Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-007, 249 Pages, 2020/10
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting "Long-term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminants in the Environment of Fukushima" concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-002, 235 Pages, 2019/08
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (hereinafter referred to 1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, JAEA has been conducting Long-term Environmental Dynamics Research concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
 ion production and transport processes on the H
ion production and transport processes on the H ion beam intensity profile in the Cs-seeded negative ion source (Joint research)
ion beam intensity profile in the Cs-seeded negative ion source (Joint research)Takato, Naoyuki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Kato, Kyohei*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Sakamoto, Keishi
JAEA-Research 2008-031, 44 Pages, 2008/03
The origin of the H ion beam non-uniformity under the Cesium seeded condition was studied in the JAEA 10 Ampere negative ion source by measuring the profiles of the beam intensity and plasma parameters. The numerical analyses, such as the trace of particles (the electron, the H
ion beam non-uniformity under the Cesium seeded condition was studied in the JAEA 10 Ampere negative ion source by measuring the profiles of the beam intensity and plasma parameters. The numerical analyses, such as the trace of particles (the electron, the H atom and the H
atom and the H ion) trajectories using the Monte Carlo method, were also applied to consider the experimental results.
ion) trajectories using the Monte Carlo method, were also applied to consider the experimental results.
Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Seki, Masahiro; Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Norimatsu, Takayoshi*; Kamada, Yutaka; Mori, Masahiro; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Inoue, Takashi; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Genshiryoku Handobukku, p.906 - 1029, 2007/11
no abstracts in English
Tobari, Hiroyuki; Seki, Takayoshi*; Takado, Naoyuki*; Hanada, Masaya; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Sakamoto, Keishi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.022_1 - 022_4, 2007/06
no abstracts in English
Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Takado, Naoyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Fusion, 46(6), p.S318 - S323, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:68.97(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The origin of the beam non-uniformity, that is one of the key issues in large Cs-seeded negative ion sources for JT-60U and ITER, was experimentally examined by measuring correlations between the intensity of the H ion beam and plasma parameters such as an electron temperature and plasma density in the JAERI 10 A negative ion source. From the correlation between the beam intensity and the plasma parameters, it was foreseen that the beam non-uniformity was due to the localization of the plasma and/or H0 atoms caused by B x
ion beam and plasma parameters such as an electron temperature and plasma density in the JAERI 10 A negative ion source. From the correlation between the beam intensity and the plasma parameters, it was foreseen that the beam non-uniformity was due to the localization of the plasma and/or H0 atoms caused by B x 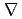 B drift of the fast electron from filaments. The filament position was modified to suppress the B x
B drift of the fast electron from filaments. The filament position was modified to suppress the B x 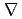 B drift, and then the spatial uniformity of the beam intensity was examined. By this modification, the root-mean-square deviation of the spatial beam intensity from the averaged value deceased to a half of that before modification while the beam intensity integrated along the longitudinal direction was kept to be constant. From this result, it was confirmed that one of the origin of the beam non-uniformity was caused by plasma localization.
B drift, and then the spatial uniformity of the beam intensity was examined. By this modification, the root-mean-square deviation of the spatial beam intensity from the averaged value deceased to a half of that before modification while the beam intensity integrated along the longitudinal direction was kept to be constant. From this result, it was confirmed that one of the origin of the beam non-uniformity was caused by plasma localization.
 ion source
ion sourceTakado, Naoyuki*; Hanatani, Junji*; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Kato, Kyohei*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi; Inoue, Takashi
Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(3), p.03A533_1 - 03A533_3, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:55.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)Surface production and transport process of H ions are numerically simulated to clarify the origin of H
ions are numerically simulated to clarify the origin of H beam non-uniformity. A three-dimensional transport code using Monte Carlo method has been applied to productions of H
beam non-uniformity. A three-dimensional transport code using Monte Carlo method has been applied to productions of H atoms and H
atoms and H ions in a large negative ion source under the Cs seeded condition. The results show that a large fraction of hydrogen atoms are produced in a high electron temperature region. This leads to a spatial non-uniformity of H
ions in a large negative ion source under the Cs seeded condition. The results show that a large fraction of hydrogen atoms are produced in a high electron temperature region. This leads to a spatial non-uniformity of H atom flux to the plasma grid where H
atom flux to the plasma grid where H atoms capture electrons and converted to H
atoms capture electrons and converted to H ions. In addition, most surface-produced H
ions. In addition, most surface-produced H ions are extracted even through the high electron temperature region without destruction.
ions are extracted even through the high electron temperature region without destruction.
