Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanigawa, Masafumi; Nakamura, Daishi; Asakawa, Naoya*; Seya, Kazuhito*; Omori, Fumio*; Koiso, Katsuya*; Horigome, Kazushi; Shimizu, Yasuyuki
JAEA-Technology 2024-001, 37 Pages, 2024/05
At plutonium conversion development facility, the neutralization sedimentation and the coagulation sedimentation (sludge) items are stored in a polyethylene container packed in the plastic bag. The neutralization sedimentation items and the coagulation sedimentation items are stored in the globe box and storage room in the facility, respectively. Some sludge items generate gases, that swelled the plastic bag. We should ensure whether the bag swelling by visual confirmation. When the swelling is confirmed, those containers are transferred to the glove box to exchange the plastic bag for new one. By keeping the above procedure, those items were stored safely in the facility since its founding. The stabilization work for enhance the safe storage was planned to reduce the gas generation of the sludge items caused by the radiolysis of water. Those sludge items have the containing a sodium nitrate that has moisture-absorption characteristic. Therefore, the stabilization method aimed to remove the sodium nitrate from the items. The work was conducted from August 2018 to August 2022. The sodium concentration in items were reduced to 3 wt% or lower. Each stabilized sludge item packed in plastic bag were confirmed its swelling for over one year in the storage place. No gas generation from all item has been observed for more than the one year. And while both the neutralization and the coagulation sedimentation items were stored they were not the increasing of the moisture in the items. As a result, those items were evaluated that will not generate gases any more and confirmed to be stabilized after this treatment. Then, those neutralization sedimentation items were stored in powder cans and transferred to powder storage room as a retained waste. Based on the above results, risks of the gas generation from sludge items were decreased enough. Therefore, the safety of the stored sludge item was improved and confirmed.
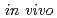 dosimetry system based on an optical fiber-coupled microsized photostimulable phosphor for stereotactic body radiation therapy
dosimetry system based on an optical fiber-coupled microsized photostimulable phosphor for stereotactic body radiation therapyYada, Ryuichi*; Maenaka, Kazusuke*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Okada, Go*; Sasakura, Aki*; Ashida, Motoi*; Adachi, Masashi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Wang, T.*; Akasaka, Hiroaki*; et al.
Medical Physics, 47(10), p.5235 - 5249, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:50.72(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)The 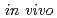 dosimeter system is capable of real-time, accurate, and precise measurement under stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) conditions. The probe is smaller than a conventional dosimeter, has excellent spatial resolution, and can be valuable in SBRT with a steep dose distribution over a small field. The developed PSP dosimeter system appears to be suitable for in vivo SBRT dosimetry.
dosimeter system is capable of real-time, accurate, and precise measurement under stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) conditions. The probe is smaller than a conventional dosimeter, has excellent spatial resolution, and can be valuable in SBRT with a steep dose distribution over a small field. The developed PSP dosimeter system appears to be suitable for in vivo SBRT dosimetry.
