Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
高見澤 悠; Lu, K.*; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 210, p.105219_1 - 105219_7, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)確率論的破壊力学(PFM)に基づく原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の構造健全性評価では、RPVの中性子照射脆化について、脆化予測の平均値と不確かさの両方を考慮することが極めて重要である。通常、脆化予測の不確かさは正規分布で与えられ、その標準偏差は脆化予測手法の開発に使用されたすべてのデータの測定値と予測値の残差から決定される。したがって、中性子照射量、周辺のデータの数やばらつきにかかわらず、同一の標準偏差が仮定される。日本原子力研究開発機構では、機械学習とベイズ統計に基づくノンパラメトリックベイズ(BNP)法を用いた脆化評価手法を開発し、PFM解析コードに導入した。BNP法は、実測データのばらつきが大きく、データ数が少ない場合に有意な不確かさを推定するため、データの希少性に応じた確率分布を予測することができ、より合理的な不確かさを与えることができる。本研究では、高経年化した日本の加圧水型軽水炉におけるRPVを対象としたPFM解析を実施し、異なる脆化評価手法や不確かさがRPVの破損頻度に及ぼす影響について調べた。その結果、BNP法に基づく脆化評価手法を用いた場合に、破損頻度が高くなるものの、その差はわずかであることから、既存の脆化評価手法の妥当性を示した。
Lu, K.; 高見澤 悠; Li, Y.; 眞崎 浩一*; 高越 大輝*; 永井 政貴*; 南日 卓*; 村上 健太*; 関東 康祐*; 八代醍 健志*; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.22-00484_1 - 22-00484_13, 2023/08
A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code, PASCAL, has been developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency for failure probability and failure frequency evaluation of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and thermal transients. To strengthen the applicability of PASCAL, considerable efforts on verifications of the PASCAL code have been made in the past years. As a part of the verification activities, a working group consisted of different organizations from industry, universities and institutes, was established in Japan. In the early phase, the working group focused on verifying the PFM analysis functions for RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) subjected to pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. Recently, the PASCAL code has been improved in order to run PFM analyses for both RPVs in PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs) subjected to a broad range of transients. Simultaneously, the working group initiated a verification plan for the improved PASCAL through independent PFM analyses by different organizations. Concretely, verification analyses for a PWR-type RPV subjected to PTS transients and a BWR-type RPV subjected to a low-temperature over pressure transient were performed using PASCAL. This paper summarizes those verification activities, including the verification plan, analysis conditions and results. Based on the verification studies, the reliability of PASCAL for probabilistic integrity assessments of Japanese RPVs was confirmed with confidence.
下平 昌樹; 河 侑成; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 鬼沢 邦雄
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/07
最新の原子炉圧力容器の構造健全性評価においては、マスターカーブ法に基づく正確な破壊靭性参照温度T の取得が必要である。破壊靭性参照温度T
の取得が必要である。破壊靭性参照温度T はMini-C(T)破壊靭性試験片によって取得可能であり、この試験片の寸法や初期亀裂形状に関しては、ASTM規格のE1921や日本電気協会電気技術規程JEAC4216に規定されている。最近、ASTM E1921では評価の正確性や試験を行う上での利便性を向上させるために、何度か予亀裂形状に関する規定の変更が行われてきた。このような規格の改定に伴うMini-C(T)試験片の許容予亀裂形状の変化は、予亀裂先端の塑性拘束状態を変化させ、T
はMini-C(T)破壊靭性試験片によって取得可能であり、この試験片の寸法や初期亀裂形状に関しては、ASTM規格のE1921や日本電気協会電気技術規程JEAC4216に規定されている。最近、ASTM E1921では評価の正確性や試験を行う上での利便性を向上させるために、何度か予亀裂形状に関する規定の変更が行われてきた。このような規格の改定に伴うMini-C(T)試験片の許容予亀裂形状の変化は、予亀裂先端の塑性拘束状態を変化させ、T 評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、ASTM E1921やJEAC4216に規定される予亀裂形状に関する要求の妥当性について議論するため、Mini-C(T)試験片の予亀裂湾曲が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響について、ワイブル応力解析を含む有限要素解析によって定量的に評価した。その結果、ASTM E1921-21で定められた最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合、亀裂先端の塑性拘束が弱められ、理想的な直線状亀裂を有するMini-C(T)試験片で得られる破壊靭性値に比べて高めの破壊靭性値が得られる可能性を示した。また、上述の最大湾曲を許容した場合、非保守的なT
