Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.66(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:99.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kunieda, Satoshi;  elik, Y.*; Furutachi, Naoya*; Niita, Koji*
elik, Y.*; Furutachi, Naoya*; Niita, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.665 - 675, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)A benchmark study of PHITS3.24 has been conducted using neutron-shielding experiments listed in the Shielding Integral Benchmark Archive and Database. Five neutron sources were selected, which are generated from (1) 43- and 68-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thin lithium target, (2) 52-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick graphite target, (3) 590-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick lead target, (4) 500-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick tungsten target, and (5) 800-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick tantalum target. For all cases, overall agreements in the results are satisfactory when using the JENDL-4.0/HE to simulate neutron- and proton-induced reactions up to 200 MeV. However, discrepancies using PHITS default settings are observed in the results. For an accurate neutron-shielding design for accelerator facilities, using JENDL-4.0/HE in the particle and heavy-ion transport code system calculation is favorable.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Tsai, P.-E.; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(6), p.684 - 690, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:792 Percentile:100(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have upgraded many features of the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) and released the new version as PHITS3.02. The accuracy and the applicable energy ranges of the code were greatly improved and extended, respectively, owing to the revisions to the nuclear reaction models and the incorporation of new atomic interaction models. In addition, several user-supportive functions were developed, such as new tallies to efficiently obtain statistically better results, radioisotope source-generation function, and software tools useful for applying PHITS to medical physics. In this paper, we summarize the basic features of PHITS3.02, especially those of the physics models and the functions implemented after the release of PHITS2.52 in 2013.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.06008_1 - 06008_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.14(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, has been developed under the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. It can deal with the transport of nearly all particles up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ion) using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. More than 2,500 researchers and technicians have used the code for a variety of applications such as accelerator design, radiation shielding and protection, medical physics, and space and geosciences. This paper briefly summarizes physics models and functions newly implemented in PHITS between versions 2.52 and 2.82.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Niita, Koji*
Hoshasen, 43(2), p.55 - 58, 2017/05
Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, has been developed under the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. It can deal with the transport of nearly all particles up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ion) using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. More than 2,500 registered researchers and technicians have used this system for various applications such as accelerator design, radiation shielding and protection, medical physics, and space- and geo-sciences. This paper summarizes the physics models and functions recently implemented in PHITS, between versions 2.52 and 2.88.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hosoyamada, Ryuji*; Niita, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(5), p.617 - 635, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:99 Percentile:99.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)We performed a benchmark study for 58 cases using the recent version 2.88 of the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) in the following fields: particle production cross-sections for nuclear reactions, neutron transport calculations, and electro-magnetic cascade. This paper reports details for 22 cases. In cases of nuclear reactions with energies above 100 MeV and electro-magnetic cascade, overall agreements were found to be satisfactory. On the other hand, PHITS did not reproduce the experimental data for an incident proton energy below 100 MeV, because the intranuclear cascade model INCL4.6 in PHITS is not suitable for the low-energy region. For proton incident reactions over 100 MeV, PHITS did not reproduce fission product yields due to the problem of high-energy fission process in the evaporation model GEM. To overcome these inaccuracies, we are planning to incorporate a high-energy version of the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0/HE, and so on.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Matsuda, Norihiro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Harada, Masahide; Maekawa, Fujio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(10), p.1585 - 1594, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:85.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.63 - 69, 2016/09
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. PHITS users apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some new models such as muon-induced nuclear reaction model and a  de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
 -YbAlB
-YbAlB at high magnetic fields
at high magnetic fieldsTerashima, Taku*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Shintaro*; Matsumoto, Yosuke*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(11), p.114715_1 - 114715_4, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.72(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 82, p.110 - 115, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:94.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)The general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through a collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is responsible for managing the entire project. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. This paper briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions useful for particular purposes, such as an event generator mode and beam transport functions.
 C
COgawa, Tatsuhiko; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Satoh, Daiki; Tsuda, Shuichi; Niita, Koji*
Physical Review C, 92(2), p.024614_1 - 024614_14, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:93.39(Physics, Nuclear)For prediction of radiological impact of heavy ions in accelerator facilities, space missions and cancer therapy, nuclear reaction models play a fundamental role. As one of such models, JAERI Quantum molecular dynamics (JQMD) has been successfully used to describe production of residue and secondary particles in nucleus-nucleus collisions. However, it has been pinpointed that JQMD underestimates projectile-like fragments produced in peripheral collisions. Moreover, no cross section data systematically measured over a wide energy range are not available, which makes it difficult to benchmark the reaction models. In this study, we develop a method to measured fragmentation cross sections using a thick target and detecting fragments produced from incident ions fragmented in the target using telescope detectors. Thus we obtained fragmentation cross sections systematically over a wide energy range. We also revise the description of reaction mechanism and ground-state nuclear structure in JQMD to take into account for peripheral collisions accurately. So far, ground-state nuclei got excited and sometimes disintegrated owing to frame transform from the laboratory system to the center-of-mass system. Fragment production cross sections calculated by the revised JQMD (JQMD2.0) are in better agreement with the literature data.
