Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Sugihara, Kenta*; Hirano, Yukinori*; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Saito, Shigeru; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Technology 2024-026, 123 Pages, 2025/03
Based on the design of the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) at the J-PARC Transmutation Experimental Facility, a conceptual study was conducted on the J-PARC proton beam irradiation facility. This research was carried out based on the recommendations of the Nuclear Transmutation Technology Evaluation Task Force of the MEXT. The recommendations state that it is desirable to consider facility specifications that can make the most of the benefits of using the existing J-PARC proton accelerator while also solving the engineering issues of the ADS. We considered facilities that could respond to a variety of needs while reducing the facilities that were not needed in the TEF-T design. In order to clarify these diverse needs, we investigated the usage status of representative accelerator facilities around the world. As a result, it became clear that the main purposes of these facilities were (1) Material irradiation, (2) Soft error testing of semiconductor devices using spallation neutrons, (3) Production of RI for medical use, and (4) Proton beam use, and we investigated the facilities necessary for these purposes. In considering the facility concept, we assumed a user community in 2022 and reflected user opinions in the facility design. This report summarizes the results of the conceptual study of the proton irradiation facility, various needs and responses to them, the roadmap for facility construction, and future issues.
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.13_1 - 13_8, 2024/11
The latest updates on PHITS, a versatile radiation transport code, focusing specifically on track-structure models are presented. Track structure calculations are methods used to simulate the movement of charged particles while explicitly considering each atomic reaction. Initially developed for radiation biology, these calculation methods aimed to analyze the radiation-induced damage to DNA and chromosomes. Several track-structure calculation models, including PHITS-ETS, PHITS-ETS for Si, PHITS-KURBUC, ETSART, and ITSART, have been developed and implemented to PHITS. These models allow users to study the behavior of various particles at the nano-scale across a wide range of materials. Furthermore, potential applications of track-structure calculations have also been proposed so far. This collection of track-structure calculation models, which encompasses diverse conditions, opens up new avenues for research in the field of radiation effects.
 from 3-GeV protons and
from 3-GeV protons and  Hg with the
Hg with the  Bi(n,xn) reactions
Bi(n,xn) reactionsSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Conf 2024-002, p.162 - 167, 2024/11
A neutron energy spectrum is important for shielding design at an Accelerator-Driven System facility (1.5-GeV p + Lead Bismuth Eutectic). A similar spectrum can be obtained at J-PARC (3-GeV proton +  Hg). To check the validity of the unfolding, the unfolding with the
Hg). To check the validity of the unfolding, the unfolding with the  Bi(n,xn) reactions and the response functions (JENDL/HE-2007 and TALYS) was applied. In our poster, we present the derivation of the spectrum and comparison with the spectrum with a Time-of-Flight technique.
Bi(n,xn) reactions and the response functions (JENDL/HE-2007 and TALYS) was applied. In our poster, we present the derivation of the spectrum and comparison with the spectrum with a Time-of-Flight technique.
Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Sitompul, Y.; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamashita, Susumu
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.03002_1 - 03002_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)In simulations of gas-liquid two-phase flows using conventional interface capture methods, we observed that when bubbles come close to each other, they tend to merge numerically, despite experimental evidence indicating that they would repel each other. Given the significant impact of sequential numerical coalescence on flow patterns, it is necessary to regulate the merging behavior of close bubbles. To address this issue, we introduced the Multi- Phase Field (MPF) method, which mitigates bubble coalescence by applying an independent fluid fraction function to each bubble. In this study, we employed the MPF based on the N-phase model to minimize numerical errors associated with surface interactions at triple junction points. Additionally, we implemented the Ordered Active Parameter Tracking (OAPT) method to efficiently store several hundreds of fluid fraction functions. To validate the MPF method, we conducted analysis of turbulent bubbly pipe flows and compared the results against experimental data from Colin et al. The validation results showed reasonable agreements with respect to the bubble distribution and the flow velocity profiles.
