Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Murata, Chinatsu; Kitahara, Masaru; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Amazawa, Hiroya; Takebe, Shinichi; Yamada, Osamu*; Kameo, Yutaka
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (62), p.20 - 31, 2020/09
On the basis of Act on Special Measures, municipalities stripped surface soil off the playground of park to decontaminate the soil which had been contaminated with radionuclides released from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. To minimize the exposure dose of the residents, it was essential to decide safe disposal of the contaminated soil which has been stored at temporary storage areas. Therefore, the ministry of the Environment and Tokai-mura office required Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to perform demonstration project of burying the contaminated soil generated by decontamination of public facilities in order to provide decision on the enforcement ordinance and guidelines of burying it. In this project, we acquired data of air dose rate and the personal exposure dose during transporting, burying, and storing the contaminated soil. In addition, we measured radioactivity concentration of dust collected from surroundings of the landfill and seepage water through contaminated soil.
 Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationAono, Ryuji; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2017-025, 32 Pages, 2017/11
We have developed analytical methods for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for
Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2017/00
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
Hoken Butsuri, 51(4), p.209 - 217, 2016/12
A large amount of contaminated rubbles were generated by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS). For safe decommissioning of F1NPS, it is important to evaluate the composition and concentration of radionuclides in the rubbles. In this paper, to characterize the rubbles collected at F1NPS in Unit-1, Unit-2 and Unit-3, radiochemical analysis was operated. As a result of radiochemical analysis,  -ray-emitting nuclides
-ray-emitting nuclides  Co,
Co,  Cs and
Cs and 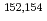 Eu,
Eu,  -ray-emitting nuclides
-ray-emitting nuclides  H,
H,  C,
C,  Sr and
Sr and  Tc, and
Tc, and  -particle-emitting nuclides
-particle-emitting nuclides 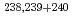 Pu,
Pu,  Am and
Am and  Cm were detected. In contrast,
Cm were detected. In contrast,  Nb and
Nb and  Eu concentrations were below the detection limit. Measured radioactive concentrations implied that
Eu concentrations were below the detection limit. Measured radioactive concentrations implied that  H,
H,  C,
C,  Co and
Co and  Sr concentrations depended on
Sr concentrations depended on  Cs concentration respectively. This analysis was characterized the radioactivity concentrations of the rubbles.
Cs concentration respectively. This analysis was characterized the radioactivity concentrations of the rubbles.
Seki, Kotaro; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Akimoto, Yuji*; Tokunaga, Takahito; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Haraga, Tomoko; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2016-013, 37 Pages, 2016/07
In this study, based on the simple and rapid analytical method established from the wastes from research facilities, we created analytical schemes which is applicable to rubble and plants collected at Fukushima Daiichi, then transported to Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA. We examined the applicability, and confirmed quantifiability of radioactivity concentration with high recovery rate without being affected by fission products such as  Sr and
Sr and  Cs.
Cs.
Omori, Hiroyuki; Nebashi, Koji; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-029, 31 Pages, 2015/03
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required for the radioactive waste generated from research facilities in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to dispose of in a near-surface repository. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid waste generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid waste generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In this report, we reported the analytical data determined in fiscal 2014 ( Cs and
Cs and  Mo) and summarized them with the radioactivity concentrations obtained in the past as basic data to consider the evaluation method of radioactivity concentrations in the stored waste taken from JPDR.
Mo) and summarized them with the radioactivity concentrations obtained in the past as basic data to consider the evaluation method of radioactivity concentrations in the stored waste taken from JPDR.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.301 - 307, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:79.30(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the severe accident at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant, large amounts of contaminated stagnant water have accumulated in turbine buildings and their surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of the radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. This evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011. The release ratios of tritium, iodine, and cesium were several tens of percent, whereas those of strontium and barium were smaller by one or two orders of magnitude. The release ratios in the Fukushima accident were equivalent to those in the TMI-2 accident.
Yasuda, Mari; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Watanabe, Koichi; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-011, 59 Pages, 2014/08
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required to be established for the near surface disposal of radioactive wastes generated from research facilities at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid wastes generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid wastes generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In the present paper, we summarized data about the radioactivity concentrations which accumulated by the analysis.
