Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nauchi, Yasushi*; Nomi, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Risa; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Shiba, Tomooki; Takada, Akira*; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Okumura, Keisuke
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
Shiba, Tomooki; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Nomi, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Risa; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Takada, Akira*; Nagatani, Taketeru; Okumura, Keisuke
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/10
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Shurshakov, V. A.*; Yarmanova, E. N.*; Nikolaev, I. V.*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Sihver, L.*; Mancusi, D.*; Endo, Akira; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
Cosmic Research, 49(4), p.319 - 324, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.15(Engineering, Aerospace)HZE particle transport codes are the indispensable tool in the shielding design of spacecrafts. We are therefore developing a general-purpose Monte Carlo code PHITS, which can deal with the transports of all kinds of hadrons and heavy ions with energies up to 200 GeV/n in 3-dimensional phase spaces. The applicability of PHITS to space researches has been well verified by comparing the neutron spectra in spacecrafts calculated by the code with the corresponding experimental data. Recently, PHITS was employed in the estimation of radiation fields in the Russian Service Module in ISS. The results of the estimation indicate that PHITS can reproduce experimental data of the dose reduction rates due to water shielding attached on the wall of the Russian crew cabin fairly well. The details of the calculation procedures will be given in the presentation, together with the results of other applications of PHITS to the space exploration.
Takahashi, Eiichi*; Kato, Susumu*; Furutani, Hirohide*; Sasaki, Akira; Kishimoto, Yasuaki*; Takada, Kenji*; Matsumura, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Hiroyasu*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 44(30), p.302001_1 - 302001_4, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.09(Physics, Applied)A recently developed ultrafast camera that can acquire 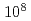 frames per second was used to investigate positive streamer discharge. It enabled single-shot evaluation of streamer evolution without the need to consider shot-to-shot reproducibility. This camera was used to investigate streamers in argon. Growing branches, the transition when a streamer forms a return stroke, and related phenomena were clearly observed.
frames per second was used to investigate positive streamer discharge. It enabled single-shot evaluation of streamer evolution without the need to consider shot-to-shot reproducibility. This camera was used to investigate streamers in argon. Growing branches, the transition when a streamer forms a return stroke, and related phenomena were clearly observed.
Tajikara, Masayoshi; Takada, Keita*; Furusawa, Akira*; Sugai, Toshihiko
Dai Yonki Kenkyu, 50(1), p.21 - 34, 2011/02
Three major fluvial terraces are developed well along the Kabura-gawa river, tributary of the Tone-gawa river. We detected cryptotephras in overbank and aeolian deposits covering the middle terrace gravels, and examined petrologic character. We also investigated petrologic character of the Iizuna-Kamitaru tephra (In-Kt) and the Iizuna-Nishiyama (In-Ny) tephra extracted from the outcrops near the Iizuna volcano. Based on these data, we identified possibly In-Kt and In-Ny tephra at the bottom of overbank deposits on the middle terrace of the Kabura-gawa river. This indicates that the middle terrace was formed through aggradation at glacial age of marine oxygen isotope stage 6. The Kabura-gawa river basin is located out of the previously reported distribution area of In-Kt. This fact implies that In-Kt is distributed more widely in the northern Kanto and southern Tohoku regions, and that In-Kt is useful as marker tephra of the middle Pleistocene in these regions.
 carbon beam
carbon beamTsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 143(2-4), p.450 - 454, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.88(Environmental Sciences)A wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter, wall-less TEPC, has been designed and used for the measurement of the y distributions for energetic heavy ions in order to verify a biological dose calculation model incorporated in the PHITS code. It is found that the dose-mean value of y obtained by the wall-less TEPC is 50 - 60% of the LET of the argon ions in water, since the delta-rays with relatively low y can be measured.
Takada, Masashi*; Yajima, Kazuaki*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Baba, Mamoru*; Homma, Toshihiro*; Endo, Akira; Tanimura, Yoshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(10), p.917 - 931, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.13(Nuclear Science & Technology)A phoswich-type neutron detector was developed in order to measure high-energy cosmic-ray neutron spectrum in aircrafts. The neutron detector consists of a 121.7 mm diameter and a 121.7 mm long EJ309 organic liquid scintillator covered with a 15 mm thick EJ299-13 outer plastic scintillator. Neutron response functions of the detector are required for an unfolding method to get the energy spectrum. The neutron response functions were evaluated from measurements using quasi-monoenergetic neutron sources of various peak energies from 35 to 78 MeV and from the MCNPX simulation. Light output and scintillation attenuation in the scintillator were measured for proton, deuteron and helium-ion beams. The measured neutron response functions well agreed with the MCNPX simulation. Neutron response matrix was created up to 300 MeV neutron energy based on the MCNPX simulation in order to cover the wide neutron energy range in the fight experiment. Photon response matrix also was created up to 50 MeV.
