Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 202, p.110461_1 - 110461_16, 2024/07
During a severe accident in a nuclear containment vessel, jets released from the primary system exhibit complex thermohydraulic behavior due to buoyancy effects and impingement on internal obstacles such as inner walls and floors. Thus, the obstacle-influenced jets are of interest in recent research activities. This paper describes an experimental investigation of the behavior of jets passing through a grid-type obstacle. The flow field was acquired by a particle image velocimetry system. The experiment captured the jet fragmentation by the grid-type obstacle and their recoupling. The mean velocity field obtained by postprocessing indicates a "Rectifying effect," with the axial velocity increasing at the center and the magnitude of the radial velocity decreasing. The meandering flow was suppressed due to this effect. In the near grid-obstacle region, the axial turbulence intensity was relatively large at the edge of each fragmented region due to shear stress. Moreover, the spatial distribution of the radial turbulence fluctuation became more complex. Further investigation is required to clarify the budget of the transport equation for turbulence fluctuation. The experimental data shown in this paper is useful for computational fluid dynamics validation.
廣瀬 意育; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏*; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 169, p.105085_1 - 105085_13, 2024/04
被引用回数:0Immersed boundary methods (IBMs) have been developed as complementary methods for computational fluid dynamics (CFD). They allow a flow simulation in a mock-up model that includes complex-shaped inner structures and/or boundaries with a non-body conformal mesh. Such a model might force us to create a complicated body-fitted mesh with a high cost in the conventional CFD (CCFD) approach. We focus on the Brinkman penalization (BP) method and its extended version, which we call here the extended Brinkman penalization method (EBP), among the different types of IBMs, aiming to apply them to the phenomena that occur during severe accidents in a nuclear reactor containment vessel and explore the possibility that the methods can partially replace the CCFD. In this paper, as a preliminary step to validate the applicability of these methods, we measure the jet flow rectified by a grating-type structure used for the validation of numerical techniques and apply them to simulate the behavior of an upward jet rectified by a horizontally placed grating-type structure modeled as an immersed body. This type of structure is generally used in reactor buildings, and it is crucial to evaluate their influence on gaseous flows because the behaviors of hydrogen produced during severe accidents may be influenced by them. The structure is selected as our subject because it has moderate complexity, enabling us to examine the effects of the IBMs and compare them with CCFD. We investigate whether these methods can reproduce a result of corresponding CCFD in which the grating is modeled as body-conformal mesh and show that the former can produce the latter with equivalent accuracy. All these results are also compared with the experimental data on the flow velocity distributions downstream of the grating measured using particle image velocimetry.
廣瀬 意育; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 168, p.105027_1 - 105027_17, 2024/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study reviewed the literature that measured critical heat flux (CHF) for downward flow in round pipes and arranged the proposed correlations. Each correlation shows relatively good prediction accuracy for experimental data from their literature, but the accuracies sometimes decrease for experimental data from other literature. No correlation accurately predicts all the experimental data of the literature, indicating an issue in extrapolating existing correlations. Therefore, we developed a correlation that can accurately predict the experimental data of the collected literature. First, we used a neural network to select the essential dimensionless quantities that comprise the correlation. Then, we regarded the prediction accuracy when all candidate dimensionless quantities extracted from the literature were used for the input variables of the network as the achievable limit prediction accuracy and searched for the minimum combination of dimensionless quantities required to achieve it. The results showed that only the dimensionless mass flux and the ratio of the heating length to the channel diameter are the essential parameters to achieve it. We developed a correlation equation using these two dimensionless quantities and achieved 17.6% of the average prediction accuracy. This result considerably improved existing correlation equations with 25%-40% average prediction accuracy for the same experimental data.
