Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 169, p.112580_1 - 112580_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by  and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt
and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt . Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt
. Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt , the nuclear fusion, d +t
, the nuclear fusion, d +t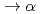 + n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion (
+ n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). Recently, the interest on
CF). Recently, the interest on  CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of
CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of  CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.80(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Torii, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; Kanda, Sotaro*; Kawagoe, Kiyotomo*; Kawall, D.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kurosawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Physical Review A, 104(2), p.L020801_1 - L020801_6, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:83.44(Optics) X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:76.09(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Tobita, Minoru*; Haraga, Tomoko; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Seki, Kotaro*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Kochiyama, Mami; Shimomura, Yusuke; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-016, 72 Pages, 2020/02
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 25 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Mo,
Mo,  Tc,
Tc, 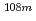 Ag,
Ag,  Sn,
Sn,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Haraga, Tomoko; Shimomura, Yusuke; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-004, 48 Pages, 2019/10
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:98.61(Quantum Science & Technology)Ueno, Yasuhiro*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.14_1 - 14_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:87.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Okafuji, Takashi*; Miura, Kazuhiro*; Sago, Hiromi*; Murakami, Hisatomo*; Kubo, Koji*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Wakai, Takashi; Shimomura, Kenta
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2017 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.591 - 595, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Haraga, Tomoko; Tobita, Minoru*; Takahashi, Shigemi*; Seki, Kotaro*; Izumo, Sari; Shimomura, Yusuke; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-017, 53 Pages, 2017/02
Fugen Nuclear Power Station was shut down and now is under decommissioning. Many radioactivity concentration data of dismantled materials have to be accumulated to calculate the scaling factors of radioactive wastes and to verify that the cleared dismantled materials conform to the clearance levels. A simple and rapid radioactivity determination method for radioactive waste samples was developed by Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management. For its demonstration, the simple and rapid radioactivity determination method was applied to metal samples, which were taken from dismantled pipes in contact with heavy water or carbon dioxide gas of Fugen. This report summarizes the radioactivity data obtained from the analysis of those samples.
Strasser, P.*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 237(1), p.124_1 - 124_9, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:89.35(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical) X-ray diffraction
X-ray diffractionShimomura, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sasaki, Takuo; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Oshita, Yoshio*; Kamiya, Itaru*
Journal of Applied Physics, 118(18), p.185303_1 - 185303_7, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:35.42(Physics, Applied)Shimomura, Kenta; Kato, Shoichi; Wakai, Takashi; Ando, Masanori; Hirose, Yuichi*; Sato, Kenichiro*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2015/05
This paper describes experimental and analytical works to confirm that the design standard for SFR components sufficiently covers possible failure mechanisms. Creep-fatigue damage evaluation method in JSME design standard for SFR components has been constructed based on experiments and/or numerical analyses of conventional austenitic stainless steels, such as 304SS. Since the material characteristics of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel are substantially different from those of austenitic stainless steels, it is required to verify the applicability of the design standards to the SFR components made of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. A series of uni-axial creep-fatigue tests were conducted using double-ended notch bar specimens made of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel under displacement controlled condition with 30 minute holding. The curvature radii of the specimens were 1.6mm, 11.2mm and 40.0mm. The specimen having 1.6mm notch and 11.2mm notch failed from outer surface but the specimen having 40.0mm notch showed obvious internal crack nucleation. In addition, though total duration time of the creep-fatigue test was only 2,000 hours, a lot of creep voids and inter granular crack growth were observed. To clarify the cause of such peculiar failure, some additional experiments were performed, as well as some numerical analyses. We could point out that such a peculiar failure aspect might result from corresponding stress distribution in the cross section. As a result of a series of investigations, possible causes of such peculiar failure could be narrowed down. A future investigation plan was proposed to clarify the most significant cause.
Nishi, Toshiaki*; Sasaki, Takuo; Ikeda, Kazuma*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Shimomura, Kenichi*; Kojima, Nobuaki*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1556, p.14 - 17, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)Sasaki, Takuo*; Shimomura, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Kamiya, Itaru*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 51(2), p.02BP01_1 - 02BP01_3, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.46(Physics, Applied)Sasaki, Takuo*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Ikeda, Kazuma*; Shimomura, Kenichi*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Kozu, Miwa*; Hu, W.; Kamiya, Itaru*; Oshita, Yoshio*; et al.
IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, 2(1), p.35 - 40, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.56(Energy & Fuels) collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 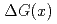 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.