評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、ASTM E1921やJEAC4216に規定される予亀裂形状に関する要求の妥当性について議論するため、Mini-C(T)試験片の予亀裂湾曲が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響について、ワイブル応力解析を含む有限要素解析によって定量的に評価した。その結果、ASTM E1921-21で定められた最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合、亀裂先端の塑性拘束が弱められ、理想的な直線状亀裂を有するMini-C(T)試験片で得られる破壊靭性値に比べて高めの破壊靭性値が得られる可能性を示した。また、上述の最大湾曲を許容した場合、非保守的なT が取得されることをワイブル応力解析によって示した。一方、JEAC4216で許容される最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合は、理想的な直線状亀裂の場合と比べてT
が取得されることをワイブル応力解析によって示した。一方、JEAC4216で許容される最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合は、理想的な直線状亀裂の場合と比べてT の有意な差は見られなかった。
の有意な差は見られなかった。
山口 義仁; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/07
原子炉圧力容器のノズル部の健全性評価において、ノズルコーナー亀裂に対する応力拡大係数が重要なパラメータである。これまで、ノズルコーナーの表面亀裂に対する様々な応力拡大係数解が提案されてきたが、その多くは亀裂の最深点にのみ着目しており、ノズルコーナーの形状寸法に関する情報は明らかになっていない。ノズルコーナー亀裂を対象とした既往の疲労試験結果によると、亀裂表面点における進展量は、最深点よりも大きいことが明らかとなっている。このことから、亀裂表面点の応力拡大係数は最深点よりも高い可能性がある。これらより、本研究では、健全性評価の信頼性を高めるため、有限要素解析を通じて、ノズルコーナーの形状寸法とき裂サイズに対応した、表面点と最深点の両方の応力拡大係数解を提案する。
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 145(2), p.021501_1 - 021501_9, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:13.27(Engineering, Mechanical)The fracture toughness in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), which is located under the weld overlay cladding on the inner surface of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV), was evaluated by considering the inhomogeneous microstructures of the HAZ. In this regard, 0.4T-C(T) specimens and Mini-C(T) specimens were manufactured to clarify the effect of the HAZ on fracture toughness. First, the fracture toughness was evaluated using 0.4T-C(T) specimens targeted on microstructural distribution due to the cladding bead location. The reference temperature (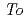 ) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12
) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12 C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The
C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The 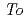 value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the
value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the 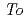 values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40
values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40 C
C 60
60 C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; 高見澤 悠; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2022-012, 39 Pages, 2023/02
供用年数の増加に伴い、発電用軽水型原子炉圧力容器(RPV)では炉心からの中性子照射により破壊靭性が低下する、いわゆる中性子照射脆化が生じる。国内では、RPVの非延性破壊を防止するため、この中性子照射脆化や、健全性評価上最も厳しい事象の1つである加圧熱衝撃事象(PTS)を考慮して、日本電気協会規程等に基づく決定論的手法により健全性評価が行われている。一方、欧米においては、近年確率論的手法の規制への導入が進んでいる。例えば米国では、PTS評価において、確率論的手法に基づく関連温度に関するスクリーニング基準が規定されており、またそのスクリーニング基準を満足しない場合には確率論的手法に基づく亀裂貫通頻度(TWCF)を指標とした評価の実施が認められている。また、供用期間中検査の試験程度や検査間隔の緩和の検討等にも確率論的手法が適用されている。ここで、確率論的手法とは具体的には確率論的破壊力学(PFM)に基づく健全性評価手法であり、長期供用に伴う機器の経年劣化に関連する様々な因子の不確実さ等を考慮して、合理的に機器の破損確率や破損頻度等を算出できる方法である。こうした背景を踏まえ、国内のRPVに対するPFMに基づく健全性評価の実施を念頭に、国内外の最新知見や専門家の意見等を反映するとともに、主として加圧水型原子炉のRPVを対象に開発が進められたPFM解析コードPASCALの整備、及びPASCALによる感度解析等により得られた知見を取りまとめて、2017年に標準的解析要領を整備し、JAEA-Research2016-022として公開した。この標準的解析要領では、破壊力学に関する知識を有する解析担当者がこれを参照することでPFM解析を実施し、TWCF等の確率論的数値指標を算出できることを目的としている。2017年以降、PFMに基づく健全性評価の更なる実用化に向けて、日本原子力研究開発機構において、沸騰水型原子炉のRPVに対するPFM解析を可能にするため、PASCALの機能を拡充するとともに、標準的解析要領の充実化を図った。本報告はその成果をまとめたものである。本報告は、以下の5つの章で構成される。まず第1章で、本報告の背景及び概要について述べる。次に第2章で、標準的解析要領の枠組みと対象範囲について述べた後、第3章にて標準的解析要領の詳細について記述する。PASCALに対する信頼性確認事例についても同章で記す。第4章では、標準的解析要領を満足し、国内の現状の代表的事例として適切と考えられる手法
高見澤 悠; Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; 眞崎 浩一*; 宮本 裕平*; Li, Y.
