Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
遠藤 駿典; 安部 亮太*; 藤岡 宏之*; 猪野 隆*; 岩本 修; 岩本 信之; 河村 しほり*; 木村 敦; 北口 雅暁*; 小林 龍珠*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 60(8), p.166_1 - 166_10, 2024/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of  -ray circular polarization emitted from neutron capture reactions provide valuable information for nuclear physics studies. The spin and parity of excited states can be determined by measuring the circular polarization from polarized neutron capture reactions. Furthermore, the
-ray circular polarization emitted from neutron capture reactions provide valuable information for nuclear physics studies. The spin and parity of excited states can be determined by measuring the circular polarization from polarized neutron capture reactions. Furthermore, the  -ray circular polarization in a neutron capture resonance is crucial for studying the enhancement effect of parity nonconservation in compound nuclei. The
-ray circular polarization in a neutron capture resonance is crucial for studying the enhancement effect of parity nonconservation in compound nuclei. The  -ray circular polarization can be measured using a polarimeter based on magnetic Compton scattering. A polarimeter was constructed, and its performance indicators were evaluated using a circularly polarized
-ray circular polarization can be measured using a polarimeter based on magnetic Compton scattering. A polarimeter was constructed, and its performance indicators were evaluated using a circularly polarized  -ray beam. Furthermore, as a demonstration, the
-ray beam. Furthermore, as a demonstration, the  -ray circular polarization was measured in
-ray circular polarization was measured in  S(n,
S(n, )
)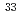 S reactions with polarized neutrons.
S reactions with polarized neutrons.
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(18), p.184903_1 - 184903_10, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)We report on the findings of a quantitative nondestructive analysis of the natural isotopic abundances of hafnium and tungsten elements using nuclear resonance fluorescence. Commercial samples of hafnium and tungsten were irradiated to six quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering in the energy range of 2.4-3.2 MeV. Multiple nuclei were simultaneously excited at each of the six
-ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering in the energy range of 2.4-3.2 MeV. Multiple nuclei were simultaneously excited at each of the six  -ray beam energies. A high-purity germanium detector array detected deexcitations of the nuclei. In total,
-ray beam energies. A high-purity germanium detector array detected deexcitations of the nuclei. In total, 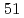 transitions were unprecedentedly employed to estimate the isotopic abundances of heavy elements nondestructively. The estimated abundances of three hafnium isotopes and three tungsten isotopes are consistent with standard known natural abundances within the experimental uncertainties. The deviation from the standard values ranges from 0.18% to 1.36%. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
transitions were unprecedentedly employed to estimate the isotopic abundances of heavy elements nondestructively. The estimated abundances of three hafnium isotopes and three tungsten isotopes are consistent with standard known natural abundances within the experimental uncertainties. The deviation from the standard values ranges from 0.18% to 1.36%. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 Ta
Ta静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Physical Review C, 109(5), p.054320_1 - 054320_8, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying levels in the odd-mass nucleus  Ta have been populated via nuclear resonance fluorescence using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam at the High Intensity
Ta have been populated via nuclear resonance fluorescence using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility at Duke University. The spin and parity of the levels were determined from the azimuthal intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
S) facility at Duke University. The spin and parity of the levels were determined from the azimuthal intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole strengths were obtained for excitation energies from 2.2 to 3.2 MeV. The results are discussed in terms of the nuclear scissors mode. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole strengths were obtained for excitation energies from 2.2 to 3.2 MeV. The results are discussed in terms of the nuclear scissors mode. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 Ni
Ni静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 早川 岳人*; 湊 太志*; 松葉 俊哉*; 宮本 修治*; 清水 則孝*; 宇都野 穣
Physical Review C, 109(1), p.014302_1 - 014302_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:84.33(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying dipole states in the singly closed-shell nucleus  Ni were studied via nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
Ni were studied via nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole (E1 and M1) strengths at excitation energies between 5.9 and 9.8 MeV were obtained based on dipole strengths taken from literature. The E1 and M1 strength distributions were compared with large-scale shell-model predictions in the
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole (E1 and M1) strengths at excitation energies between 5.9 and 9.8 MeV were obtained based on dipole strengths taken from literature. The E1 and M1 strength distributions were compared with large-scale shell-model predictions in the 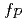 -shell using the SDPFSDG-MU interaction.
