Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O; Journal of Risk and Reliability, 237(5), p.947 - 957, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.72(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is a method used to assess the risks associated with large and complex systems. However, the timing at which nuclear power plant structures, systems, and components are damaged is difficult to estimate if the risk of an external event is evaluated using conventional PRA based on event trees and fault trees. A methodology coupling thermal-hydraulic analysis with external event simulations using Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics (RAPID) is therefore proposed to overcome this limitation. A flood propagation model based on Bernoulli's theorem was applied to represent internal flooding in the turbine building of the pressurized water reactor. Uncertainties were also taken into account, including the flow rate of the floodwater source and the failure criteria for the mitigation systems. The simulated recovery actions included the operator isolating the floodwater source and using a drainage pump; these actions were modeled using several simplifications. Overall, the results indicate that combining isolation and drainage can reduce the conditional core damage probability upon the occurrence of flooding by approximately 90%.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2023-001, 26 Pages, 2023/05
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been developed using computer simulation programs to assess the radioactive source term from those facilities. The proposed approach consists analyses with three computer programs. At first, the simulation of boiling behavior in the HLLW tank is conducted with SHAWED code. Next step, the thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code based on the results at the first step simulation such as flowed out mixed steam flow rate, temperature and volatilized Ru from the tank. The final analysis step is carried out for estimating amount of released radioactive materials with SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitric acid, nitrogen oxide and Ru based on the condition also simulated MELCOR. Series of sample simulations of the accident at a hypothetical typical facility are presented with the data transfer between those codes in this report.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2022-011, 37 Pages, 2022/12
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing plant. Two major mechanisms are expected for fission products (FPs) transfer from liquid to vapor phase. One is non-volatiles FPs transfer in the form of mists to the vapor phase in the tank, the other is volatilization of such as Ruthenium. These FPs transferred to the vapor phase in the tank could be released with water and nitric-acid mixed steam and NO gas flow to the environment. NO
gas flow to the environment. NO is generated from denitration of nitrate fission products during dry out phase. These phenomena occurred in this accident originate from the liquid waste boiling in the tank. It is essential for the risk assessment of this accident to simulate thermo-hydraulic and chemical behaviors in the waste tank quantitatively with a versatile computer program. The SHAWED (
is generated from denitration of nitrate fission products during dry out phase. These phenomena occurred in this accident originate from the liquid waste boiling in the tank. It is essential for the risk assessment of this accident to simulate thermo-hydraulic and chemical behaviors in the waste tank quantitatively with a versatile computer program. The SHAWED (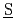 imulation of
imulation of 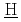 igh-level radio
igh-level radio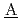 ctive
ctive 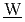 aste
aste 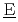 vaporation and
vaporation and 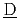 ryness) has been developed to realize these requirements. In this report, detailed description of major analytical models is explained based on the features of this accident, and some simulation examples are also described for the use in an actual risk assessment.
ryness) has been developed to realize these requirements. In this report, detailed description of major analytical models is explained based on the features of this accident, and some simulation examples are also described for the use in an actual risk assessment.
Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Takahara, Shogo; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM16) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/09
Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 223, p.108503_1 - 108503_12, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:91.89(Engineering, Industrial)Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-013, 20 Pages, 2022/01
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. An idea has been proposed to implement a steam condenser as an accident countermeasure. This measure is expected to prevent nitric acid steam diffusing in facility building and to increase gaseous Ru trapping ratio into condensed water. A simulation study has been carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building to analyze the efficiency of steam condenser. In this study, SCHERN computer code simulates chemical behaviors of Ru in nitrogen oxide, nitric acid and water mixed vapor based on the conditions obtained from simulation with thermal-hydraulic computer code MELCOR. The effectiveness of steam condenser has been analyzed quantitively in preventing mixed vapor diffusion and gaseous Ru trapping effect. Some issues to be solved in analytical model has been also clarified in this study.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-005, 25 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an empirical correlation equation of Ru mass transfer coefficient across the vapor-liquid surface, which can be useful for quantitative simulation of Ru mitigating behavior, has been obtained from data analyses of small-scale experiments conducted to clarify gaseous Ru migrating behavior under steam-condensing condition. A simulation study has been also carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building successfully to demonstrate the feasibility of quantitative estimation of amount of Ru migrating in the facility using the obtained correlation equation implemented in SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitrogen oxide based on the condition also simulated thermal-hydraulic computer code.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-008, 35 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides (NO ) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects to the migration behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NO
) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects to the migration behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NO with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. The analysis program, SCHERN has been under developed to simulate chemical behavior including Ru coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building. This technical guide for SCHERN-V2 presents the overview of covered accident, analytical models including newly developed models, differential equations for numerical solution, and user instructions.
with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. The analysis program, SCHERN has been under developed to simulate chemical behavior including Ru coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building. This technical guide for SCHERN-V2 presents the overview of covered accident, analytical models including newly developed models, differential equations for numerical solution, and user instructions.