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-006, 221 Pages, 2023/02
原子炉圧力容器(RPV: Reactor Pressure Vessel)は原子炉冷却材圧力バウンダリを構成する重要機器の1つであり、中性子照射等に伴う高経年化を考慮した構造健全性確保が極めて重要である。国立研究開発法人日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA: Japan Atomic Energy Agency)では、RPVの構造健全性評価に関する研究の一環として、確率論的破壊力学(PFM: Probabilistic Fracture Mechanics)解析コードPASCAL(PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWR)の開発を進めている。本コードは、加圧水型軽水炉(PWR: Pressurized Water Reactor)及び沸騰水型軽水炉(BWR: Boiling Water Reactor)を対象に、影響因子が持つ不確実さを考慮し、加圧熱衝撃(PTS: Pressurized Thermal Shock)事象や低温過圧事象(LTOP: Low-Temperature Over Pressure)等の過渡によるRPVの炉心領域部の破損確率や破損頻度を求めるものである。破壊力学や確率論的計算手法等に関する最新知見や国内RPVに適した評価手法・評価モデルを踏まえ、新規解析機能の導入を進めるとともに、系統的なコード検証活動を通じて信頼性向上を図ってきた。平成12年度に公開したPASCALでは、PWRのPTS事象を対象に、RPVの破損確率を解析する基本的な枠組みを整備した。平成18年度に公開したPASCAL2では、内部亀裂の評価手法や様々な非破壊検査による亀裂の検出性に関する評価モデル等を導入し、過渡事象データベースを整備した。平成22年度に公開したPASCAL3では、肉盛溶接クラッド部に着目して、亀裂の評価機能等を改良した。平成29年度に公開したPASCAL4では、応力拡大係数解や破壊靭性の不確実さを考慮した評価モデル等の改良により解析機能の高度化を図るとともに、影響因子の不確実さを認識論的不確実さと偶然的不確実さに分類し、不確実さを考慮した信頼度評価機能等を整備した。平成30年度以降は、これまでPWRのPTS事象を対象としたRPV内面側亀裂の評価機能に加えて、BWRの起動事象、LTOP事象等を想定したRPV外面側亀裂の評価機能等の整備を進めてきた。これらの機能整備を踏まえ、国内PWR及びBWRのRPVを対象とした確率論的健全性評価に資する解析コードとして、PASCAL5へとバージョンアップした。PASCAL5はPFM解析モジュールであるPASCAL-RV、PASCAL-RVの入力データの生成やRPV炉心領域部を対象とした破損頻度の算出を行うモジュールであるPASCAL-Manager、付録として附属する簡易的な熱応力解析を
Lu, K.; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 199, p.104706_1 - 104706_13, 2022/10
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:53.83(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL was developed in Japan for probabilistic integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) transients. To strengthen the practical applications of PFM methodology in Japan, PASCAL has been upgraded to a new version, PASCAL5, which enables PFM analyses of RPVs in both PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs) subjected to a broad range of transients, including PTS and normal operational transients. In this paper, the recent improvements in PASCAL5 are described such as the incorporated stress intensity factor solutions and corresponding calculation methods for external surface cracks and embedded cracks near the RPV outer surface. In addition, the analysis conditions and evaluation models recommended for PFM analyses of Japanese RPVs in BWRs are investigated. Finally, PFM analysis examples for core region of a Japanese BWR-type model RPV subjected to two transients (i.e., low-temperature over pressure and heat-up transients) are presented using PASCAL5.