茂木 孝介; 柴本 泰照; 日引 俊詞*; 塚本 直史*; 金子 順一*
International Journal of Energy Research, 2024, p.6029412_1 - 6029412_22, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.18(Energy & Fuels)自然対流熱伝達と強制対流熱伝達が共存する流れを複合対流と呼ぶ。特に強制対流が下降流の場合をopposing flow複合対流と呼ぶ。既往研究において様々な単相opposing flow複合対流の熱伝達相関式が提案されているが、それらは様々な試験装置流路形状、作動流体、熱流動パラメータの範囲で実施された実験結果に基づいている。無次元支配因子の定義や実験的に確認された適用範囲も相関式ごとに異なるため、使用に際してその適用範囲や外挿性を踏まえた上でどの相関式を選択すべきかを整理しておくことは重要である。本稿では既存のopposing flow複合対流の熱伝達相関式と、熱水力システムコードに実装されている単相流壁面熱伝達相関式についてレビューした。また、複数の既往実験データと各相関式との比較を行い、相関式の予測性能を評価した。その結果、Jackson and Fewster相関式、Churchill相関式、Swanson and Catton (IJHMT)相関式は全ての実験データを精度よく予測可能であった。また、乱流複合対流では等温・等熱流束の熱的境界条件による熱伝達率への影響は顕著ではなく、既存の相関式は熱伝達率予測に適用可能であった。さらに、代表長さに水力学相当直径を用いることにより試験装置流路形状の違いに関わらず相関式が適用可能であり、支配パラメータの無次元化により作動流体によらず相関式が適用可能であることを確認した。幅広い無次元数範囲に対して相関式の外挿性を調査した所、Jackson and Fewster相関式、Churchill相関式、Aicher and Martin相関式は自然対流熱伝達、強制対流熱伝達への優れた外挿性を有しており、実験で妥当性が確認されたパラメータ範囲を超えて相関式が適用できることを示した。
相馬 秀; 石垣 将宏*; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 416, p.112754_1 - 112754_18, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The wall function (WF) enables analyzing condensation flow in a nuclear reactor containment vessel with reasonable computational costs. However, conventional wall treatments rely on the logarithmic laws for velocity, temperature, and concentration, limiting applicability. In this paper, we applied the analytical wall function approach to the condensation flow analysis of steam/air mixtures. This approach features the analytical integration of transport equations considering the buoyancy, the material property change, and the convective terms. We conducted CFD analysis with the analytical wall function models for the forced, mixed, and natural convection and confirmed good prediction, especially when the log law does not hold.
相馬 秀; 石垣 将宏*; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 10 Pages, 2024/00
When analyzing containment thermal-hydraulics, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool because multi-dimensional and local analysis is required for some accident scenarios. According to the previous study, neglecting steam bulk condensation in the CFD analysis leads to a significant error in boundary layer profiles. Validating the condensation model requires the experimental data near the condensing surface, however, available boundary layer data is quite limited. It is also important to confirm whether the heat and mass transfer analogy (HMTA) is still valid in the presence of bulk condensation. In this study, the boundary layer measurements on the vertical condensing surface in the presence of air were performed with the rectangular channel facility WINCS, which was designed to measure the velocity, temperature, and concentration boundary layers. We set the laminar flow condition and varied the Richardson number (1.0-23) and the steam volume fraction (0.35-0.57). The experimental results were used to validate CFD analysis and HMTA models. For the former, we implemented a bulk condensation model assuming local thermal equilibrium into the CFD code and confirmed its validity. For the latter, we validated the HMTA-based correlations, confirming that the mixed convection correlation reasonably predicted the sum of wall and bulk condensation rates.
岡垣 百合亜; 柴本 泰照; 和田 裕貴; 安部 諭; 日引 俊詞*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.955 - 968, 2023/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pool scrubbing is an important filtering process that prevents radioactive aerosols from entering the environment in the event of severe accidents in a nuclear reactor. In this process of transporting aerosol particles using bubbles, bubble hydrodynamics plays a crucial role in modeling pool scrubbing and significantly affects particle removal in a bubble. The pool scrubbing code based on Lumped Parameter (LP) approach includes the particle removal model, and its hydrodynamic parameters are determined based on simple assumptions. We aim to apply the three-dimensional Computer Fluid Dynamics (CFD) approach to understand the detailed bubble interaction. This study validated the applicability of the CFD simulation to bubble hydrodynamics at the flow transition from a globule to a swarm region, which is critical in the stand-alone pool scrubbing code-SPARC-90. Two types of solvers based on the Volume Of Fluid (VOF) and the Simple Coupled Volume Of Fluid with Level Set (S-CLSVOF) methods were used to capture the gas-liquid interface in the CFD simulation. We used the experimental data for validation. As a result, the VOF and S-CLSVOF methods accurately predicted the bubble size and void fraction distributions. In addition, we confirmed that the bubble rise velocity of the S-CLSVOF method almost agreed with the experimental results.