-shell using the SDPFSDG-MU interaction.
 -ray elastic scattering
-ray elastic scatteringOmer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 小泉 光生; 羽島 良一*; 橋本 智*; 宮本 修治*
LASTI Annual Report, 24, p.20 - 22, 2023/12
Nondestructive elemental analysis is highly valued in many fields such as archeology, paleontology, space sciences, nuclear security, and nuclear nonproliferation. These fields usually impose estimating the elemental composition of bulk, large, and inhomogeneous samples nondestructively. Common elemental analysis techniques such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) may fail in such situations due to self-absorption of low energy X-rays within thin layers of the sample. In the present study, we propose a novel nondestructive method that may be useful in distinguishing the elemental composition of a given sample based on the elastic scattering of linearly polarized and high-energy  -rays. Linear polarization of
-rays. Linear polarization of  -rays causes asymmetry of the elastic scattering cross sections with respect to the polarization plane of the incident
-rays causes asymmetry of the elastic scattering cross sections with respect to the polarization plane of the incident  -rays. At specific
-rays. At specific  -ray energies and scattering angles, the asymmetry ratio, R, of the cross sections in two orthogonal planes is characteristic of each element. The measurement of asymmetry ratio of 1.62 MeV linearly polarized
-ray energies and scattering angles, the asymmetry ratio, R, of the cross sections in two orthogonal planes is characteristic of each element. The measurement of asymmetry ratio of 1.62 MeV linearly polarized  -rays at NewSUBARU facility is presented. This work is a contribution of the JAEA to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband).
-rays at NewSUBARU facility is presented. This work is a contribution of the JAEA to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband).
中村 詔司; 芝原 雄司*; 木村 敦; 遠藤 駿典; 静間 俊行*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1133 - 1142, 2023/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)近年、鉛冷却高速炉や加速器駆動システムの研究が進められており、Pb同位体の中性子捕獲断面積の高精度化が求められている。 Pbは、天然存在比は小さいが中性子捕獲反応により長寿命放射性核種
Pbは、天然存在比は小さいが中性子捕獲反応により長寿命放射性核種 Pb(1730万年)を作るため、その重要性は高いと考えられる。しかし、原子炉を用いた通常の放射化法では、生成する
Pb(1730万年)を作るため、その重要性は高いと考えられる。しかし、原子炉を用いた通常の放射化法では、生成する Pbからの放射線が弱いため測定するのが難しい。そこで、マススペクトロメトリーを適用した断面積測定を行った。本発表ではマススペクトロメトリーを適用した
Pbからの放射線が弱いため測定するのが難しい。そこで、マススペクトロメトリーを適用した断面積測定を行った。本発表ではマススペクトロメトリーを適用した Pbの中性子捕獲断面積測定について実験の詳細と得られた結果を報告する。
Pbの中性子捕獲断面積測定について実験の詳細と得られた結果を報告する。
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 小泉 光生; 平 義隆*; Zen, H.*; 大垣 英明*; 羽島 良一
UVSOR-50, P. 37, 2023/08