下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 塙 悟史
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011304_1 - 011304_7, 2022/02
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.96(Engineering, Mechanical)JEAC4206-2016における原子炉圧力容器の構造健全性評価では、材料の破壊靭性が、想定欠陥であるクラッド下半楕円亀裂の先端における応力拡大係数よりも高いことが求められている。しかしながら、破壊靭性試験片と想定亀裂の亀裂深さやクラッドの有無といった違いにより、塑性拘束状態や破壊靭性評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、クラッド下亀裂が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響を調べるため、3点曲げ破壊靭性試験及び有限要素解析を実施した。その結果、クラッド下亀裂の塑性拘束が表面亀裂のそれに比べて弱いことを解析によって示した。さらに、クラッド下亀裂の弱い塑性拘束の影響により、クラッド下亀裂の破壊靭性が表面亀裂よりも見かけ上高くなることを実験及びローカルアプローチによって明らかにした。
岩田 景子; 高見澤 悠; 河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 岡本 芳浩; 本田 充紀; 勝山 仁哉; 西山 裕孝
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.143 - 152, 2022/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:31.55(Instruments & Instrumentation)The main causes of the irradiation embrittlement of RPVs are the formation of a solute cluster and the matrix defect. To investigate these embrittlement mechanisms, it is necessary to complementarily apply microstructure analyses. The extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) technique can detect changes in the atomic structure because of a vacancy-type defect or interstitial atoms introduced by irradiation around selected atoms. In this study, to investigate such microstructural changes due to irradiation, we performed an EXAFS examination for high-copper RPV steels subjected to ion irradiation. We investigated microstructures of the crystal structure around specific element such as Cu, Mn, and Ni, which are known to be the atoms included in the solute atom clusters and lattice defects such as vacancy-type defects. The results indicated that the solute atoms clusteris thought to aggregate in the Fe matrix while maintaining the bcc structure and that not only a vacancy-type defect but also a tensile configuration-type dumbbell pair could be located around both Cu and Ni atoms.
高見澤 悠; 端 邦樹; 西山 裕孝; 外山 健*; 永井 康介*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153203_1 - 153203_10, 2021/12
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:39.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)原子炉圧力容器鋼における中性子照射脆化に及ぼすシリコンの影響を明らかにするため、三次元アトムプローブにより、高照射量領域まで中性子照射された監視試験片中の溶質原子クラスタを分析した。高Cu含有材では、Ni, Mn, Siがクラスタ中心のCu原子を囲むように凝集し、コアシェル構造を形成するのに対して、低Cu含有材ではNi, Mn, Siがクラスタ中を均一に分布していた。クラスタ内のCu原子の数はCu含有量の減少と共に減少したが、それを補うようにSi原子数が増加した。材料中の公称のSi含有量の増加とともに、クラスタのギニエ半径は減少し、数密度が増加した。結果として、クラスタの体積率は一定であった。延性脆性遷移温度移行量とクラスタの体積率とギニエ半径の積の平方根が良い相関関係を示すことから、脆化の主要因は、溶質原子クラスタを転位が切断するメカニズムによる硬化であることが示された。また、Si含有量の増加により、クラスタの体積率は一定のままギニエ半径が減少することで脆化の程度を減少させることが示された。
高見澤 悠; 西山 裕孝
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(5), p.051502_1 - 051502_8, 2021/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:25.22(Engineering, Mechanical)本研究では、照射脆化予測に取込むべき化学成分を特定し、原子炉圧力容器鋼の照射脆化予測の不確実性を評価した。日本の加圧水型原子炉の監視試験データに対してノンパラメトリックベイズ(BNP)法を用いた統計分析を行った。BNP法は入力データの複雑さと不確かさを考慮可能な機械学習手法である。脆化への影響が大きい入力変数の組合せを評価可能な統計的指標を導入し、中性子照射量, Cu, Ni, Si含有量の4つの変数の組合せが脆化予測に最も効果的であることを明らかにした。また、化学成分では脆化量に対してCu含有量の影響が最も大きく、Ni, Siの順番で影響が大きいことを示した。関連温度移行量( RT
RT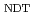 )をBNP法を用いて算出した結果、計算値と実測値の残差の標準偏差は8.4
)をBNP法を用いて算出した結果、計算値と実測値の残差の標準偏差は8.4 Cであり、現行の国内脆化予測法(JEAC4201-2007(2013年追補))と同等かそれ以上の予測性有していることを確認した。BNP法によって計算された
Cであり、現行の国内脆化予測法(JEAC4201-2007(2013年追補))と同等かそれ以上の予測性有していることを確認した。BNP法によって計算された RT
RT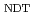 の事後分布の95%確信区間(入力データの不確実性を考慮した場合にデータが存在し得る範囲)は国内脆化予測法のマージンと同等かそれよりも小さく、JEAC4201-2007(2013年追補)において、適切なマージンが設定されていることを定量的に示した。
の事後分布の95%確信区間(入力データの不確実性を考慮した場合にデータが存在し得る範囲)は国内脆化予測法のマージンと同等かそれよりも小さく、JEAC4201-2007(2013年追補)において、適切なマージンが設定されていることを定量的に示した。
岩田 景子; 端 邦樹; 飛田 徹; 廣田 貴俊*; 高見澤 悠; 知見 康弘; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
The crack arrest fracture toughness, K , values for highly-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels are estimated according to a linear relationship between crack arrest toughness reference temperature, T