Kato, Kyohei*; Takado, Naoyuki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi; Inoue, Takashi
Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(3), p.03A535_1 - 03A535_3, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:51.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)To clarify physics mechanism of plasma spatial nonuniformity observed in tandem-type negative-ion sources, primary electron-transport process has been analyzed by a three-dimensional Monte Carlo simulation code. In the model, equations of motion for electrons are numerically solved. Geometry and magnetic-field configuration of the JAEA 10 Ampere negative ion source are taken into account. Various collision processes with neutral particles are also included in the model. The simulation results show that (1) the primary electrons have been lost from the source region to the extraction region due to magnetic drift in the magnetic filter, and then (2) there is another magnetic drift near the sidewalls, where a sum of magnetic field of the filter and the cusp field for plasma confinement allows electron drift towards the extraction region. A sequence of these magnetic drifts would increase the electron temperature in local area of extraction region, which resulted in loss of negative ions.
 -ion beams for ITER neutral beam system
-ion beams for ITER neutral beam systemTaniguchi, Masaki; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Dairaku, Masayuki; Sakamoto, Keishi
Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(3), p.03A514_1 - 03A514_4, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:61.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the ITER NB systems, conventional gas insulation technology cannot be utilized because of the conductivity of the insulation gas caused by the radiation from the tokamak plasma. To overcome this problem, a vacuum insulated beam source (VIBS), where the whole beam source is immersed in vacuum, has been developed in JAERI. Recently, voltage holding capability of the VIBS was drastically improved by installing the large stress ring and these progress enables us to perform the high power operation of the VIBS accelerator. For high current density H beam acceleration, modifications were made on KAMABOKO source. At present, H
beam acceleration, modifications were made on KAMABOKO source. At present, H beam current density is 146 A/m
beam current density is 146 A/m at 836 keV (input arc power; 40 kW, operation pressure; 0.3 Pa). The acceleration of 900 keV, 0.1 A level beam was accomplished for 175 shots during the test campaign. The beam acceleration was quite stable and the degradation of the voltage holding due to the beam acceleration and/or Cs seeding was not observed.
at 836 keV (input arc power; 40 kW, operation pressure; 0.3 Pa). The acceleration of 900 keV, 0.1 A level beam was accomplished for 175 shots during the test campaign. The beam acceleration was quite stable and the degradation of the voltage holding due to the beam acceleration and/or Cs seeding was not observed.
Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Takado, Naoyuki*; Inoue, Takashi; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Dairaku, Masayuki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 77(3), p.03A515_1 - 03A515_3, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:72.78(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 ion beam in a large negative ion source
ion beam in a large negative ion sourceHanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Takado, Naoyuki*; Inoue, Takashi; Morishita, Takatoshi; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 74(1-4), p.311 - 317, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Morishita, Takatoshi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; Seki, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.790 - 795, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:57.93(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The R&D of a 1 MeV accelerator and a large negative ion source has been carried out at JAERI for the ITER NB system. The R&D is in progress at present toward: (1) 1 MeV acceleration of H ion beams at the ITER relevant current density of 200 A/m
ion beams at the ITER relevant current density of 200 A/m , and (2) improvement of uniform negative ion production over wide extraction area in large negative ion sources. Recently, H
, and (2) improvement of uniform negative ion production over wide extraction area in large negative ion sources. Recently, H ion beams of 1 MeV, 140 mA level have been generated with a substantial beam current density (100 A/m
ion beams of 1 MeV, 140 mA level have been generated with a substantial beam current density (100 A/m ). In the uniformity study, it has been clarified that electron temperature in the ion extraction region is locally high (
). In the uniformity study, it has been clarified that electron temperature in the ion extraction region is locally high ( 1 eV), which resulted in destruction of negative ions at a high reaction rate. Interception of fast electrons leaking through a transverse magnetic field called "magnetic filter" has been found effective to lower the local electron temperature, followed by an improvement of negative ion beam profile.