 C beam
C beamTsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 55(17), p.5089 - 5101, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:59.44(Engineering, Biomedical)The frequency distribution of the lineal energy of 290 MeV/u carbon beam was measured using a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter (wall-less TEPC) in a cylindrical volume with simulated diameter 0.72  m in verifying the accuracy of a dose calculation model. The measured lineal energy distribution as well as its dose-mean value agreed fairly well with the corresponding data from microdosimetric calculations using the PHITS code within the experimental uncertainty. It is found that a wall-less TEPC is needed to measure the precise energy deposition spectra of the delta rays produced secondarily by energetic heavy ion beams. The measured data also indicate that more than 11% of the energy escaped from the path of the trajectory of the carbon beam.
m in verifying the accuracy of a dose calculation model. The measured lineal energy distribution as well as its dose-mean value agreed fairly well with the corresponding data from microdosimetric calculations using the PHITS code within the experimental uncertainty. It is found that a wall-less TEPC is needed to measure the precise energy deposition spectra of the delta rays produced secondarily by energetic heavy ion beams. The measured data also indicate that more than 11% of the energy escaped from the path of the trajectory of the carbon beam.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
HIMAC-134 (CD-ROM), p.227 - 228, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
KEK Proceedings 2009-12, p.36 - 44, 2010/01
Knowledge of energy deposition at micrometer dimensions along heavy ion tracks is essential to understand the biological effects of radiation. Wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter (wall-less TEPC) was produced for the purpose of measurement of lineal energy distribution including secondary-produced high-energy electrons, delta-rays. The measurement using the wall-less TEPC was performed at Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator at NIRS, Japan. It is found that lineal energy distributions could be measured for primary carbon beam with energy of 400MeV per nucleon and delta-rays. Detail of the experiment, energy calibration and estimation of delta-rays production will be presented.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Takada, Masashi*; Yajima, Kazuaki*; Nakamura, Takashi
Nuclear Technology, 168(1), p.113 - 117, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)The details of the features of DARWIN will be presented at the meeting, together with the recent improvements of the system such as the implementation of the function for estimating neutron spectra using the unfolding technique.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
NIRS-M-226, HIMAC-132, p.264 - 265, 2009/06
A wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter was designed and applied to measuring deposit energy distribution of heavy ion beams, including the contribution of delta-rays produced along heavy ion tracks. Lineal energy distributions were obtained for 400 MeV/u carbon and 490 MeV/u silicon beams.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Takada, Masashi*; Yajima, Kazuaki*; Nakamura, Takashi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 99(1), P. 589, 2008/11
A dose monitoring system applicable to various radiations with wide energy ranges, DARWIN, has been developed for measuring dose rates in workspaces and surrounding environments of accelerator facilities. DARWIN satisfies the following features: (1) capable of monitoring doses from neutrons, photons and muons over wide energy ranges, from thermal energy to 1 GeV, 150 keV to 100 MeV, and 1 MeV to 100 GeV, respectively, (2) high sensitivity and precision, more than 10 times as sensitive as conventional moderator-based survey instruments for neutrons, (3) easy to operate with a simple user-interface, and (4) light weighted for movability. The commercial version of DARWIN is expected to be available in near future.
Hayashi, Koji; Shibata, Akira; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Sozawa, Shizuo; Takada, Fumiki; Omi, Masao; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
JAEA-Technology 2008-016, 51 Pages, 2008/03
The irradiation capsule 74M-52J was irradiated during total 136 cycles at reactor core of JMTR and the maximum neutron dose reached on 3.9 10
10 n/m
n/m at the capsule outer-tube made of a type 304 stainless steel. In order to produce mechanical test specimens from the outer tube, a punching technique was developed as a simple remote-handling method in a hot-cell. From comparison between the punching and the mechanical cutting methods, it was clarified that the punching technique was applicable to practical use. Moreover, an evaluation test of mechanical properties using specimens sampled from the 74M-52 was performed in-water high temperature condition, less than 288
at the capsule outer-tube made of a type 304 stainless steel. In order to produce mechanical test specimens from the outer tube, a punching technique was developed as a simple remote-handling method in a hot-cell. From comparison between the punching and the mechanical cutting methods, it was clarified that the punching technique was applicable to practical use. Moreover, an evaluation test of mechanical properties using specimens sampled from the 74M-52 was performed in-water high temperature condition, less than 288 C. The result shows that the residual elongation is 18% at 150
C. The result shows that the residual elongation is 18% at 150 C and 13% at 288
C and 13% at 288 C. It was confirmed that the type 304 stainless steel irradiated up to such high dose shows enough ductility.