Sitompul, Y.; Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.05004_1 - 05004_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:94.62(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)In fast reactor designs, it is of critical importance to avoid gas entrainment phenomena due to free-surface vortices. Numerical analysis is one of the key methods to understand these phenomena. However, the challenges in computational efficiency and accuracy of the previous numerical methods lead to exploring the Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) as an alternative, known for its computational efficiency and capability in simulating complex flows. In this study, we implement free-surface LBM to accelerate gas entrainment analysis, significantly reducing computational costs while maintaining accuracy compared to traditional methods. Simulation results using LBM align well with experimental data, offering a promising avenue for faster analysis in future fast reactor designs.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Sugihara, Kenta; Ina, Takuya; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 29, 3 Pages, 2024/06
Gas-liquid two-phase flow analysis is one of the most important research topics in nuclear engineering because it is essential for safety evaluation and reactor design. However, it requires large-scale multi-scale simulations, and advanced numerical approaches are needed. To meet this challenge, we have continued to develop the Poisson solver for the multiphase flow analysis code JUPITER. In this study, we aim to improve the convergence of the pressure Poisson solver by formulating the Navier-Stokes equation without using the incompressible approximation. The convergence performance was measured on 8 GPUs for bubbly flow analysis in a circular tube. The results show that the computation time and the number of iterations are reduced by half compared to those using the incompressible approximation, which indicates the usefulness of the formulation in the present study.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sugihara, Kenta*
Physical Review C, 109(5), p.054610_1 - 054610_12, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Nuclide production cross sections are crucial in nuclear research, development, space exploration, and astrophysical investigations. Despite their importance, limited experimental data availability restricts the practicality of phenomenological approaches to comprehensive cross-section estimation. To address this, we propose a Gaussian process-based machine learning (ML) model capable of transferring knowledge from elements with abundant data to those with limited or no experimental data. Our ML model not only enables comprehensive cross-section estimations for various elements but also demonstrates predictive capabilities akin to physics models, even in regions with scarce training data.
 Mg,
Mg,  Si,
Si,  Fe,
Fe,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Zn
ZnSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 549, p.165299_1 - 165299_12, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.127 - 135, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:144 Percentile:99.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
 Ti and
Ti and  Nb at 0.8 and 3.0 GeV
Nb at 0.8 and 3.0 GeVSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 545, p.165153_1 - 165153_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Instruments & Instrumentation) Pb and
Pb and  Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeV
Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeVIwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sugihara, Kenta*;  elik, Y.*; et al.
elik, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165107_1 - 165107_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The lack of double-differential cross-section (DDX) data for neutron production below the incident proton energy of 200 MeV hinders the validation of spallation models in technical applications, such as research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs). The present study aims to obtain experimental DDX data for ADS spallation target materials in this energy region and identify issues related to the spallation models by comparing them with the analytical predictions. The DDXs for the (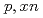 ) reactions of
) reactions of  Pb and
Pb and  Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30
Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30 to 150
to 150 using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamashita, Susumu
JAEA-Research 2023-006, 47 Pages, 2023/10
This report presents a new surface capturing method based on the phase field model for gas-liquid two-phase flows simulation. In the conventional phase field model, the interface correction strength parameter was determined from the maximum flow velocity in the computational domain, but because the interface correction was applied uniformly to the entire space, it was also applied to locations that did not require correction. In the new method, the phase field parameter or the intensity of the phase field model is extended to have a spatial distribution, allowing us to set the optimal parameters depending on the local flow velocity fields. We also propose a method to derive the optimal phase field parameter based on systematic parameter scans using error analysis of the interface advection test and bubble rising calculations. Through benchmark tests of gas-liquid two-phase flows, the proposed model is verified, and it is shown that the proposed model has higher accuracy than the conventional phase field model.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01023_1 - 01023_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron, lead, and bismuth have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics. The measured TTNYs and DDXs were compared with calculations by the Monte Carlo transport code PHITS with its default physics model of INCL version 4.6 combined with GEM and those with the JENDL-4.0/HE nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Nakano, Keita*; Sugihara, Kenta*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.132 - 136, 2023/01