Lind, T.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Nishi, Yoshihisa*; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Cousin, F.*; Fernandez Moguel, L.*; Andrews, N.*; Sevon, T.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 376, p.111138_1 - 111138_12, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:93.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)This is the third part of the three part paper describing the accidents at the FDNPS as analyzed in the Phase 2 of the OECD/NEA project "Benchmark Study of the Accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant" (BSAF). In this paper, we describe the accident progression in unit 3. In the BSAF project, eight organizations from five countries analyzed severe accident scenarios for Unit 3 at the Fukushima Daiichi site using different severe accident codes. The present paper for Unit 3 describes the findings of the comparison of the participants' results against each other and against plant data, the evaluation of the accident progression and the final status inside the reactors. Special focus is on the status of the reactor pressure vessel, melt release and fission product release and transport. Unit 3 specific aspects, e.g., the complicated accident progression following repeated containment venting actuations and attempts at coolant injection at the time of the major core degradation, are highlighted and points of consensus as well as remaining uncertainties and data needs will be summarized. FP transport is analyzed, and the calculation results are compared with dose rate measurements in the containment. The release of I-131 and Cs-137 to the environment is compared with analysis conducted by using WSPEEDI code.
Herranz, L. E.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Lind, T.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Godin-Jacqmin, L.*; L pez, C.*; Dolganov, K.*; Cousin, F.*; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Kim, T. W.*; et al.
pez, C.*; Dolganov, K.*; Cousin, F.*; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Kim, T. W.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 369, p.110849_1 - 110849_7, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:94.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)Phase 2 of the OECD/NEA Project "Benchmark Study of the Accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (BSAF)" was established in mid-2015. The objectives have been similar to Phase 1 of the project but with an extended analysis period of 3 weeks, a major focus on FP behaviour and releases to the environment and the comparison to various data and results of backwards calculations of the source term. Nine organizations of six countries submitted results of their calculated severe accident scenarios for Unit 1 at the 1F site using different severe accident codes. This paper describes the findings of the comparison of the participants results for Unit1 against each other and against plant data, the evaluation of the accident progression and the final status inside the reactors. Special focus is on RPV status, melt release and FP behaviour and release. Unit specific aspects will be highlighted and points of consensus as well as remaining uncertainties and data needs will be summarised.
Sonnenkalb, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Lind, T.*; Morreale, A. C.*; Kanda, Kenichi*; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Kim, S. I.*; Cousin, F.*; Fernandez Moguel, L.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 369, p.110840_1 - 110840_10, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:95.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)This is the second paper in a series of 3 in which results of severe accident analyses for Unit 2 of Fukushima Daiichi are presented, gained in Phase 2 of the OECD/NEA project "Benchmark Study of the Accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (BSAF)". Nine organizations of six countries submitted results of their calculated severe accident scenarios for Unit 2 of Fukushima Daiichi using different severe accident codes. The present paper describes the findings of the comparison of the participants' results for Unit 2 against each other and against plant data, the evaluation of the accident progression and the final status inside the reactors. Special focus is on reactor pressure vessel status, melt release and fission product behavior and release. Unit 2 specific aspects will be highlighted and points of consensus as well as remaining uncertainties and data needs will be summarized.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of 30th European Safety and Reliability Conference and 15th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (ESREL 2020 and PSAM-15) (Internet), p.2279 - 2286, 2020/11
Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is one of the methods used to assess the risks associated with large and complex systems. When the risk of an external event is evaluated using conventional PRA, a particular limitation is the difficulty in considering the timing at which nuclear power plant structures, systems, and components fail. To overcome this limitation, we coupled thermal-hydraulic and external-event simulations using Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics (RAPID). Internal flooding was chosen as the representative external event, and a pressurized water reactor plant model was used. Equations based on Bernoulli's theorem were applied to flooding propagation in the turbine building. In the analysis, uncertainties were taken into account, including the flow rate of the flood water source and the failure criteria for the mitigation systems. In terms of recovery action, isolation of the flood water source by the operator and drainage using a pump were modeled based on several assumptions. The results indicate that the isolation action became more effective when combined with drainage.
Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Zheng, X.; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki
Proceedings of 30th European Safety and Reliability Conference and 15th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (ESREL 2020 and PSAM-15) (Internet), p.2195 - 2201, 2020/11
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.308 - 315, 2020/10
Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is a method for improving the realism and completeness of conventional PRA. However, enormous calculation costs are incurred by these improvements. One solution is to select an appropriate sampling method. In this paper, we applied the Monte Carlo, Latin hypercube, grid-point, and quasi-Monte Carlo sampling methods to the dynamic PRA of a simplified accident sequence and compared the results for each method. Quasi-Monte Carlo sampling was found to be the most effective method in this case.
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.72 - 82, 2019/08
JAEA participated in the OECD/NEA BSAF2 project with our integrated severe accident analysis code, THALES2/KICHE, in order to analyze and discuss the accident progression and source term of the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi NPS. One of important characteristics of THALES2/KICHE code is that it has the capability of predicting iodine chemistry based on reaction kinetics in the aqueous phase. JAEA performed the three week analysis for the accident at unit 1 on the basis of the boundary conditions and assumptions proposed by the BSAF2 project and our own assumptions. In addition to the failure of the drywell, it was assumed in the present analysis that continuous leakage occurred through the containment venting line due to incomplete closing of valves in the line. The releases of fission products, especially for iodine and cesium, within three weeks after the earthquake were estimated to be approximately 6% and 1% of the initial inventory, respectively.
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.100 - 111, 2019/08
JAEA participated in the OECD/NEA BSAF2 project with our integrated severe accident analysis code, THALES2/KICHE, in order to analyze and discuss the accident progression and source term of the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi NPS. One of important characteristics of THALES2/KICHE code is that it has the capability of predicting iodine chemistry based on reaction kinetics in the aqueous phase. JAEA performed the three week analysis for the accident at unit 2 on the basis of the boundary conditions and assumptions proposed by the BSAF2 project and our own assumptions. One of focusing points in the BSAF2 project was the trend of measured data of reactor vessel from 20:00 March 14 to 02:00 March 15. An assumption was made that the lower part of the suppression chamber failed to form a water leakage path. The released iodine and cesium within three weeks after the earthquake were predicted to be approximately 3% and 0.1% of the initial inventory, respectively.
Ishikawa, Jun; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.536 - 547, 2019/08
Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Kazuo
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-006, 17 Pages, 2019/07
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides (NOx) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects strongly to the transport behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NOx with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. An analysis program has been developed to simulate chemical reaction coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Naoki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 18(2), p.69 - 80, 2019/06
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that nitrogen oxide affects strongly to the transport behavior of Ru. Chemical reactions of nitrogen oxide with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. An analysis method has been developed with coupling two types of computer codes to simulate not only thermo-hydraulic behavior but also chemical reactions in the flow paths of carrier gases. A simulation study has been also carried out with a typical facility building.
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2018 (ASRAM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2018/10
In the accidents at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station, Tsunami caused loss of electric power supply and this event led to core melt and failure of Containment vessel. Finally, fission products were released to the environment. Currently, the activities for understanding of accident progressions are carried out based on the measured data during the accident, accident progression analysis using integrated severe accident analysis codes and investigation of inside of reactor buildings and containment vessels. On the other hand, there are some research activities with combination of accident progression analysis and accident consequence analysis. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the research project of combination of these analyses using the computational simulation codes has been started. The results obtained from the combination analysis are expected to have broad width of uncertainty because of many uncertainty factors in this combined analysis. In order to perform the analysis efficiently, sensitivity analysis for failure location on containment vessel and its failure size were carried out by THALES2/KICHE developed by JAEA at first. This analysis was performed on unit 1, since it was the first plant to release radioactive materials to the environment during the accident and its consequence had no effect from other plants. The authors focused on the failure of containment vessel head flange, penetration seal and vacuum breaker pipe, and possibility of partial open of vent valve based on the investigations of reactor building inside performed by TEPCO. This paper presents the results obtained from this sensitivity analysis.