Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takayama, Yusuke; Sato, Daisuke*; Sugita, Yutaka
Kansai Geo-Symposium 2024; Chikasui Jiban Kankyo, Bosai, Keisoku Gijutsu Ni Kansuru Shinpojiumu Rombunshu, p.115 - 119, 2024/11
During the initial phases after closure of a high-level radioactive waste repository, the temperature of the buffer material will increase. Therefore, fundamental properties regarding the temperature dependence of bentonite, which is the main material of the buffer material, have been tested. The number of tests for the temperature dependence of displacement behavior is less than the number of tests for the temperature dependence of swelling pressure and permeability. In this paper, two tests were conducted using a consolidation test device that can control temperature conditions. One is a cyclic loading and unloading test under temperature conditions from room temperature to 80  C. The second is a temperature rise and fall test from room temperature to 80
C. The second is a temperature rise and fall test from room temperature to 80  C under stable loading condition. It was clarified that large deformations occur in the specimen under high temperature conditions, that the deformation associated with temperature changes is affected by the past stress path, and that irreversible deformation occurs under normal consolidation conditions.
C under stable loading condition. It was clarified that large deformations occur in the specimen under high temperature conditions, that the deformation associated with temperature changes is affected by the past stress path, and that irreversible deformation occurs under normal consolidation conditions.
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kameo, Yutaka; Sato, Soichi; Kumagai, Yuta; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Nagai, Takayuki; Niibori, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masayuki; et al.
Introduction to Dismantling and Decommissioning Chemistry, 251 Pages, 2024/09
This book focuses on the dismantling and decommissioning of nuclear facilities and reactors that have suffered severe accidents. In Part 1, we introduce basic aspects ranging from fuel chemistry, analytical chemistry, radiation chemistry, corrosion, and decontamination chemistry to waste treatment and disposal. Then, Part 2 covers the chemistry involved in the decommissioning of various nuclear facilities, and discusses what chemical approaches are necessary and possible for the decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, how decommissioning should be carried out, and what kind of research and development and also human resource development are required for this.
Kinase, Akari; Goto, Katsunori*; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-004, 60 Pages, 2024/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3 and stored at the waste storage facility L. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc, 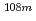 Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
 Be and
Be and  Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxes
Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxesSakurai, Hirohisa*; Kurebayashi, Yutaka*; Suzuki, Soichiro*; Horiuchi, Kazuho*; Takahashi, Yui*; Doshita, Norihiro*; Kikuchi, Satoshi*; Tokanai, Fuyuki*; Iwata, Naoyoshi*; Tajima, Yasushi*; et al.
Physical Review D, 109(10), p.102005_1 - 102005_18, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Secular variations of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are inseparably associated with the galactic activities and should reflect the environments of the local galactic magnetic field, interstellar clouds, and nearby supernova remnants. The high-energy muons produced in the atmosphere by high-energy GCRs can penetrate deep underground and generate radioisotopes in the rock. As long lived radionuclides such as  Be and
Be and  Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of
Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of  Be and
Be and  Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced
Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced  Be and
Be and  Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Watanabe, Yutaka*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(4), p.126 - 130, 2023/04
Gamma-radiolysis experiments with gas-liquid coexistent samples were carried out to investigate effects of gas-phase radiolysis on corrosive environment for materials in solutions under irradiation. After gamma-ray irradiation, hydrogen peroxide, nitrate ion, nitrite ion were detected in the liquid phase. The production yields of nitrate ion and nitrite ion increased with increasing gas-phase volume and oxygen concentration. This result indicated that chemical reactions including oxygen and nitrogen in the gas phase were required for the production of nitrate ion and nitrite ion. To magnify the effects of gas-phase radiolysis in the gas-liquid coexistent samples, absorption dose rate in the liquid phase was reduced by one-hundredth using lead shield. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide and the pH in the shielded liquid phase were similar to those in the irradiated pure water, which did not contact with gas phase. This result indicated that the effects of nitrate ion and nitrite ion dissolved in the liquid phase on water radiolysis were not important in the current experimental system, in which the effects of gas-phase radiolysis were increased by 100-times.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:213 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi; Kimura, Shun; Mochizuki, Akihito; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Takeda, Masaki; Hayano, Akira; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-013, 276 Pages, 2020/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). According to the research plan described in the 3rd Mid- and Long- term Plan of JAEA, "Near-field performance study", "Demonstration of repository design option", and "Verification of crustal-movement buffering capacity of sedimentary rocks" are important issues of the Horonobe URL Project, and schedule of future research and backfill plans of the project will be decided by the end of 2019 Fiscal Year. The present report summarizes the research and development activities of these 3 important issues carried out during 3rd Medium to Long-term Research Phase.
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Aono, Ryuji; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Testing 2019-003, 20 Pages, 2019/12
In the Radioactive Waste Management Technology Section, the radioactive liquid waste generated in the test using natural uranium in the past has been stored based on the contents of permission. Although we decided to perform solidification treatment in order to reduce the risk in storage, no rational treatment method has been established so far. Therefore, we examined adsorption treatment of natural uranium using uranium adsorbent (Tannix), and finally stabilized treatment by cement solidification. The treatment methods and findings obtained for a series of operations in waste liquid treatment are summarized in this report for reference when treating similar liquid waste.