J-PARC accelerator facility is the only accelerator facility in Japan that can provide proton beams in the energy range of 400 MeV or higher. In the J-PARC accelerator facility, it is difficult to install users' experimental equipment inside the proton beam duct in order to maintain stable user operation. In addition, due to the characteristics of the synchrotron accelerator, it is not possible to supply a low-intensity beam enough to confirm the detector. In addition, it is important to improve the intranuclear cascade model (INCL) for high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as accelerator-driven transmutation systems (ADS), etc. In order to improve the INCL, DDX of the forward-most emitted particles is important, but new data should be obtained since there are few experimental data available. In order to promote space utilization and to improve the accuracy of the INCL, energy spectra of scattered protons at the Al beam window placed at the inlet of the 3NBT dump were measured. In the experiment, plastic scintillators were used with 400 MeV proton beam. The results show that the spectra have sharp peaks due to elastic scattering. The calculation of the PHITS code using INCL reproduced the sharp peak due to elastic scattering well, although it overestimated the contribution of quasi-elastic scattering in the experimental data. In conclusion, it is clear that the present method can be used to utilize protons in several GeV regions for space exploration.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 409, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Seiya*; Kawahara, Jun*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Sugihara, Kenta; Takase, Shinsuke*; Moriguchi, Shuji*; Hashimoto, Hirotada*
Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 17(1), p.2211143_1 - 2211143_23, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:85.26(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)In tsunami inundations or slope disasters of heavy rain, a lot of floating debris or driftwood logs are included in the flows. The damage to structures from solid body impacts is more severe than the damage from the water pressure. In order to study free-surface flows that include floating debris, developing a high-accurate simulation code of free-surface flows with high performance for large-scale computations is desired. We propose the single-phase free-surface flow model based on the cumulant lattice Boltzmann method coupled with a particle-based rigid body simulation. The discrete element method calculates the contact interaction between solids. An octree-based AMR (Adaptive Mesh Refinement) method is introduced to improve computational accuracy and time-to-solution. High-resolution grids are assigned near the free surfaces and solid boundaries. We conducted two kinds of tsunami flow experiments in the 15 and 70 m water tanks at Hachinohe Institute of Technology and Kobe University to validate the accuracy of the proposed model. The simulation results have shown good agreement with the experiments for the drifting speed, the number of trapped wood pieces, and the stacked angles.
Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamashita, Susumu
Dai-36-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/12
The conventional Allen-Cahn type multi-phase field method was modified to conserve not only the sum of the masses of all phases but also the mass of each phase. The interface advection calculations within a two-dimensional rotational velocity field were performed as a verification problem, and the conservation was successfully achieved. The proposed method was used to calculate the horizontally aligned pair of bubbles rising, and it was found that the bouncing phenomenon between bubbles can be calculated at 1/50 resolution of the high-resolution calculation by Zhang et al. using the volume of fluid method.
Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamashita, Susumu
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 5 Pages, 2022/06
The phase-field method has been successfully applied to various multi-phase flow problems as an interface tracking method for gas-liquid interfaces. However, the accuracy of the phase-field method depends on hyper-parameters, which are empirically adjusted for each problem. The phase-field method sustains sharp interfaces by the balance between the numerical viscosity of the advection term and the interface modification by the diffusion and anti-diffusion terms. Based on this fact, we propose a method for deriving the optimal hyper-parameters in a non-empirical manner by performing a basic error analysis of the interface advection.
Yamada, Tomonori; Yamashita, Susumu; Sugihara, Kenta; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 89(7), p.500 - 506, 2013/08
no abstracts in English