茂木 孝介; 柴本 泰照; 久木田 豊
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109679_1 - 109679_10, 2023/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Inertial deposition of small (less than a few  m in diameter) aerosol particles in mm-scale bubbles is an old but unsettled issue in modeling of pool scrubbing phenomenon. Whereas existing practical models give no specific consideration to the bubble-internal transport, some studies have shown that inertial transport affects considerably the particle deposition rate. We show, on the basis of Lagrangian simulations of particles advected by steady internal circulation in a spherical bubble, that particle centrifugal velocity becomes scale invariant for low- Stokes numbers (St
m in diameter) aerosol particles in mm-scale bubbles is an old but unsettled issue in modeling of pool scrubbing phenomenon. Whereas existing practical models give no specific consideration to the bubble-internal transport, some studies have shown that inertial transport affects considerably the particle deposition rate. We show, on the basis of Lagrangian simulations of particles advected by steady internal circulation in a spherical bubble, that particle centrifugal velocity becomes scale invariant for low- Stokes numbers (St 
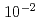 ) when the characteristic timescale is chosen to be that for transversal particle motion at the Stokes terminal velocity corresponding to the local fluid acceleration. Because a scaling law can be derived by running simulations with a small number of particles, it can provide a practical tool for considering the influence of inertial particle transport within the bubble on the decontamination factor.
) when the characteristic timescale is chosen to be that for transversal particle motion at the Stokes terminal velocity corresponding to the local fluid acceleration. Because a scaling law can be derived by running simulations with a small number of particles, it can provide a practical tool for considering the influence of inertial particle transport within the bubble on the decontamination factor.
安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(5), p.1742 - 1756, 2023/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The hydrogen behavior in a nuclear containment vessel is a significant issue when discussing the potential of hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. After the Fukushima-Daiichi accident in Japan, we have investigated in-depth the hydrogen transport mechanisms by utilizing experimental and numerical approaches. Computational fluid dynamics is a powerful tool for better understanding the transport behavior of gas mixtures, including hydrogen. This paper describes a large-eddy simulation of gas mixing driven by a high-buoyancy flow. We focused on the interaction behavior of heat and mass transfers driven by the horizontal high-buoyant flow during density stratification. For validation, the experimental data of the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility were used. With a high-power heater for the gas-injection line in the CIGMA facility, a high temperature flow of approximately 390 C was injected into the test vessel. By using the CIGMA facility, we can extend the experimental data to the high temperature region. The phenomenological discussion in this paper help understand the heat and mass transfer induced by the high-buoyancy flow in the containment vessel during a severe accident.
C was injected into the test vessel. By using the CIGMA facility, we can extend the experimental data to the high temperature region. The phenomenological discussion in this paper help understand the heat and mass transfer induced by the high-buoyancy flow in the containment vessel during a severe accident.
Hamdani, A.; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104415_1 - 104415_16, 2022/11
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis and validation works from the previous experimental study on the natural convection driven by outer surface cooling in the presence of density stratification consisting of air and helium (as a mimic gas of hydrogen). The experiment was conducted in the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The numerical simulation was carried out to analyze the detailed effect of the cooling region on the erosion of the helium stratification layer. The temporal and spatial evolution of the helium concentration and the gas temperature inside the containment vessel was predicted and validated against the experimental data. In addition, two stratification behaviors that depend on the cooling location were presented and discussed. The CFD simulation confirmed that an upper head cooling caused two counter-rotating vortexes in the helium-rich zone. Meanwhile, the upper half body cooling caused two counter-rotating vortexes in the helium-poor zone. These findings are important to understand the mechanism of the density stratification process driven by natural convection in the containment vessel.