 -YbAl
-YbAl Fe
Fe B
B (
(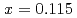 ) at low temperatures and high magnetic fields
) at low temperatures and high magnetic fieldsTerashima, Taku*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Shintaro*; Matsumoto, Yosuke*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 592(1), p.012020_1 - 012020_6, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:43.09(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Valence fluctuation phenomena in rare-earth intermetallic compounds have attracted attention because the quantum criticality of the valence transition has been proposed theoretically. Recently, it was found that  -YbAlB
-YbAlB shows quantum criticality without tuning and has a strong mixed-valence state. In this study, we measured the magnetization curve and X-ray magnetoabsorption in
shows quantum criticality without tuning and has a strong mixed-valence state. In this study, we measured the magnetization curve and X-ray magnetoabsorption in  -YbAl
-YbAl Fe
Fe B
B (
(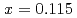 ), which is a locally isostructural polymorph of
), which is a locally isostructural polymorph of  -YbAlB
-YbAlB . The magnetization and X-ray experiments were performed in fields up to 55 and 40 T, respectively. A small increase in the Yb valence was observed at fields where the magnetization curve exhibited a change in slope.
. The magnetization and X-ray experiments were performed in fields up to 55 and 40 T, respectively. A small increase in the Yb valence was observed at fields where the magnetization curve exhibited a change in slope.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.69 - 74, 2015/02
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. All components of PHITS such as its source, executable and data-library files are assembled in one package and then distributed to many countries. More than 1,000 researchers apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions for specific applications, such as an event generator mode and a radiation damage calculation function.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Noda, Shusaku; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; Chiba, Satoshi; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.879 - 882, 2014/04
PHITS is a general purpose 3-dimensional Monte-Carlo particle transport simulation code developed under collaboration of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), Research Organization for Information Science and Technology (RIST), High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) and a couple of other institutes in Japan and Sweden. General features of the PHITS code together with details of the established model will be presented at the meeting.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; et al.
Igaku Butsuri, 33(2), p.88 - 95, 2013/10
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(9), p.913 - 923, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:564 Percentile:99.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)An upgraded version of the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS 2.52, was developed and released to public. The new version has been greatly improved from the previous released version, PHITS 2.24, in terms of not only the code itself but also the contents of its package such as attached data libraries. Owing to these improvements, PHITS became a more powerful tool for particle transport simulation applicable to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
RIST News, (54), p.14 - 24, 2013/01
Features of the latest version of the PHITS code (version 2.52) is described.
Nagao, Keisuke*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Miura, Yayoi*; Osawa, Takahito; Bajo, Kenichi*; Matsuda, Shintaro*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Ireland, T.*; Kitajima, Fumio*; et al.
Science, 333(6046), p.1128 - 1131, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:131 Percentile:95.12(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A steroid surface materials record regolith processes and a history of cosmic-ray irradiation. Noble gas isotopes in three rocky grains from Itokawa have been determined. High concentrations of solar He, Ne, and Ar, as high as those in lunar soils, are released at variable temperatures from each sample. The isotopic compositions are essentially identical to those of solar wind but distinguishable in He relative abundance. These noble gas characteristics can be explained by repeated implantation and preferential loss of solar He by removal of weathered He-rich rim on the grain surface through friction among regolith grains on Itokawa. Residence time of regolith materials on Itokawa is alculated to be shorter than 10 Myr, suggesting that regolith materials of small asteroids would escape easily to space.
Ohashi, Hayato*; Suda, Shintaro*; Tanuma, Hajime*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Kai, Takeshi; Sasaki, Akira; Sakaue, Hiroyuki*; Nakamura, Nobuyuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 163, p.012071_1 - 012071_4, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:89.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Extreme ultra-violet (EUV) emission spectra of multiply charged tin ions were measured in the wavelength range of 10-22 nm following charge exchange collisions or the electron impact excitation of tin ions. In charge exchange collisions, we observed both the resonance lines and the emission lines corresponding to the transitions between the excited states. On the other hand, we observed mainly the resonance lines in the electron impact experiments. We can distinguish the resonance lines from other emission lines in the charge exchange spectrum by comparison with the emission lines in the electron impact spectrum.