Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawashima, Hisato; Sengoku, Seio; Uehara, Kazuya; Tamai, Hiroshi; Shoji, Teruaki*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Shibata, Takatoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.168 - 186, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental efforts on JFT-2M have been devoted to understand SOL/Divertor plasmas and to investigate power and particle controllability. Open divertor configuration was used for the first decade of JFT-2M started in 1984. We found out the SOL/Divertor plasma properties such as in/out asymmetry, heat and particle diffusivities, and SOL current at ELMs. Handling of power and particle was demonstrated by active control methods such as local pumping, edge ergodization, divertor biasing, and edge heating. For improvement of power and particle control capability of divertor, it was modified to closed configuration in 1995, which demonstrated the baffling effects with narrower divertor throat. Dense and cold divertor state (n
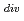 = 4
= 4 10
10 m
m and T
and T
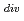 = 4 eV), compatible with the improved confinement modes (e.g. H-mode), was realized by strong gas puffing. Being related with the core confinement at H-mode, the edge plasma fluctuations were identified by an electrostatic probe. These are reviewed in this paper.
= 4 eV), compatible with the improved confinement modes (e.g. H-mode), was realized by strong gas puffing. Being related with the core confinement at H-mode, the edge plasma fluctuations were identified by an electrostatic probe. These are reviewed in this paper.
Miura, Yukitoshi; Mori, Masahiro; Shoji, Teruaki; Matsumoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Kensaku; Ida, Katsumi*; Kasai, Satoshi*
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.96 - 121, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:11.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)The improved modes observed in JFT-2M are characterized by the two improvements, i.e. one is the H-mode at the edge, and other modes are core improvement with peaked profiles near the center. The improvement of the pellet injected H-mode was a combination of H-mode and the core improvement. The discovery of limiter H-mode had an impact on the physics understanding of the H-mode and showed the formation of transport barrier at a place without discontinuity of the magnetic field line topology. The appearance of ELMs by applying ergodic fields was investigated and it was clarified that n 4 helical components were effective to produce ELMs. A SOL biasing had effects to compress neutrals at divertor region. It would be understood that the compressed neutrals at divertor region might make a situation of low L/H threshold power. High recycling steady (HRS) H-mode could be reproducibly obtained by boronization. It was found that HRS appears at the pedestal collisionality greater than 1.
4 helical components were effective to produce ELMs. A SOL biasing had effects to compress neutrals at divertor region. It would be understood that the compressed neutrals at divertor region might make a situation of low L/H threshold power. High recycling steady (HRS) H-mode could be reproducibly obtained by boronization. It was found that HRS appears at the pedestal collisionality greater than 1.
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Yamamoto, Takumi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Oasa, Kazumi; Kawashima, Hisato; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Toshihide; Shoji, Teruaki*; Shibata, Takatoshi; Kikuchi, Kazuo; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.139 - 167, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)The main results obtained by the various heating and current drive systems, external coil system and divertor bias system are reviewed from the viewpoint of the advanced active control of the tokamak plasma. Also, the features of each system are described. The contribution of the JFT-2M in these areas are summarized.
Nakakura, Kensuke*; Yagenji, Akira*; Shoji, Teruaki*; Araki, Masanori; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Tanaka, Eiichi*; Shima, Hiroaki*
JAERI-Tech 2005-058, 61 Pages, 2005/09
The design of International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) had been done during the period of Engineering Design Activities (EDA) and its final deign report was published on July 2001. After that the further design studies have been performed as activities in the CTA and ITA periods. As for Tokamak complex, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) performed preliminary study for both static and dynamic analyses with a few types of analysis models based on the Technical Guidelines for Aseismic Design of Nuclear Power Plants etc during EDA. In comparison with reactor building for nuclear fission power plant, its outside is not so different from reactor building's one. However, its structural characteristics inside building are apparently different from reactor building's one, because the bio shield of Tokamak complex has a lot of large penetration of ports. Therefore, characteristic of dynamic analysis models for Tokamak complex needs to be evaluated in order to perform the detailed design of Tokamak complex in account for site-dependent conditions. This report describes results of characteristic evaluation with representative analytical models for Tokamak complex, which are modeled with Finite Element Method and Lumped mass, and it is confirmed that adopted evaluation method of the bio shield wall and floor's stiffnesses around the bio shield wall for Lumped mass model is adequate.