茂木 孝介; 柴本 泰照; 久木田 豊
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.1037 - 1046, 2022/08
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lagrangian particle tracking simulations are performed on aerosol particle removal from a spherical bubble rising in a water pool. The bubble internal circulation is assumed to be given by the Hill's vortex stream function. Monodispersed particles in the 0.1-1.0 um radius range are simulated. The results are discussed with a focus on the development of particle concentration profile and its influence on removal rates, with the aid of comparisons with Eulerian models including the lumped-parameter model by Fuchs. The results are discussed with a focus on the development of particle concentration profile and its influence on removal rates, with the aid of comparisons with Eulerian models including the lumped-parameter model by Fuchs. It is shown that a quick growth of bubble-surface diffusion layer causes a transition of dominant removal mechanisms from unsteady Brownian diffusion to inertial migration. Fuchs's model, not designed to consider such transition, overpredicts the removal rates for small particles. It is also shown that inertial migration produces a surface-peaked concentration profile in the bubble, resulting in higher removal rates than predicted by Fuchs's lumped-parameter model.
廣瀬 意育; 久木田 豊; 柴本 泰照; 佐川 淳*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2022/03
Electric impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-invasive and radiation-free imaging method applicable to gas/liquid two-phase flow measurements. It determines the electrical resistivity distribution of an object from measurements of boundary potentials in response to current injection. Due to the severely ill posed nature of the problem, the quality of reconstructed image depends much on the quality and amount of information available from potential measurements. We have proposed a DC pulse-driven EIT system design equipped with countermeasures for the influences of electrode polarization on potential measurements (Hirose et al., in preparation). The usefulness of EIT in two-phase flow measurement is however restricted by the intrinsically limited spatial resolution. Due to the diffusive nature of electricity, the spatial resolution degrades quickly with the distance from the boundary. In this study, we attempt to improve the spatial resolution by adding thin electrodes inserted into the flow field away from the boundary. Although this means that non-invasiveness is traded off, the influence of invasive electrodes on flow field could be estimated and limited on the basis of experiences gained with other intrusive methods, e.g., needle probes for measurement of interfacial area. The benefit taken by the addition of invasive electrodes, on the other hand, would depend on two-phase flow regime and other flow parameters. In the present paper we consider dispersed bubbly flow and simulate the bubbles with thin cylindrical insulators. The results obtained with and without invasive electrodes are compared to discuss the effectiveness and limitations in measurement of two-phase flow.
相馬 秀; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照; 石垣 将宏*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/03
The experimental data of boundary layer profiles are necessary to validate condensation models applied in numerical simulation of CFD codes and also to develop wall treatment models for heat and mass transfer in the presence of significant buoyancy and suction. The available data for velocity, temperature, and concentration boundary layer, however, is quite limited. In this study, we present experimental results of measuring boundary layer profiles by our experimental facility WINCS (WINd tunnel for Condensation of Steam and air mixture). WINCS is a once-through type of wind tunnel having a 1.5m-long measuring part of rectangular duct. The velocity and temperature profiles were obtained with laser doppler velocimetry and thermocouple, respectively. The temperature data was then used to calculate the steam concentration boundary layer by assuming local thermodynamic equilibrium. The laminar boundary layer profiles were obtained in the present condition. The dropwise condensation and fimwise condensation are available in this apparatus. We also conducted numerical simulations with CFD codes and compared the experimental and numerical results of boundary layer profiles and heat fluxes. The wall condensation model based on Stefan flow and bulk condensation model were used in the numerical analysis. The comparison, in general, shows good agreement between the experimental and numerical results.
安部 諭; 小尾 善男*; 佐藤 聡; 岡垣 百合亜; 柴本 泰照
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/03
A modeling of heat transfers with boiling transition (BT) and that after the occurrence of BT, called post-BT, is one of the key technical issues to estimate the duration of surface dryout and the peak cladding temperature during DBA (Design Basis Accident) and BDBA (Beyond Design Basis Accident) in light water reactors. Recently, CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) has emerged as a powerful tool for representing the heat transfer mechanism. Our main purpose is to obtain in-depth physical insight into the BT and post-BT phenomena by combining experiment and CFD simulation research. This paper introduces our developing activity for an integrated three-field two-fluid CFD methodology based on the Eulerian-Eulerian approach toward the accurate prediction of the dryout behavior from annular-mist to mist flow regimes. We implemented following interaction terms and functions into OpenFOAM ver.7, an opensource code developed by OpenFOAM foundation, as (1) Interaction terms between liquid film and droplets due to deposition and entrainment, (2) Interaction terms on the liquid interface between the liquid film and the gas phase on friction and heat conduction, (3) Heat transfer from the heated wall to the liquid film, (4) Dryout occurrence judgement and the switching function on the boundary condition. The dryout occurrence judgment is based on a correlation on critical film thickness, which is originally applied into the MARS (Multi-dimensional Analysis of Reactor Safety) code. A trial calculation with the developed solver called two Phase Three Field Euler Foam was performed to check the solver operation. The CFD could simulate temperature increase behavior due to the dryout occurrence, whereas here were still challenges in reproducing the transition from mist flow to single-phase vapor flow.