1 eV), which resulted in destruction of negative ions at a high reaction rate. Interception of fast electrons leaking through a transverse magnetic field called "magnetic filter" has been found effective to lower the local electron temperature, followed by an improvement of negative ion beam profile.
Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Morishita, Takatoshi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; Seki, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.790 - 795, 2005/08
The R&D of a 1 MeV accelerator and a large negative ion source have been carried out at JAERI. The paper presents following progress as a step toward ITER NB system. (1) Accelerator R&D: According to success in improvement of voltage holding capability, the acceleration test of H ions up to 1 MeV class energy is in progress. H
ions up to 1 MeV class energy is in progress. H ion beams of 1 MeV, 100 mA class have been generated with a substantial beam current density (100 A/m
ion beams of 1 MeV, 100 mA class have been generated with a substantial beam current density (100 A/m ), and the current density is still increasing by the ion source tuning. (2) Large ion source R&D: One of major causes that limited the NB injection performance was spatial unifomity of negative ion production in existing negative-ion based NB systems. The present study revealed that the negative ions produced in the extraction region of the source were locally destructed by fast electrons leaking through magnetic filter. Some countermeasures and their test results are also described.
), and the current density is still increasing by the ion source tuning. (2) Large ion source R&D: One of major causes that limited the NB injection performance was spatial unifomity of negative ion production in existing negative-ion based NB systems. The present study revealed that the negative ions produced in the extraction region of the source were locally destructed by fast electrons leaking through magnetic filter. Some countermeasures and their test results are also described.
 negative hydrogen ion beams in a 1 MeV vacuum insulated beam source
negative hydrogen ion beams in a 1 MeV vacuum insulated beam sourceTaniguchi, Masaki; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Hanada, Masaya; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Seki, Takayoshi*; Sakamoto, Keishi
AIP Conference Proceedings 763, p.168 - 175, 2005/04
The accelerator for the ITER NB system is required to produce 1 MeV, 40 A D-ion beams for 16.5 MW neutral beam injection per module. In the ITER NB system, conventional gas insulated beam source cannot be adopted because of the radiation-induced conductivity of the insulation gas. Thus a vacuum insulated beam source (VIBS), where the whole beam source is immersed in vacuum, had been developed in JAERI. Recently, voltage holding capability of the VIBS was drastically improved by installing the large stress ring, which reduces the electric field concentration at the negative side triple junction. Having improved the voltage holding capability of the VIBS, the H ion beams were extracted with seeding cesium to enhance the negative ion currents. Up to now, we had been succeeded in accelerating the H
ion beams were extracted with seeding cesium to enhance the negative ion currents. Up to now, we had been succeeded in accelerating the H beam of 102 A/m
beam of 102 A/m (140 mA) at 800 keV. The beam acceleration was quite stable and accomplished for several hundreds shots in several experimental campaigns.
(140 mA) at 800 keV. The beam acceleration was quite stable and accomplished for several hundreds shots in several experimental campaigns.
Tobari, Hiroyuki; Seki, Takayoshi; Hanada, Masaya; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Seki, Takayoshi; Hanada, Masaya; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; Takado, Naoyuki*; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tobari, Hiroyuki; Seki, Takayoshi; Hanada, Masaya; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Seki, Takayoshi; Hanada, Masaya; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Takado, Naoyuki*; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Takayoshi; Harjo, S.; Abe, Jun; Nakatani, Takeshi; Aizawa, Kazuya; Moriai, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Yasu, Yoshiji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English