Tanaka, Kiwamu; Shimada, Asako; Hoshi, Akiko; Yasuda, Mari; Ozawa, Mayumi; Kameo, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.1032 - 1043, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:92.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Watanabe, Koichi; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Higuchi, Hidekazu
JAEA-Data/Code 2013-008, 16 Pages, 2013/11
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required to be established for the near surface disposal of radioactive wastes generated from research facilities at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid wastes generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid wastes generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In the present paper, we summarized data about the radioactivity concentrations which accumulated by the analysis.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(1), p.13 - 19, 2012/03
After the severe accident in the Fukushima-1 Nuclear Power Plant, large amount of contaminated stagnant water has been produced in turbine buildings and those surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. The present evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011.
Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Watanabe, Koichi; Sakai, Akihiro; Kameo, Yutaka; Kogure, Hiroto; Higuchi, Hidekazu; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-011, 31 Pages, 2011/10
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required to be established for the near surface disposal of radioactive wastes generated from research facilities at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid wastes generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid wastes generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In the present paper, we summarized data (262 data) about the radioactivity concentrations of the 7 important nuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Cs) which accumulated by the analysis.
Cs) which accumulated by the analysis.
Aono, Ryuji; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Konda, Miki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
A large amount of contaminated rubble was generated by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS). For safe decommissioning of F1NPS, it is important to evaluate the composition and concentration of radionuclides in the rubble. To characterize the rubble collected at F1NPS, radiochemical analysis was conducted. From the rubble collected from reactor buildings,  H,
H,  C,
C,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Se,
Se,  Sr,
Sr,  Tc,
Tc,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu, 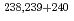 Pu,
Pu,  Am and
Am and  Cm were detected. The radioactivity concentrations of
Cm were detected. The radioactivity concentrations of  Co,
Co,  Sr and
Sr and  Pu are correlated that of
Pu are correlated that of  Cs. The radioactive ratio of
Cs. The radioactive ratio of  Co/
Co/ Cs,
Cs,  Sr/
Sr/ Cs and
Cs and  Pu/
Pu/ Cs were similar between the rubble collected from 1st floor and 5th floor of unit 1 reactor building. This result implied that regardless of sampling location in reactor building, the radioactive ratios of
Cs were similar between the rubble collected from 1st floor and 5th floor of unit 1 reactor building. This result implied that regardless of sampling location in reactor building, the radioactive ratios of  Co/
Co/ Cs,
Cs,  Sr/
Sr/ Cs and
Cs and  Pu/
Pu/ Cs were consistent.
Cs were consistent.
Yasuda, Mari; Watanabe, Koichi; Hoshi, Akiko; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kameo, Yutaka; Katayama, Atsushi; Higuchi, Hidekazu
no journal, ,
Analytical methods were developed for determination of Se-79, Sr-90 and Tc-99 in stagnant water generated from Fukushima-1 Nuclear Power Plant. The recoveries of these elements were enough to determine the concentrations of Se-79, Sr-90 and Tc-99. The interference of beta emitter could not be found by beta spectrometry. The present method could be applied to stagnant water.
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Tokunaga, Takahito; Numayama, Satoru; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Watanabe, Koichi; Hoshi, Akiko; Katayama, Atsushi; Higuchi, Hidekazu; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray emitting nuclides, H-3, C-14, Sr-90
-ray emitting nuclides, H-3, C-14, Sr-90Kameo, Yutaka; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ozawa, Mayumi; Sato, Kenji; Unno, Toshimichi; Kimiyama, Kazuhiro; Seki, Shuhei; Hoshi, Akiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kameo, Yutaka; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Shimada, Asako; Ueno, Takashi; Hoshi, Akiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Yasuda, Mari; Shimada, Asako; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Meguro, Yoshihiro; Kato, Jun; Kishimoto, Katsumi; Kameo, Yutaka; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Koma, Yoshikazu; Ashida, Takashi
no journal, ,
The authors are working in study for radioactive wastes generated in Fukushima Daiichi. Radioactive inventory estimation of wastes is important in the study for the processing and disposal of radioactive waste. And then so many real wastes have to be analyzed for their inventory evaluation. In addition to this waste analysis, there are several needs for analysis. For example a large volume of the contaminated water is being decontaminated, and operational status and ability of this system should be checked by analysis of the treated water. And also groundwater and sea water are analyzing to understand contaminated situation, to estimate a leakage position, and to confirm leakage prevention. In future fuel debris will be analyzed for its material accountancy. In this presentation, actual situation of analyses in Fukushima Daiichi will be explained, mainly focus on analyses for the inventory evaluation of the radioactive waste.