核共鳴蛍光(NRF)を用いた非破壊分析において、試料温度によるドップラー効果による影響を調べることを目的とした研究を開始した。今回は、波長1980nmのファイバーレーザーを加速エネルギー746MeVの電子ビームと衝突させて生成した最大エネルギー5.54MeVのレーザーコンプトンガンマ線を Pb標的に照射し、共鳴散乱ガンマ線を3台の高純度ゲルマニウム検出器を用いて測定した。その結果、レーザーコンプトンガンマ線最大エネルギーよりも高いエネルギーで、複数のガンマ線ピークが観測された。これらのガンマ線は、実験室内の制動放射線によって発生した中性子が測定装置の周囲の物質と反応した後に放出された中性子捕獲即発ガンマ線であると考えられる。そのため、バックグラウンドガンマ線の低減のため、ゲルマニウム検出器の周囲を厚さ10cmの鉛を用いて遮蔽した。その結果、即発ガンマ線のバックグラウンドは抑制され、
Pb標的に照射し、共鳴散乱ガンマ線を3台の高純度ゲルマニウム検出器を用いて測定した。その結果、レーザーコンプトンガンマ線最大エネルギーよりも高いエネルギーで、複数のガンマ線ピークが観測された。これらのガンマ線は、実験室内の制動放射線によって発生した中性子が測定装置の周囲の物質と反応した後に放出された中性子捕獲即発ガンマ線であると考えられる。そのため、バックグラウンドガンマ線の低減のため、ゲルマニウム検出器の周囲を厚さ10cmの鉛を用いて遮蔽した。その結果、即発ガンマ線のバックグラウンドは抑制され、 Pbの共鳴散乱ガンマ線を観測することができた。
Pbの共鳴散乱ガンマ線を観測することができた。
平 義隆*; 遠藤 駿典; 河村 しほり*; 南部 太郎*; 奥泉 舞桜*; 静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; Zen, H.*; 岡野 泰彬*; 北口 雅暁*
Physical Review A, 107(6), p.063503_1 - 063503_10, 2023/06
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:64.27(Optics)偏光レーザーと電子による逆コンプトン散乱は偏光ガンマ線を生成する手法の一つであり、100%偏光のレーザーを用いることで100%の偏光ガンマ線を得ることができる。しかしながら、偏光具合はガンマ線の散乱角度に依存して変化する。本研究ではMeVのエネルギーのガンマ線の円偏光度を測定することが可能である磁化鉄を用いて、ガンマ線の円偏光度の空間分布を実験的に測定した。ガンマ線の磁化鉄の透過率の非対称性が確認され、中心軸付近において円偏光しているガンマ線が、散乱角度が大きくなると円偏光から直線偏光に変化することが確認された。
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
第43回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 3 Pages, 2022/11
Gamma-rays originated from laser Compton scattering (LCS) are convenient photon sources for nondestructive interrogation of nuclear materials. LCS can be used with nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF), the two of which are considered photon-based active interrogation techniques. However, an accurate estimation of the incident LCS  -ray flux is crucial. The
-ray flux is crucial. The  -ray flux is customarily measured using high purity germanium (HPGe) detectors, usually calibrated using standard point-like radioactive
-ray flux is customarily measured using high purity germanium (HPGe) detectors, usually calibrated using standard point-like radioactive  -ray sources. These standard sources are entirely different from LCS beams in terms of detection geometry. Therefore, the calibration process must be corrected to meet the LCS beam conditions. Here, we demonstrate how to implement the required corrections and provide experimental validation of these corrections.
-ray sources. These standard sources are entirely different from LCS beams in terms of detection geometry. Therefore, the calibration process must be corrected to meet the LCS beam conditions. Here, we demonstrate how to implement the required corrections and provide experimental validation of these corrections.
 Pb
Pb静間 俊行*; 遠藤 駿典; 木村 敦; Massarczyk, R.*; Schwengner, R.*; Beyer, R.*; Hensel, T.*; Hoffmann, H.*; Junghans, A.*; R mer, K.*; et al.