安部 諭; Hamdani, A.; 石垣 将宏*; 柴本 泰照
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 166, p.108791_1 - 108791_18, 2022/02
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes an experimental investigation of natural convection driven by outer surface cooling in the presence of density stratification consisting of an air-helium gas mixture (as mimic gas of hydrogen) in an enclosed vessel. The unique cooling system of the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (whose test vessel is a cylinder with 2.5-m diameter and 11-m height) is used, and findings reveal that the cooling location relative to the stratification plays an important role in determining the interaction behavior of the heat and mass transfer in the enclosed vessel. When the cooling region is narrower than the stratification thickness, the density-stratified region expands to the lower part while decreasing in concentration (stratification dissolution). When the cooling region is wider than the stratification thickness, the stratification is gradually eroded from the bottom with decreasing layer thickness (stratification breakup). This knowledge is useful for understanding the interaction behavior of heat and mass transfer during severe accidents in nuclear power plants.
廣瀬 意育; 佐川 淳*; 柴本 泰照; 久木田 豊
Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 81, p.102006_1 - 102006_9, 2021/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:10.51(Engineering, Mechanical)An electrical impedance tomography (EIT) system design is proposed for imaging of phase distribution in gas-water two-phase flow from boundary measurement of electrical potentials in response to direct current (DC) injection. DC injection simplifies substantially the system design, but introduces problems due to polarization of injection electrodes. Electrode polarization means charge accumulation on the electrode-water interface causing a drift in the interfacial potential difference. The polarization problems are coped with by using dedicated electrodes for injection and potential measurement, and using a current source unaffected by the polarization of current-carrying electrodes (CCEs). Furthermore, the polarization of CCEs is controlled, to lessen the possible influence on the sensing electrodes (SEs), by using a short (milliseconds in width) pulse for injection with a charge balanced injection strategy. The impact of electrode polarization and the effectiveness of countermeasures introduced in the present design are discussed through comparisons of measured boundary potentials and of images reconstructed for a simple object simulating large bubbles in water.
安部 諭; 岡垣 百合亜; 佐藤 聡; 柴本 泰照
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 159, p.108321_1 - 108321_12, 2021/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:45.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Heat transfer in the rod bundle is augmented by the mixing vanes on the spacer grid. We conducted a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation with three isotropic turbulence models - standard  -epsilon, realizable
-epsilon, realizable  -epsilon, and SST
-epsilon, and SST  -omega models - to investigate the relationship between heat transfer and turbulence behaviors downstream a simulant spacer (with four vanes) in a single tube under single-phase flow conditions. Quantitatively, the predicted heat transfer coefficient (HTC), secondary flow intensity, and turbulence intensity with the SST
-omega models - to investigate the relationship between heat transfer and turbulence behaviors downstream a simulant spacer (with four vanes) in a single tube under single-phase flow conditions. Quantitatively, the predicted heat transfer coefficient (HTC), secondary flow intensity, and turbulence intensity with the SST  -omega model displayed a better agreement (than the other isotropic models) with the correlation based on previous studies. Furthermore, the turbulence production was localized in the near-spacer region (z/D
-omega model displayed a better agreement (than the other isotropic models) with the correlation based on previous studies. Furthermore, the turbulence production was localized in the near-spacer region (z/D  10, where D is the inner diameter), which corresponds with the HTC argumentation region. These results indicate that examining the turbulence production when discussing the HTC augmentation downstream the spacer is essential.
