer risk for a Japanese radiation worker cohort is epidemiologically evaluated using the personal dose equivalent (Hp(10)). On the other hand, Hp(10) is not recommended for epidemiological evaluation of cancer risks, since the Hp(10) is widely used for radiological protection purposes. In addition, the cancer risk depends on organ doses rather than Hp(10). Thus, we developed a new method for estimating organ doses from Hp(10) of radiation workers. The developed method enables epidemiological analysis against Japanese radiation workers by considering the response characteristics of personal dosimeters, exposure geometry and energy, and body size of radiation workers in Japan. In the future, we will reconstruct organ dose conversion factor and will evaluate the risk of cancer mortality and morbidity using the organ dose in Japan.
Morishita, Kazuki; Sato, Takumi; Onishi, Takashi; Seki, Takayuki*; Sekine, Shinichi*; Okitsu, Yuichi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-024, 27 Pages, 2021/10
In the case of Plutonium (Pu)-bearing organic materials, organic materials are decomposed by alpha rays emitted mainly from Pu to generate hydrogen gas and other substances. Therefore, to safely store Pu-bearing organic materials for an extended period of time, organic materials must be eliminated. In addition, carbide and nitride fuels must be converted into oxides for safe storage in order to prevent the exothermal reaction of these fuels with oxygen/moisture in air. A survey of the literature on the stabilization treatment of Pu-bearing organic materials confirmed that organic materials can be decomposed and removed by heating at 950  C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950
C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950  C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950
C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950  C was lower than 2.1
C was lower than 2.1 10
10 Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950
Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950  C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
Ratliff, H.; Matsuda, Norihiro; Abe, Shinichiro; Miura, Takamitsu*; Furuta, Takuya; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 484, p.29 - 41, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:87.58(Instruments & Instrumentation)Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 587, p.412153_1 - 412153_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.90(Physics, Condensed Matter)The site occupancy of deuterium (D) atoms in face-centered-cubic nickel (fcc Ni) was measured along a cooling path from 1073 to 300 K at an initial pressure of 3.36 GPa via in situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms predominantly occupy the octahedral (O) sites and slightly occupy the tetrahedral (T) sites of the fcc metal lattice. The O-site occupancy increases from 0.4 to 0.85 as the temperature is lowered from 1073 to 300 K. Meanwhile, the T-site occupancy remains c.a. 0.02. The temperature-independent behavior of the T-site occupancy is unusual, and its process is not yet understood. From the linear relation between the expanded lattice volume and D content, a D-induced volume expansion of 2.09(13) 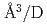 atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2
atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2 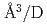 atom previously reported for Ni and Ni
atom previously reported for Ni and Ni Fe
Fe alloy.
alloy.
Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Iizuka, Riko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.9934_1 - 9934_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:19.04(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Neutron powder diffraction profiles were collected for iron deuteride (FeDx) while the temperature decreased from 1023 to 300 K for a pressure range of 4-6 GPa. The  ' deuteride with a double hexagonal close-packed (dhcp) structure, which coexisted with other stable or metastable deutrides at each temperature and pressure condition, formed solid solutions with a composition of FeD
' deuteride with a double hexagonal close-packed (dhcp) structure, which coexisted with other stable or metastable deutrides at each temperature and pressure condition, formed solid solutions with a composition of FeD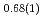 at 673 K and 6.1 GPa and FeD
at 673 K and 6.1 GPa and FeD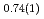 at 603 K and 4.8 GPa. Upon stepwise cooling to 300 K, the D-content x increased to a stoichiometric value of 1.0 to form monodeuteride FeD
at 603 K and 4.8 GPa. Upon stepwise cooling to 300 K, the D-content x increased to a stoichiometric value of 1.0 to form monodeuteride FeD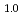 . In the dhcp FeD
. In the dhcp FeD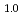 at 300 K and 4.2 GPa, dissolved D atoms fully occupied the octahedral interstitial sites, slightly displaced from the octahedral centers in the dhcp metal lattice, and the dhcp sequence of close-packed Fe planes contained hcp-stacking faults at 12%. Magnetic moments with 2.11
at 300 K and 4.2 GPa, dissolved D atoms fully occupied the octahedral interstitial sites, slightly displaced from the octahedral centers in the dhcp metal lattice, and the dhcp sequence of close-packed Fe planes contained hcp-stacking faults at 12%. Magnetic moments with 2.11  0.06 B/Fe-atom aligned ferromagnetically in parallel on the Fe planes.
0.06 B/Fe-atom aligned ferromagnetically in parallel on the Fe planes.
Higashino, Ritsuko*; Sato, Yuji*; Masuno, Shinichiro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Funada, Yoshinori*; Abe, Nobuyuki*; Tsukamoto, Masahiro*
Laser 3D Manufacturing VII (Proceedings of SPIE Vol.11271), p.1127114_1 - 1127114_7, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:94.28(Engineering, Manufacturing)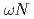 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.67(Physics, Nuclear)Abe, Shinichiro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kuroda, Junya*; Manabe, Seiya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Liao, W.*; Ito, Kojiro*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
Proceedings of IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:56.23(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Single event upsets (SEUs) caused by neutrons have been recognized as a serious reliability problem for microelectronic devices on the ground level. In our previous work, it was found that hydride placed in front of the memory chip has considerably impact on SEU cross sections because H ions generated via elastic scattering of neutrons with hydrogen atoms are only emitted in a forward direction. In this study, the effect of components neighboring transistors on neutron-induced SEUs was investigated for 65-nm bulk SRAMs by using PHITS. It was found that the shape of the SEU cross section around few MeV comes from the thickness and the position of components placed in front of transistors when that components do not contains hydrogen atoms. By considering components adjoin memory cells in the test board used in the simulation, measured data at J-PARC BL10 were reproduced well. In addition, it was found that the effect of components neighboring transistors on neutron-induced SERs does not negligible in terrestrial environment.