mer, K.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(4), p.044326_1 - 044326_11, 2022/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:31.55(Physics, Nuclear)ドレスデン・ヘルムホルツセンター(HZDR)の制動放射光施設( ELBE)において、最大運動エネルギー10.5MeV制動放射線を用いて、
ELBE)において、最大運動エネルギー10.5MeV制動放射線を用いて、 Pbの電気双極子及び四重極強度分布を核共鳴蛍光法で調べた。その結果、3.6から8.4MeVのエネルギーで136個の共鳴準位を同定した。これらの励起状態のスピンは、入射
Pbの電気双極子及び四重極強度分布を核共鳴蛍光法で調べた。その結果、3.6から8.4MeVのエネルギーで136個の共鳴準位を同定した。これらの励起状態のスピンは、入射 線に対して90
線に対して90 と127
と127 の散乱角度で観測された
の散乱角度で観測された 線の角度分布比から推測されたものである。この実験結果をもとに、自己無撞着エネルギー密度汎関数(EDF)を用いた準粒子・フォノン模型(QPM)による予測との比較により、E1遷移確率について議論した。
線の角度分布比から推測されたものである。この実験結果をもとに、自己無撞着エネルギー密度汎関数(EDF)を用いた準粒子・フォノン模型(QPM)による予測との比較により、E1遷移確率について議論した。
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 198, p.110241_1 - 110241_7, 2022/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:51.78(Chemistry, Physical)In beam geometries where a directed  -ray beam hits the surface of a coaxial high purity germanium detector (HPGe), the detector efficiency is sensitive to the position where
-ray beam hits the surface of a coaxial high purity germanium detector (HPGe), the detector efficiency is sensitive to the position where  -rays initially hit the detector surface because the structure of the detector is nonuniform. This may cause inaccuracy of the detector efficiency when measured using standard sources that are point-like sources emitting
-rays initially hit the detector surface because the structure of the detector is nonuniform. This may cause inaccuracy of the detector efficiency when measured using standard sources that are point-like sources emitting  -rays isotropically. Obtaining a precise estimation of the full energy peak efficiency of the coaxial HPGe detector in the beam geometry for on-axis and off-axis measurements requires a Monte Carlo simulation. We performed a Monte Carlo simulation that calculates the detector efficiency in the beam geometry. The effects of the off-axis distance and
-rays isotropically. Obtaining a precise estimation of the full energy peak efficiency of the coaxial HPGe detector in the beam geometry for on-axis and off-axis measurements requires a Monte Carlo simulation. We performed a Monte Carlo simulation that calculates the detector efficiency in the beam geometry. The effects of the off-axis distance and  -ray beam size on the efficiency are quantitatively analyzed. We found that the intrinsic efficiency in the beam geometry is maximized when the beam hits the detector at specific off-axis distances. Our Monte Carlo calculations have been supported by a nuclear resonance fluorescence experiment using laser Compton scattering
-ray beam size on the efficiency are quantitatively analyzed. We found that the intrinsic efficiency in the beam geometry is maximized when the beam hits the detector at specific off-axis distances. Our Monte Carlo calculations have been supported by a nuclear resonance fluorescence experiment using laser Compton scattering  -ray beam.
-ray beam.
遠藤 駿典; 静間 俊行*; Zen, H.*; 平 義隆*; Omer, M.; 河村 しほり*; 安部 亮太*; 奥平 琢也*; 北口 雅暁*; 清水 裕彦*
UVSOR-49, P. 38, 2022/08
To measure the circular polarization of gamma-rays, the gamma-ray polarimeter was developed. The analyzing power of the polarimeter was measured using circularly polarized gamma-rays in UVSOR BL1U. Magnetic hysteresis of the polarimeter was also observed. The analyzing power was obtained as 2.12 0.04%.
0.04%.