, values for highly-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels are estimated according to a linear relationship between crack arrest toughness reference temperature, T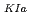 , and the temperature corresponding to a fixed arrest load, equal to 4 kN, T
, and the temperature corresponding to a fixed arrest load, equal to 4 kN, T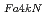 , obtained by instrumented Charpy impact test. The relationship between T
, obtained by instrumented Charpy impact test. The relationship between T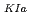 derived from the instrumented Chrapy impact test and fracture toughness reference temperature, T
derived from the instrumented Chrapy impact test and fracture toughness reference temperature, T , was expressed as an equation proposed in a previous report. The coefficients in the equation could be fine-tuned to obtain a better fitting curve using the present experimental data and previous K
, was expressed as an equation proposed in a previous report. The coefficients in the equation could be fine-tuned to obtain a better fitting curve using the present experimental data and previous K data. The K
data. The K curve for RPV;A533B class1 steels irradiated up to 1.3
curve for RPV;A533B class1 steels irradiated up to 1.3 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV) was compared with a K
1 MeV) was compared with a K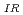 curve defined in JEAC4206-2016. It was shown that the K
curve defined in JEAC4206-2016. It was shown that the K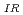 curve was always lower than the 1%ile curve of K
curve was always lower than the 1%ile curve of K for these irradiated RPV steels. This result indicates that the conservativeness of the method defined in JEAC4206-2016 to evaluate K
for these irradiated RPV steels. This result indicates that the conservativeness of the method defined in JEAC4206-2016 to evaluate K using K
using K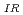 curve is confirmed for highly-irradiated RPV steels.
curve is confirmed for highly-irradiated RPV steels.
河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 高見澤 悠; 飛田 徹; 勝山 仁哉; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/07
The semi-elliptical crack sized 10 mm in depth  60 mm in length shall be postulated near the inner surface of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) in pressurized thermal shock events. We investigated the fracture toughness distribution in the postulated crack area under the PTS events of unirradiated and highly-neutron irradiated RPV steels. Vickers hardness in heat-affected zone (HAZ) due to stainless overlay cladding and 10 mm from the cladding were higher than that of a quarter thickness position, where the surveillance specimens are machined, for both unirradiated (E1) and irradiated (up to 1
60 mm in length shall be postulated near the inner surface of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) in pressurized thermal shock events. We investigated the fracture toughness distribution in the postulated crack area under the PTS events of unirradiated and highly-neutron irradiated RPV steels. Vickers hardness in heat-affected zone (HAZ) due to stainless overlay cladding and 10 mm from the cladding were higher than that of a quarter thickness position, where the surveillance specimens are machined, for both unirradiated (E1) and irradiated (up to 1  10
10 n/cm
n/cm , WIM) materials. Fracture toughness of HAZ and 10 mm from the cladding was higher for the above highly-neutron irradiated material. The same result was obtained in the unirradiated material. Therefore, it was confirmed that fracture toughness obtained from surveillance specimens can provide conservative assessment of structural integrity of RPV.