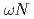 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:37.19(Physics, Nuclear)Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:98.57(Quantum Science & Technology)Uchiyama, Yusuke*; Azuma, Kohei*; Odani, Sachika*; Iwasaki, Toshiki*; Tsumune, Daisuke*; Kamidaira, Yuki; Shimizu, Yasuyuki*; Onda, Yuichi*
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, B2 (Kaigan Kogaku) (Internet), 73(2), p.I_685 - I_690, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Makino, Risa; Mukai, Yasunobu; Ishiyama, Koichi; Kurita, Tsutomu; Nakamura, Hironobu
Dai-37-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/02
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hironobu; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Makino, Risa; Mukai, Yasunobu; Ishiyama, Koichi; Kurita, Tsutomu; Ikeda, Atsushi*; Yamaguchi, Katsuhiro*
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
Regarding the Integrated Safeguards (IS) in Japan, the implementation of IS has been started on September 2004, and the concept has been introduced to the JNC-1 facilities since August 2008. Then, random interim inspection with short notice and reducing person-days of inspection (PDI) was introduced instead of traditional scheduled IIV in order to improve deterrence of the nuclear material diversion with timeliness goal. And it was agreed that it should be evaluated and reviewed because RII was designed when inter-campaign. In JAEA, we decided to restart PCDF campaign to reduce potential safety risks of reprocessing facilities. To adopt the RII scheme to the process operation in campaign, JAEA proposed a new scheme to JSGO and IAEA without increasing PDI and reducing detection probability. As a result of the discussion, it was agreed and successfully introduced since March 2014. The new scheme for PCDF consists of scheduled inspection (fixed-day RII), reduction of estimated material for the verification, implementation of remote monitoring with data provision, improvement of operational status check list, introduction of NRTA and MC&A data declaration with timeliness. Though the operator's workloads for information provision were increased, we could manage to balance IS requirement with implementation of our operation successfully. This contribution was helped to safeguards implementation and our operation for 2 years.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Mukai, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Nakamura, Hironobu; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its long-term research and development plan, development of a real-time measurement technology to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously as part of an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities. In the reprocessing plant, since solutions containing both Pu and FP exist, a new detector development project to monitor Pu with FP is being carried out from 2015 to 2017. This project is mainly conducted in the High Active Liquid Waste Storage (HALWS) in Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP). In this paper, an overview of the technology development, simulation results of preliminary evaluation of the characteristics of radiation emitted from the HALW tank at TRP, and the future research plan are presented.
Makino, Risa; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Suzuki, Hisanori; Ikeda, Atsushi*; Menlove, H. O.*; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Nakamura, Hironobu
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/01
The Inventory Verification Sample system (INVS) is a non-destructive assay system for samples to quantify the Pu amount in Pu nitrate solutions and MOX with 31.3% of counting efficiency. It has been used for IAEA verification measurement for many years at the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility for the samples taken at the timing of PIV etc. as a partial defects verification system (uncertainty: about 3-5%). If the measurement uncertainty can be improved (to  1%), it is expected that the usage can be extended to the operator's own measurements in MC&A to reduce the number of destructive analyses. In order to improve the measurement uncertainty for solution samples, after optimization of detector parameter and sample position, we conducted 3 different types of calibration method that is passive calibration curve, known-
1%), it is expected that the usage can be extended to the operator's own measurements in MC&A to reduce the number of destructive analyses. In order to improve the measurement uncertainty for solution samples, after optimization of detector parameter and sample position, we conducted 3 different types of calibration method that is passive calibration curve, known- and multiplicity method to achieve the target uncertainty. To perform calibration and control the measurement quality, MOX fuel pellets with known Pu amount are fabricated and used. In the range of concentration of typical solution samples, we could confirm good correlations between measured doubles and
and multiplicity method to achieve the target uncertainty. To perform calibration and control the measurement quality, MOX fuel pellets with known Pu amount are fabricated and used. In the range of concentration of typical solution samples, we could confirm good correlations between measured doubles and  Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, it was confirmed that the conventional calibration curve method could meet our target uncertainty (
Pu effective mass in the three methods. Especially, it was confirmed that the conventional calibration curve method could meet our target uncertainty ( 1%).
1%).
Kimura, Takashi; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Yamazaki, Katsuyuki; Endo, Yuji; Nakamura, Hironobu
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2013/10
no abstracts in English
 spp. under the ISS environmental conditions for performing exposure experiments of microbes in the Tanpopo mission
spp. under the ISS environmental conditions for performing exposure experiments of microbes in the Tanpopo missionKawaguchi, Yuko*; Yang, Y.*; Kawashiri, Narutoshi*; Shiraishi, Keisuke*; Takasu, Masako*; Narumi, Issey*; Sato, Katsuya; Hashimoto, Hirofumi*; Nakagawa, Kazumichi*; Tanigawa, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Origins of Life and Evolution of Biospheres, 43(4-5), p.411 - 428, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:79.51(Biology)Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Yamazaki, Katsuyuki; Kimura, Takashi; Endo, Yuji; Nakamura, Hironobu
Proceedings of INMM 54th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2013/07
Japanese regulation of reprocessing safety and security was revised in March 2012, and almost all requirements except for nuclear material accountancy and control described in the INFCIRC225/rev.5 are included into the regulation. We have many things to do to meet the requirements within 2 years pursuant to the regulation. Separately from the revised regulation, we think that utilizing the process monitoring data not only for the safety control but also for the nuclear material security would be useful in establishing more effective and efficient nuclear material security. Since we observe the process monitoring data to confirm the operational condition including unusual change for the safety purpose, it is though that the various alarm information through the process monitoring data help to detect the risk of sabotage and unauthorized removal. As future challenge, we would like to establish a possible method of utilizing the process monitoring data in combination with the physical protection to make it possible to give more effective and efficient nuclear material security.