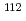 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction in an
Cd reaction in an  -process branching point
-process branching point早川 岳人*; 藤 暢輔; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司; 静間 俊行*; 岩本 信之; 千葉 敏*; 梶野 敏貴*
Physical Review C, 103(4), p.045801_1 - 045801_5, 2021/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:13.22(Physics, Nuclear)A  -decay unstable isomer with a half-life of 14.1 y at 264 keV in
-decay unstable isomer with a half-life of 14.1 y at 264 keV in  Cd is a branching point in the
Cd is a branching point in the  process, from which a weak branch reaches to a rare tin isotope
process, from which a weak branch reaches to a rare tin isotope  Sn whose astrophysical origin has been an open problem. We have measured
Sn whose astrophysical origin has been an open problem. We have measured  rays decaying to the ground state or the isomer in the
rays decaying to the ground state or the isomer in the 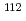 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction using high-energy resolution detectors in conjunction with a time-of-flight method. The relative production ratios of the isomer to the total following the neutron capture reactions on
Cd reaction using high-energy resolution detectors in conjunction with a time-of-flight method. The relative production ratios of the isomer to the total following the neutron capture reactions on 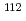 Cd have been evaluated in an energy region of up to 9 keV, and the spin and parity of several resonances have been assigned.
Cd have been evaluated in an energy region of up to 9 keV, and the spin and parity of several resonances have been assigned.
 S
S郷 慎太郎*; 井手口 栄治*; 横山 輪*; 青井 考*; Azaiez, F.*; 古高 和禎; 初川 雄一; 木村 敦; 木佐森 慶一*; 小林 幹*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:43.33(Physics, Nuclear)Excited states in  S were investigated by in-beam
S were investigated by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy using the
-ray spectroscopy using the  Mg(
Mg( O, 2
O, 2 1
1 ) fusion-evaporation reaction. The de-exciting
) fusion-evaporation reaction. The de-exciting  -rays were measured with germanium detector arrays along with the measurement of evaporated charged particles in a
-rays were measured with germanium detector arrays along with the measurement of evaporated charged particles in a 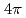 segmented Si detector array. The level scheme was extended up to 12470 keV. The obtained level structure is compared with the large-scale shell-model calculations. The possibility of isoscalar-pair excited states is discussed for
segmented Si detector array. The level scheme was extended up to 12470 keV. The obtained level structure is compared with the large-scale shell-model calculations. The possibility of isoscalar-pair excited states is discussed for 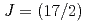 states with comparison between the experimental and theoretical results.
states with comparison between the experimental and theoretical results.
 Pb
Pb静間 俊行*; 湊 太志; Omer, M.*; 早川 岳人*; 大垣 英明*; 宮本 修治*
Physical Review C, 103(2), p.024309_1 - 024309_8, 2021/02
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:51.13(Physics, Nuclear) Pbの低エネルギー双極子強度を準モノクロ=線形偏極フォトンビームの光核散乱を使って調べ、6.8MeVまでの励起エネルギーにおける電磁双極子(
Pbの低エネルギー双極子強度を準モノクロ=線形偏極フォトンビームの光核散乱を使って調べ、6.8MeVまでの励起エネルギーにおける電磁双極子( )および磁気双極子強度(
)および磁気双極子強度( )を導出した。今回の(
)を導出した。今回の(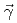 ,
,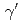 )反応の結果は、過去に行われた(
)反応の結果は、過去に行われた( ,
, )反応のデータと合わせて、中性子閾値近傍のエネルギーにおける
)反応のデータと合わせて、中性子閾値近傍のエネルギーにおける と
と の光吸収反応断面積を求めるために使った。得られた測定結果は、乱雑位相近似法+粒子振動カップリング法による理論計算の結果と比較し、核構造の観点から議論を行う。
の光吸収反応断面積を求めるために使った。得られた測定結果は、乱雑位相近似法+粒子振動カップリング法による理論計算の結果と比較し、核構造の観点から議論を行う。
 -ray beam
-ray beamOmer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 951, p.162998_1 - 162998_6, 2020/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:29.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)Compton scattering of a single-energy  -ray results in a one-to-one relationship between the incident and scattered photon energies. This relationship is altered when the incident beam has a definite energy distribution because of the broadening occurring in the energy distribution upon Compton scattering. This broadening causes a change in the spectral density of the Compton-scattered spectra. To restore the spectral density, the energy distribution of the scattered radiation must be manifested as a function of the scattering kinematics. Here, we propose a simple analytic way to calculate the energy spread of the scattered photons in terms of the geometry of the scattering process and the energy spread of the incident photon beam. The predictions of the model agree with measurements of Compton scattering of quasi-monochromatic
-ray results in a one-to-one relationship between the incident and scattered photon energies. This relationship is altered when the incident beam has a definite energy distribution because of the broadening occurring in the energy distribution upon Compton scattering. This broadening causes a change in the spectral density of the Compton-scattered spectra. To restore the spectral density, the energy distribution of the scattered radiation must be manifested as a function of the scattering kinematics. Here, we propose a simple analytic way to calculate the energy spread of the scattered photons in terms of the geometry of the scattering process and the energy spread of the incident photon beam. The predictions of the model agree with measurements of Compton scattering of quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams, carried out at the High Intensity