, WIM) materials. Fracture toughness of HAZ and 10 mm from the cladding was higher for the above highly-neutron irradiated material. The same result was obtained in the unirradiated material. Therefore, it was confirmed that fracture toughness obtained from surveillance specimens can provide conservative assessment of structural integrity of RPV.
河 侑成; 岡野 成威*; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 望月 正人*
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/07
Residual stress is one of the most important influence factors in the structural integrity assessment of the nuclear components. However, at the present, there are few examples of residual stress measurements for thick butt-welded plates such as the reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In this study, the residual stresses generated by butt-welding of thick plates of RPV steel, which have almost the same thickness of 140 mm as actual boiling water reactor RPV, were measured for post-welded heat-treated condition using the deep-hole-drilling technique. In addition, thermo-elastic-plastic creep analyses by or without considering the phase transformation in the heat-affected zone using the finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed to evaluate the residual stress produced by butt-welding and post-weld heat treatment. In the analysis considering phase transformation using the commercial FEM analysis code Abaqus, the fractions of the phases, such as martensite, bainite and ferrite, are calculated based on the kinetics of phase transformation. By comparing the analytical results with the experimentally determined values, we found good agreements for the residual stress distributions within the weld and the base material near the welded part. In the presentation, the effect of phase transformation on residual stress distribution of butt-weldment of thick plate will be discussed.
端 邦樹; 高見澤 悠; 北條 智博*; 海老原 健一; 西山 裕孝; 永井 康介*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 543, p.152564_1 - 152564_10, 2021/01
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:87.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)加圧水型軽水炉(PWR)または試験炉において0.3-1.2 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E 1MeV)の範囲で中性子照射された原子炉圧力容器鋼(リン含有量: 0.007-0.012wt.%)について、粒界リン偏析量をオージェ電子分光分析により測定した。粒界リン偏析量は照射量に依存して増加した。速度論に基づくシミュレーションでも同様の粒界リン偏析量の増加を確認した。また、リン含有量が0.015wt.%(現在の国内原子炉圧力容器鋼の最大値相当)の材料では、1.0
1MeV)の範囲で中性子照射された原子炉圧力容器鋼(リン含有量: 0.007-0.012wt.%)について、粒界リン偏析量をオージェ電子分光分析により測定した。粒界リン偏析量は照射量に依存して増加した。速度論に基づくシミュレーションでも同様の粒界リン偏析量の増加を確認した。また、リン含有量が0.015wt.%(現在の国内原子炉圧力容器鋼の最大値相当)の材料では、1.0 10
10 n/cm
n/cm まで照射した場合、粒界に偏析するリンの割合は10%程度増加することが予測された。PWR及び試験炉での照射材の結果を比較したところ、明確な照射速度効果は確認されなかった。文献データも含めたリン含有量0.026wt.%(海外炉のA533B鋼の中でも比較的高いリン含有量)までの材料に対して、粒界リン偏析量、照射硬化、延性脆性遷移温度(DBTT)シフトの各関係について調べたところ、照射硬化とDBTTシフトの間に直線関係が確認された。この直線関係は、このようなリン含有量の高い材料においてもDBTTの上昇は照射硬化で説明することができること、すなわち非硬化型脆化である粒界脆化の顕在化の可能性が低いことを示している。