 -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Haraga, Tomoko; Ouchi, Kazuki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Hoshino, Hitoshi*; Tanana, Rei*; Fujihara, Takashi*; Kurokawa, Hideki*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1032, p.188 - 196, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:45.84(Chemistry, Analytical)The development of safe, rapid and highly sensitive analytical methods for radioactive samples, especially actinide (An) ions, represents an important challenge. Here we propose a methodology for selecting appropriate emissive probes for An ions with very low consumption and emission of radioactivity by capillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence detection (CE-LIF), using a small chemical library of probes with eight different chelating moieties. It was found that the emissive probe, which possesses the tetradentate chelating moiety, was suitable for detecting uranyl ions. The detection limit for the uranyl-probe complex using CE-LIF combined with dynamic ternary complexation and on-capillary concentration techniques was determined to be 0.7 ppt. This method was successfully applied to real radioactive liquid samples collected from nuclear facilities.
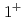 state of
state of 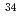 Al; Investigation on the neutron
Al; Investigation on the neutron 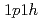 excitation across
excitation across 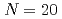 in the island of inversion
in the island of inversionXu, Z. Y.*; Heylen, H.*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Boulay, F.*; Daugas, J. M.*; de Groote, R. P.*; Gins, W.*; Kamalou, O.*; Koszor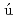 s,
s, 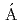 .*; Lykiardopoupou, M.*; et al.
.*; Lykiardopoupou, M.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 782, p.619 - 626, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.66(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationAono, Ryuji; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2017-025, 32 Pages, 2017/11
We have developed analytical methods for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for
Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Sato, Hisaki*; Takeuchi, Yutaka*; Kakiuchi, Kazuo*; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Nagase, Fumihisa
Proceedings of 2017 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting (WRFPM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2017/09
Since JFY2015, new Japanese national program has been initiated for the purpose of establishing the technical basis to apply ATF for the existing LWRs. SiC is one of ATF candidates material and the comprehensive applicability is being studied in the program, such as fuel rod design, core and plant design, safety evaluation for design basis accident (DBA) and severe accident (SA) as well. As one of the works in the program, the new procedure including fuel rod performance analysis during DBA was developed and the preliminary analysis was conducted. As a result, it was concluded that the typical transient and LOCA behavior between Zircaloy and SiC was not so much different.
Haraga, Tomoko; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Kameo, Yutaka; Saito, Shingo*
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (55), p.22 - 27, 2017/03
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2017/00
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Hoken Butsuri, 51(4), p.209 - 217, 2016/12
A large amount of contaminated rubbles were generated by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS). For safe decommissioning of F1NPS, it is important to evaluate the composition and concentration of radionuclides in the rubbles. In this paper, to characterize the rubbles collected at F1NPS in Unit-1, Unit-2 and Unit-3, radiochemical analysis was operated. As a result of radiochemical analysis,  -ray-emitting nuclides
-ray-emitting nuclides  Co,
Co,  Cs and
Cs and 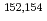 Eu,
Eu,  -ray-emitting nuclides
-ray-emitting nuclides  H,
H,  C,
C,  Sr and
Sr and  Tc, and
Tc, and  -particle-emitting nuclides
-particle-emitting nuclides 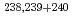 Pu,
Pu,  Am and
Am and  Cm were detected. In contrast,
Cm were detected. In contrast,  Nb and
Nb and  Eu concentrations were below the detection limit. Measured radioactive concentrations implied that
Eu concentrations were below the detection limit. Measured radioactive concentrations implied that  H,
H,  C,
C,  Co and
Co and  Sr concentrations depended on
Sr concentrations depended on  Cs concentration respectively. This analysis was characterized the radioactivity concentrations of the rubbles.
Cs concentration respectively. This analysis was characterized the radioactivity concentrations of the rubbles.
Seno, Yasuhiro*; Noguchi, Akira*; Nakayama, Masashi; Sugita, Yutaka; Suto, Shunkichi; Tanai, Kenji; Fujita, Tomoo; Sato, Haruo*
JAEA-Technology 2016-011, 20 Pages, 2016/07
Cementitious materials are expected to be used for the construction of an underground repository for the geological disposal of radioactive wastes. Ordinary Portland Cement(OPC) would conventionally be used in the fields of civil engineering and architecture, however, OPC has the potential to generate a highly alkaline plume (pH 12.5), which will likely degrade the performance of other barriers in the repository such as the bentonite buffer and/or host rock. Low alkaline cementitious materials are therefore being developed that will mitigate the generation of a highly alkaline plume. JAEA has developed a High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) as a candidate low alkaline cementitious material. The workability of the HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by conducting In-situ full scale construction tests in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. This report summarizes the results of immersion tests to assess the long-term pH behavior of hardened HFSC cement pastes made with mix designs that are expected to be able to be used in the construction of an underground repository in Japan.
12.5), which will likely degrade the performance of other barriers in the repository such as the bentonite buffer and/or host rock. Low alkaline cementitious materials are therefore being developed that will mitigate the generation of a highly alkaline plume. JAEA has developed a High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) as a candidate low alkaline cementitious material. The workability of the HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by conducting In-situ full scale construction tests in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. This report summarizes the results of immersion tests to assess the long-term pH behavior of hardened HFSC cement pastes made with mix designs that are expected to be able to be used in the construction of an underground repository in Japan.
 Li
LiIshiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Jung, H. S.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 376, p.379 - 381, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)Takahashi, Satoru*; Okuda, Yasutake*; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Aonuma, Hitoshi*; Sato, Yutaka*; Iwata, Kenji*
Journal of Signal Processing, 20(2), p.65 - 74, 2016/03