-ray beams, carried out at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility, Duke University. As a benchmark of our method, we measured the intensity profile of energy-distributed
S) facility, Duke University. As a benchmark of our method, we measured the intensity profile of energy-distributed  -ray beams by direct measurements as well as by Compton scattering. We found that only when the spectral density of the scattered radiation is restored, the measured intensity profile agrees with the actual profile of the incident beam. The proposed method can continuously measure the flux of an energy-distributed
-ray beams by direct measurements as well as by Compton scattering. We found that only when the spectral density of the scattered radiation is restored, the measured intensity profile agrees with the actual profile of the incident beam. The proposed method can continuously measure the flux of an energy-distributed  -ray beams in the real time and on a bin-by-bin basis. Such online monitoring of
-ray beams in the real time and on a bin-by-bin basis. Such online monitoring of  -ray beams is indispensable for in-beam measurements and applications. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
-ray beams is indispensable for in-beam measurements and applications. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
日本核物質管理学会第40回年次大会プロシーディングス集, p.59 - 62, 2019/11
Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a phenomenon that a nuclide-specific  -ray is resonantly absorbed and re-emitted. This method is considered useful for the nondestructive detection of nuclear materials. In order to demonstrate how accurate the NRF method is able to measure the isotopic abundance, we performed NRF experiments on natural tungsten as a surrogate of nuclear materials at the High Intensity
-ray is resonantly absorbed and re-emitted. This method is considered useful for the nondestructive detection of nuclear materials. In order to demonstrate how accurate the NRF method is able to measure the isotopic abundance, we performed NRF experiments on natural tungsten as a surrogate of nuclear materials at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility, Duke University. Our results show that the relative deviations between the reference and measured abundances are less than
S) facility, Duke University. Our results show that the relative deviations between the reference and measured abundances are less than  4%. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
4%. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 Al; Its low-lying multiplet structure
Al; Its low-lying multiplet structure静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 清水 則孝*; 宇都野 穣
Physical Review C, 100(1), p.014307_1 - 014307_6, 2019/07
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:57.02(Physics, Nuclear)Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a promising technique for the nondestructive assay (NDA) of nuclear materials. One of the features of the NRF is the angular distribution of the emitted photons in response to a linearly polarized incident beam. Here we irradiate the calibration standard of  Al to linearly polarized beam. The spin and parity of the 3.004-MeV level in
Al to linearly polarized beam. The spin and parity of the 3.004-MeV level in  Al have been determined by measuring the angular correlation function of radiation emitted from levels populated by resonant absorption of polarized photons. The nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments were carried out at the High Intensity
Al have been determined by measuring the angular correlation function of radiation emitted from levels populated by resonant absorption of polarized photons. The nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments were carried out at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility at Duke University using quasi-monoenergetic linearly polarized photon beams. The spin and parity of levels in
S) facility at Duke University using quasi-monoenergetic linearly polarized photon beams. The spin and parity of levels in  Al were deduced from a comparison of the measured angular distribution ratios and azimuthal intensity asymmetries with theoretical predictions. The observed resonance properties were compared with shell model calculations using the universal sd interaction. The Monte Carlo shell model calculations were also performed to investigate low-energy structure of
Al were deduced from a comparison of the measured angular distribution ratios and azimuthal intensity asymmetries with theoretical predictions. The observed resonance properties were compared with shell model calculations using the universal sd interaction. The Monte Carlo shell model calculations were also performed to investigate low-energy structure of  Al. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Al. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 Pb for the evaluation of the neutron capture cross section of
Pb for the evaluation of the neutron capture cross section of  Pb
Pb静間 俊行; 岩本 信之; 牧永 あや乃*; Massarczyk, R.*; Schwengner, R.*; Beyer, R.*; Bemmerer, D.*; Dietz, M.*; Junghans, A.*; K gler, T.*; et al.