まで照射した場合、粒界に偏析するリンの割合は10%程度増加することが予測された。PWR及び試験炉での照射材の結果を比較したところ、明確な照射速度効果は確認されなかった。文献データも含めたリン含有量0.026wt.%(海外炉のA533B鋼の中でも比較的高いリン含有量)までの材料に対して、粒界リン偏析量、照射硬化、延性脆性遷移温度(DBTT)シフトの各関係について調べたところ、照射硬化とDBTTシフトの間に直線関係が確認された。この直線関係は、このようなリン含有量の高い材料においてもDBTTの上昇は照射硬化で説明することができること、すなわち非硬化型脆化である粒界脆化の顕在化の可能性が低いことを示している。
鈴土 知明; 高見澤 悠; 西山 裕孝; Caro, A.*; 外山 健*; 永井 康介*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 540, p.152306_1 - 152306_10, 2020/11
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:74.60(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)熱時効したFe-Cr合金はスピノーダル分解によって硬化を引き起こし、これはいわゆる475C脆性の直接的な原因である。スピノーダル分解が原子的相互作用によってどのように硬化を引き起こすのかを示すため、数値シミュレーションと実験を実施した。数値的な結果では、硬さが短距離秩序(SRO)パラメーターと比例することを示され、実験でもこの関係を統計誤差内で再現した。どちらの結果も、隣接するCr-Cr原子ペアが本質的に硬化を引き起こすことを示唆した。なぜなら、SROがそのようなペアの出現確率に一意的に依存しているからである。硬化の主な原因がそのようなCr-Crペア付近を通過する転位のピン止め効果であることが示唆されたが、このアイデアはさらなるモデリング研究により裏付けられた。
下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 塙 悟史
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
JEAC4206「原子炉圧力容器に対する供用期間中の破壊靭性の確認方法」では、加圧熱衝撃事象時の原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の健全性評価において、原子炉圧力容器内面のステンレスオーバーレイクラッド(クラッド)下亀裂(UCC)を想定し、亀裂先端の応力拡大係数がRPV鋼の破壊靭性値を上回らないことを定めている。本研究では、クラッドの存在が破壊靭性値に与える影響を評価することを目的に、UCCまたは表面亀裂を有する試験体を用いた3点曲げ破壊靭性試験と有限要素解析(FEA)を行い、UCCに対する塑性拘束効果の影響を調べた。その結果、UCCの破壊靭性値が表面亀裂に比べて高いことを実験的に示した。また、有限要素解析により、クラッドの存在によりUCCの塑性拘束効果が弱められることを示した。
高見澤 悠; 西山 裕孝; 平野 隆*
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
原子炉圧力容器(RPV)は中性子照射前後のシャルピー衝撃試験で得られる延性脆性遷移温度(DBTT)に基づき中性子照射による材料劣化を予測した上で構造健全性評価が行われている。シャルピー衝撃試験で得られるDBTTには試験に依存した様々な不確かさが含まれる。本研究では、原子力機構がこれまでに取得したRPV鋼の未照射材・中性子照射材データを用いて、ベイズ統計に基づく解析モデルを構築し、試験片の採取位置のばらつき、試験片の数、試験温度を考慮した上でDBTTの不確かさを評価可能な手法を整備した。上記の手法を用いて国内RPV鋼に対する評価を行い、試験数や試験温度がDBTTの不確かさに及ぼす影響を定量的に明らかにした。
河 侑成; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 461, p.276 - 282, 2019/12
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:41.18(Instruments & Instrumentation)The microstructural distribution in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) under the stainless overlay cladding of low alloy steel was investigated by metallurgical observation and finite element analysis (FEA). The distribution of the coarse-grain (CG) HAZ and the fine-grain (FG) HAZ in low alloy steel by metallurgical observation agreed well with the FEA results. Base metal contained mixed bainite with ferrite, whereas the CGHAZ and the FGHAZ contained mixed lower bainite with martensite and mixed upper bainite with ferrite, respectively. Ferrite fraction in FGHAZ was higher than those other areas. After ion irradiation at a fluence of 0.5 dpa, irradiation hardening and the formation of solute clusters were observed at the base metal, FGHAZ, and the CGHAZ. Atom probe tomography analysis revealed that irradiation hardening increased with increasing volume fraction of clusters, although irradiation hardening at the FGHAZ was greater than that at the CGHAZ, which contained more clusters than the FGHAZ. This difference in irradiation hardening may be due to the differences in the amount of ferrite, carbide precipitates and so on in the different microstructures.