Dobashi, Kunio*; Shimizu, Yasuo*; Matsuzaki, Shinichi*; Nagamine, Takeaki*; Sato, Takahiro; Okubo, Takeru; Yokoyama, Akihito; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Arakawa, Kazuo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 87, 2012/01
Matsuzaki, Shinichi*; Shimizu, Yasuo*; Dobashi, Kunio*; Nagamine, Takeaki*; Sato, Takahiro; Okubo, Takeru; Yokoyama, Akihito; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Arakawa, Kazuo*; et al.
International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology, 23(1), p.1 - 11, 2010/01
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:67.98(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Chujo, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
 -forbidden transitions in
-forbidden transitions in 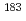 Os
OsShizuma, Toshiyuki; Matsuura, Katsuyuki*; Toh, Yosuke; Hayakawa, Takehito; Oshima, Masumi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Matsuda, Makoto; Furuno, Kohei*; Sasaki, Yasuyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 696(3-4), p.337 - 370, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:73.35(Physics, Nuclear)High-spin states in 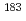 Os have been studied using the 170Er(18O,5n) reaction at a beam energy of 85 MeV. Nine rotational bands based on 1-, 3-, 5- and 7-quasiparticle excitations have been observed. Nilsson configurations are assigned for the newly observed bands using g-factors deduced from M1/E2 branching ratios within the bands. In addition, two isomers with K=(43/2+) and (43/2-) have been identified. The K=(43/2+) isomer decays directly to the K=9/2+ ground state band with a large difference in the
Os have been studied using the 170Er(18O,5n) reaction at a beam energy of 85 MeV. Nine rotational bands based on 1-, 3-, 5- and 7-quasiparticle excitations have been observed. Nilsson configurations are assigned for the newly observed bands using g-factors deduced from M1/E2 branching ratios within the bands. In addition, two isomers with K=(43/2+) and (43/2-) have been identified. The K=(43/2+) isomer decays directly to the K=9/2+ ground state band with a large difference in the  quantum number,
quantum number, 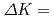 17. The decay rates are disccused in terms of a tunneling model where high-
17. The decay rates are disccused in terms of a tunneling model where high- (isomeric) and low-
(isomeric) and low- states interact via fluctuations towards triaxial nuclear shapes.
states interact via fluctuations towards triaxial nuclear shapes.
Kato, Akane; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Kitao, Takahiko; Nakamura, Hironobu
no journal, ,
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) had reprocessed 1,140 tons spent fuel (SF) since 1977 to 2007, and the Post-Fukushima safety regulations triggered TRP to decide to shut the plant and shifted to decommissioning phase from 2018. The estimated entire duration of TRP decommissioning is expected to be 70 years. The early stage of the TRP decommissioning includes the recovery of remaining nuclear material in the process and transferring those nuclear material between multiple facilities ("Flush-out"), vitrification activity of remaining high active liquid waste and transferring collected nuclear material to the storage facility, and the management of radioactive waste. The Flush-out is as the first step of TRP decommissioning and it is in progress since July 2022 for two years prior to the start of serious decommissioning activities such as the decontamination, dismantling/removing the process. Since these decommissioning activities are unexperienced challenges and they are not related to "SF reprocessing", therefore ensuring appropriate nuclear material control and accountancy (MC&A) and the transparency in terms of safeguards verification implemented by IAEA are important role as the operator. In this paper, we report about the residual nuclear material recovery process and relevant MC&A and safeguards measures in the Flush-out as the first stage of TRP decommissioning project.
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Yang, Y.*; Kawashiri, Narutoshi*; Shiraishi, Keisuke*; Shimizu, Yasuyuki*; Takahashi, Yuta*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English