gler, T.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 98(6), p.064317_1 - 064317_12, 2018/12
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:62.41(Physics, Nuclear) Pbの双極子強度分布を核共鳴蛍光散乱実験によって調べた。実験はHZDRの線形加速器ELBEにおいて、10.5MeVの電子ビームにより生成された制動放射を使って行われた。その結果、3.7から8.2MeVの励起エネルギーにおいて88本の励起状態を識別した。測定解析で得られた散乱断面積と
Pbの双極子強度分布を核共鳴蛍光散乱実験によって調べた。実験はHZDRの線形加速器ELBEにおいて、10.5MeVの電子ビームにより生成された制動放射を使って行われた。その結果、3.7から8.2MeVの励起エネルギーにおいて88本の励起状態を識別した。測定解析で得られた散乱断面積と 線崩壊分岐比から光吸収断面積を導出し、既存の(
線崩壊分岐比から光吸収断面積を導出し、既存の( ,
, )反応断面積と併せて核反応モデルコードCCONEにより光核反応断面積を評価した。これらの評価で得た
)反応断面積と併せて核反応モデルコードCCONEにより光核反応断面積を評価した。これらの評価で得た Pbに対する物理情報を基にして、不安定な
Pbに対する物理情報を基にして、不安定な Pbの中性子捕獲断面積を導出した。
Pbの中性子捕獲断面積を導出した。
 Pb with photonuclear data
Pb with photonuclear data岩本 信之; 静間 俊行*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 178, p.06004_1 - 06004_3, 2018/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Optics)Transmutation and reduction of high level radioactive wastes (e.g. minor actinides) produced in nuclear reactors are expected by an accelerator driven system (ADS). Japan Atomic Energy Agency proposed that Pb and Bi are used as a spallation target and coolant. The neutronics design was performed without including  Pb, which is a long-lived radioactive nuclide with half-life of 1.7
Pb, which is a long-lived radioactive nuclide with half-life of 1.7 10
10 years and thus has long-lasting radiotoxicity.
years and thus has long-lasting radiotoxicity.  Pb is produced by the neutron capture reaction on
Pb is produced by the neutron capture reaction on  Pb. In order to evaluate the accumulated amount of
Pb. In order to evaluate the accumulated amount of  Pb, the neutron capture cross section of
Pb, the neutron capture cross section of  Pb is needed. However, it has not been measured in the keV to MeV neutron energy region. In the present work the calculations of cross sections were performed by the nuclear reaction calculation code, CCONE. Measured photonuclear data of (
Pb is needed. However, it has not been measured in the keV to MeV neutron energy region. In the present work the calculations of cross sections were performed by the nuclear reaction calculation code, CCONE. Measured photonuclear data of ( ,
, ) reaction and photoneutron cross sections were used to evaluate photon strength function of
) reaction and photoneutron cross sections were used to evaluate photon strength function of  Pb. The (
Pb. The ( ,
, ) reaction data used were newly obtained by an experiment at HZDR. The fixed photon strength function was applied to calculate the neutron capture cross sections of
) reaction data used were newly obtained by an experiment at HZDR. The fixed photon strength function was applied to calculate the neutron capture cross sections of  Pb. The resulting cross section is smaller than the data of
Pb. The resulting cross section is smaller than the data of  Pb in the relevant energy region.
Pb in the relevant energy region.