Senda, Ikuo*; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Tada, Eisuke; Shoji, Teruaki
JAERI-Data/Code 2003-012, 73 Pages, 2003/07
The tokamak transient simulation code, named SAFALY, was revised recently and the sensitivity analyses on the parameters in the code were carried out. This report is composed of two volumes. The formulation and the parameters in modeling the plasma and in-vessel components are described in the first volume. In this second volume, the results of the sensitivity studies are reported. The sensitivity studies were performed in two steps. In the first step, the responses of plasmas in the occurrence of plasma disturbances were analyzed for various initial conditions. For each disturbance, the initial condition of the plasma, which gave the largest increase of the fusion power, was identified. In the second step, by using initial conditions derived in the first step, the sensitivities of plasma reactions with respect to variation of the parameters in SAFALY code were analyzed. In the analyses, the increase of the fueling, the increase of the plasma confinement improvement factor and the increase of the auxiliary heating power were considered as plasma disturbances.
Senda, Ikuo*; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Tada, Eisuke; Shoji, Teruaki
JAERI-Data/Code 2003-008, 37 Pages, 2003/06
Tokamak transient simulation code, named SAFALY, was revised. SAFALY code has been developed to simulate transient events in Tokamaks. Modeling of the plasma and algorithms of the simulation were revised. The code was also modified to deal with the variation of the plasma current. The code was improved to allow flexible modeling of in-vessel components. The data transfer between SAFALY and related codes was arranged to prepare data required in analyses with SAFALY, such as the distributions of heat/neutron loads and the radiation form factor between in-vessel components. The report is composed of two volumes. The formulation and the parameters in modeling plasma and in-vessel components are described in this first volume. Examples of simulation results, using the design of ITER-FDR in 2001, are presented and general properties of plasmas' responses with respect to perturbations are discussed. The results of the sensitivity studies with respect to simulation parameters and initial conditions will be reported in the second volume.
Omori, Junji*; Kitamura, Kazunori*; Araki, Masanori; Oono, Isamu*; Shoji, Teruaki
JAERI-Tech 2002-053, 86 Pages, 2002/07
no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo; Shoji, Teruaki; Tsunematsu, Toshihide
Nuclear Fusion, 42(5), p.568 - 580, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.10(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Mori, Masahiro; Shoji, Teruaki; Araki, Masanori; Saito, Keiji*; Senda, Ikuo; Omori, Junji*; Sato, Shinichi*; Inoue, Takashi; Ono, Isamu*; Kataoka, Takahiro*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 44(1), p.16 - 89, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Shimomura, Yasuo; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Yamamoto, Shin; Maruyama, So; Mizoguchi, Tadanori*; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Kitamura, Kazunori*; Ioki, Kimihiro*; Inoue, Takashi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(Suppl.), 224 Pages, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Araki, Masanori; Sato, Shinichi*; Senda, Ikuo; Omori, Junji*; Shoji, Teruaki
Fusion Engineering and Design, 58-59, p.887 - 892, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo; Shoji, Teruaki; Araki, Masanori; ITER Japan Home Team; ITER Joint Central Team
International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, 13(1-4), p.349 - 357, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo*; Shoji, Teruaki; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Matsukawa, Makoto; Ushigusa, Kenkichi
Nucl. Eng. Des., 45(1), p.15 - 29, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo*; Shoji, Teruaki; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; ; Fujieda, Hirobumi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 42, p.395 - 399, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Takase, Haruhiko; Senda, Ikuo; Araki, Masanori; Shoji, Teruaki; Tsunematsu, Toshihide
IAEA-CN-69/FTP/28, 4 Pages, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ; ; ; Oikawa, Toshihiro; ; ; et al.
Fusion Energy 1996, p.885 - 890, 1997/05
no abstracts in English
Miura, Yukitoshi; ; ; Hoshino, Katsumichi; ; ; Kasai, Satoshi; Kawakami, Tomohide; Kawashima, Hisato; Maeda, M.*; et al.
Fusion Energy 1996, p.167 - 175, 1997/05
no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo*; Shoji, Teruaki; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; ; Fujieda, Hirobumi*
Nuclear Fusion, 37(8), p.1129 - 1145, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.08(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Harano, Hideki*; Nishitani, Takeo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kimura, Haruyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Shoji, Teruaki; Senda, Ikuo*; et al.
Proc. of 5th IAEA Technical Committee Meeting on Alpha Particles in Fusion Research, p.45 - 48, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Senda, Ikuo*; Shoji, Teruaki; ; Fujieda, Hirobumi*; Tsunematsu, Toshihide
JAERI-Tech 96-016, 23 Pages, 1996/03
no abstracts in English