C. It was confirmed that the type 304 stainless steel irradiated up to such high dose shows enough ductility.
Satoh, Daiki; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Takada, Masashi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Takashi; Niita, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 583(2-3), p.507 - 515, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:84.69(Instruments & Instrumentation)Previously-published data of secondary neutron spectra from thick targets of C, Al, Cu and Pb bombarded with heavy ions from He to Xe are revised by using a new set of neutron-detection efficiency values for a liquid organic scintillator calculated with SCINFUL-QMD. Additional data have been measured for bombardment of C target by 400-MeV/nucleon C ions and 800 MeV/nucleon Si-ions. The set of spectra are compared with the calculation results using a Monte-Carlo heavy-ion transport code, PHITS. It was found that PHITS is able to reproduce the secondary neutron spectra in a wide neutron-energy regime.
Satoh, Daiki; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*; Takada, Masashi*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 126(1-4), p.555 - 558, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.38(Environmental Sciences)In order to assess the neutron dose with DARWIN, a set of reliable response functions for neutron is required. Although the response function for neutron has been already determined below 100 MeV, the evaluation method is not established for high-energy neutrons. This is a reason to restrict the applicable energy of DARWIN at 100 MeV. To extend the applicable energy, we developed SCINFUL-QMD code which is capable of calculating the response function up to a few GeV. To verify the SCINFUL-QMD, response functions above 100 MeV have been measured at the HIMAC of National institute of Radiological Sciences. Neutrons were produced by bombardment 800 MeV/u Si and 400 MeV/u C ions with a graphite target. The experimental results showed a good agreement with predictions of SCINFUL-QMD. The G-function was evaluated up to 1 GeV based on the calculation of SCINFUL-QMD.
Satoh, Daiki; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Takada, Masashi*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*; Sato, Shinji*
NIRS-M-203 (CD-ROM), p.198 - 199, 2007/06
An innovative intelligent neutron monitor named "DARWIN" was applied to measuring dose in a high-energy neutron field produced through nuclear spallation by 800-MeV/u Si-ion bombardment with a thick graphite target. The measured dose was compared with calculated dose from neutron spectrum in the field. The comparison validated the reliability of DARWIN for dose measurement against high-energy neutrons.
Shibata, Akira; Takada, Fumiki
JAEA-Technology 2007-031, 24 Pages, 2007/03
The fracture toughness which represents resistance for brittle or ductile fracture is one of the most important material property concerning linear and non-linear fracture mechanics analyses. In order to respond to needs of collecting data relating to fracture toughness of pressure vessel and austenitic stainless steels, fracture toughness test for irradiated materials has been performed in JMTR Hot Laboratory. On the other hand, there has been no computer program for analysis of fracture toughness using the test data obtained from the test apparatus installed in the hot cell. Therefore, only load-displacement data have been provided to users to calculate fracture toughness of irradiated materials. Recently, request of analysis of fracture toughness have been increased. Thus a computer program, which calculates the amount of the crack extension, the compliance and the fracture toughness from the data acquired from the test apparatus installed in the hot cell, has been developed. In the program unloading elastic compliance method is applied based on ASTM E1820-01. Through the above development, the request for the fracture toughness analysis can be satisfied and the fracture toughness of irradiated test specimens can be provided to users.
Satoh, Daiki; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Takada, Masashi*; Ishibashi, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(7), p.714 - 719, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:90.13(Nuclear Science & Technology)Response functions of a BC501A liquid organic scintillator for neutrons up to 800MeV have been measured at the heavy-ion medical accelerator of the National Institute of Radiological Sciences, Japan. A thick graphite target was bombarded with 400-MeV/u C ions and 800-MeV/u Si ions to produce high-energy neutrons whose kinetic energy was determined by the time-of-flight method. The measured response functions were compared with the results calculated using SCINFUL-QMD code, which experimentally verified the accuracy of SCINFUL-QMD up to 800MeV. This work will contribute to extending the energies measurable with our new radiation dose-monitoring system (DARWIN), which is based on the BC501A scintillator.
Satoh, Daiki; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*; Sato, Shinji*; Takada, Masashi*
NIRS-M-192, p.224 - 225, 2006/05
Light output of liquid organic scintillator NE213 has been measured for proton, deuteron, triton,  He nucleus and alpha particle. A thick graphite target was bombarded with 400-MeV/u C ions to the produce charged particles. Time-of-flight method was adopted to determine the kinetic energy of the charged particles. Light output for proton was also measured using mono-energy beams of 100 and 160 MeV. The experimental results gave a new database of light output.
He nucleus and alpha particle. A thick graphite target was bombarded with 400-MeV/u C ions to the produce charged particles. Time-of-flight method was adopted to determine the kinetic energy of the charged particles. Light output for proton was also measured using mono-energy beams of 100 and 160 MeV. The experimental results gave a new database of light output.