10, where D is the inner diameter), which corresponds with the HTC argumentation region. These results indicate that examining the turbulence production when discussing the HTC augmentation downstream the spacer is essential.
孫 昊旻; 柴本 泰照; 廣瀬 意育; 久木田 豊
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(9), p.1048 - 1057, 2021/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)以前のわれわれのプールスクラビング実験において、入口粒子数密度の上昇に伴って除染係数(DF)が減少する結果が得られており、その理由については過去の研究を含めて明らかにされていなかった。本研究では、現象の要因を粒子表面での水蒸気の凝縮による粒子成長であると仮定し、上昇気泡内の質量とエネルギーのバランスに基づく簡易評価モデルを構築し、同モデルを用いて評価した。粒子表面での水蒸気凝縮は、凝縮による気泡内の水蒸気濃度を低下させると同時に、凝縮潜熱放出による温度上昇効果をもたらし、気泡内蒸気過飽和度を減少させ、凝縮を抑制する。本効果は粒子数濃度に依存する。評価モデルでは、気泡の上昇距離の関数として粒子の成長と慣性DFを計算し、その結果、実験で観察されたDFの傾向を再現した。
竹田 武司; 和田 裕貴; 柴本 泰照
World Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 11(1), p.17 - 42, 2021/01
Many experiments have been conducted on accidents and transients of pressurized water reactor (PWR) employing the rig of safety assessment/large-scale test facility (ROSA/LSTF). Major results of the related integral effect tests with the LSTF were reviewed to experimentally identify thermal-hydraulic phenomena involved, regarding the PWR accident sequences in accordance with the new regulatory requirements for the Japanese light-water nuclear power plants. Key results of the recent integral effect tests utilizing the LSTF and future plans were presented relevant to multiple steam generator tube rupture accident with recovery operation, small-break loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) with accident management measure on core exit temperature reliability, and small-break LOCA with thermal stratification under cold water injection from emergency core cooling system into cold legs.
安部 諭; Studer, E.*; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 368, p.110785_1 - 110785_14, 2020/11
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:75.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)The hydrogen behavior in a nuclear containment vessel is one of the significant issues raised when discussing the potential of hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool for better understanding the turbulence transport behavior of a gas mixture, including hydrogen. Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) is a practical-use approach for simulating the averaged gaseous behavior in a large and complicated geometry, such as a nuclear containment vessel; however, some improvements are required. We implemented the dynamic modeling for  based on the previous studies into the OpenFOAM ver 2.3.1 package. The experimental data obtained by using a small scale test apparatus at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was used to validate the RANS methodology. Moreover, Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) was performed to phenomenologically discuss the interaction behavior. The comparison study indicated that the turbulence production ratio by shear stress and buoyancy force predicted by the RANS with the dynamic modeling for
based on the previous studies into the OpenFOAM ver 2.3.1 package. The experimental data obtained by using a small scale test apparatus at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was used to validate the RANS methodology. Moreover, Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) was performed to phenomenologically discuss the interaction behavior. The comparison study indicated that the turbulence production ratio by shear stress and buoyancy force predicted by the RANS with the dynamic modeling for  was a better agreement with the LES result, and the gradual decay of the turbulence fluctuation in the stratification was predicted accurately. The time transient of the helium molar fraction in the case with the dynamic modeling was very closed to the VIMES experimental data. The improvement on the RANS accuracy was produced by the accurate prediction of the turbulent mixing region, which was explained with the turbulent helium mass flux in the interaction region. Moreover, the parametric study on the jet velocity indicates the good performance of the RANS with the dynamic modeling for
was a better agreement with the LES result, and the gradual decay of the turbulence fluctuation in the stratification was predicted accurately. The time transient of the helium molar fraction in the case with the dynamic modeling was very closed to the VIMES experimental data. The improvement on the RANS accuracy was produced by the accurate prediction of the turbulent mixing region, which was explained with the turbulent helium mass flux in the interaction region. Moreover, the parametric study on the jet velocity indicates the good performance of the RANS with the dynamic modeling for  on the slower erosive process. This study concludes that the dynamic modeling for
on the slower erosive process. This study concludes that the dynamic modeling for  is a useful and practical approach to improve the prediction accuracy.
is a useful and practical approach to improve the prediction accuracy.