Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, F.*; Tang, X.*; Fei, Y.*; Zhang, J.*; Liu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Che, G.*; Zhao, Z.*; Zheng, Y.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(17), p.14054 - 14059, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We synthesized a crystalline graphane nanoribbon (GANR) via pressure-induced polymerization of 2,2'-bipyrazine (BPZ). By performing Rietveld refinement of in situ neutron diffraction data, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, infrared spectra, and theoretical calculation, we found that BPZ experienced Diels-Alder polymerization between the 

 stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (
stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (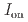 /
/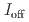 =18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
=18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saturated sp -carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
-carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
Che, G.*; Fei, Y.*; Tang, X.*; Zhao, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Wang, X.*; Ju, J.*; Dong, X.*; Wang, Y.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 27(2), p.1112 - 1118, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:65.57(Chemistry, Physical)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatic molecules has emerged as an effective method for synthesizing various carbon-based materials. In this work, PIP of 1,4-difluorobenzene (1,4-DFB) was investigated.  high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H
high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H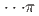 interaction along the [01
interaction along the [01 ] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H
] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H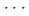 F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01
F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01 ] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:82.25(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviors induced by the combination of external and internal hydrogen (H) in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy were systematically investigated via in situ 3D characterization techniques. SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy could initiate and propagate in the potential crack region where the H concentration exceeded a critical value, in which the nanoscopic H-induced decohesion of  -MgZn
-MgZn precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
Zhang, J.*; Kuang, L.*; Mou, Z.*; Kondo, Toshiaki*; Koarashi, Jun; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Li, Y.*; Tang, X.*; Wang, Y.-P.*; Pe uelas, J.*; et al.
uelas, J.*; et al.
Plant and Soil, 481(1-2), p.349 - 365, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:73.14(Agronomy)Tang, J.*; Seo, O.*; Rivera Rocabado, D. S.*; Koitaya, Takanori*; Yamamoto, Susumu*; Namba, Yusuke*; Song, C.*; Kim, J.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Koyama, Michihisa*; et al.
Applied Surface Science, 587, p.152797_1 - 152797_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.59(Chemistry, Physical)The hydrogen absorption and diffusion mechanisms on cube-shaped Pd nanoparticles (NPs) which are important hydrogen-storage materials were studied using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT calculations. In the surface region, hydrogen absorption showed almost similar behavior regardless of the NPs size. It was found that the octahedral sites are more favorable than the tetrahedral sites for hydrogen occupation. We also clarified that the hydrogen atoms absorbing on the smaller-sized Pd NPs diffuse to the subsurface more actively because of the weakened Pd-H bond by the surface disordering, which plays an important role in hydrogen adsorption at a low H pressure.
pressure.
Wang, X.*; Tang, X.*; Zhang, P.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Liu, J.*; Hui, K.*; Wang, Y.*; Dong, X.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 12(50), p.12055 - 12061, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.30(Chemistry, Physical)Substituted polyacetylene is expected to improve the chemical stability, physical properties, and additional functions of the polyacetylene backbones, but its diversity is very limited. Here, by applying external pressure on solid acetylenedicarboxylic acid, we report the first crystalline poly-dicarboxylacetylene with every carbon on the trans-polyacetylene backbone bonded to a carboxyl group, which is very hard to synthesize by traditional methods. This unique structure combines the extremely high content of carbonyl groups and high conductivity of a polyacetylene backbone, which exhibits a high specific capacity and excellent cycling/rate performance as a Li-ion battery (LIB) anode. We present a completely functionalized crystalline polyacetylene and provide a high-pressure solution for the synthesis of polymeric LIB materials and other polymeric materials with a high content of active groups.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:33.92(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gao, D.*; Tang, X.*; Wang, X.*; Yang, X.*; Zhang, P.*; Che, G.*; Han, J.*; Hattori, Takanori; Wang, Y.*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 23(35), p.19503 - 19510, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:37.22(Chemistry, Physical)Pressure-induced phase transition and polymerization of nitrogen-rich molecules are widely focused due to its extreme importance for the development of green high energy density materials. Here, we present a study of the phase transition and chemical reaction of 1H-tetrazole up to 100 GPa by using  Raman, IR, X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction techniques and theoretical calculation. A phase transition above 2.6 GPa was identified and the high-pressure structure was determined with one molecule in a unit cell. The 1H-tetrazole polymerizes reversibly below 100 GPa, probably through a carbon-nitrogen bonding instead of nitrogen-nitrogen bonding. Our studies updated the structure model of the high pressure phase of 1H-tetrazole, and presented the possible intermolecular bonding route for the first time, which gives new insights to understand the phase transition and chemical reaction of nitrogen-rich compounds, and benefit for designing new high energy density materials.
Raman, IR, X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction techniques and theoretical calculation. A phase transition above 2.6 GPa was identified and the high-pressure structure was determined with one molecule in a unit cell. The 1H-tetrazole polymerizes reversibly below 100 GPa, probably through a carbon-nitrogen bonding instead of nitrogen-nitrogen bonding. Our studies updated the structure model of the high pressure phase of 1H-tetrazole, and presented the possible intermolecular bonding route for the first time, which gives new insights to understand the phase transition and chemical reaction of nitrogen-rich compounds, and benefit for designing new high energy density materials.
Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Gao, D.*; Li, Y.*; Zheng, H.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Fu, R.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(41), p.17662 - 17669, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:79.04(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Solid-state topochemical polymerization (SSTP) is a promising method to construct functional crystalline polymeric materials, but in contrast to various reactions that happen in solution, only very limited types of SSTP reactions are reported. Diels-Alder (DA) and dehydro-DA (DDA) reactions are textbook reactions for preparing six-membered rings in solution but are scarcely seen in solid-state synthesis. Here, using multiple cutting-edge techniques, we demonstrate that the solid 1,4-diphenylbutadiyne (DPB) undergoes a DDA reaction under 10-20 GPa with the phenyl as the dienophile. The crystal structure at the critical pressure shows that this reaction is "distance-selected". The distance of 3.2 between the phenyl and the phenylethynyl facilitates the DDA reaction, while the distances for other DDA and 1,4-addition reactions are too large to allow the bonding. The obtained products are crystalline armchair graphitic nanoribbons, and hence our studies open a new route to construct the crystalline carbon materials with atomic-scale control.
between the phenyl and the phenylethynyl facilitates the DDA reaction, while the distances for other DDA and 1,4-addition reactions are too large to allow the bonding. The obtained products are crystalline armchair graphitic nanoribbons, and hence our studies open a new route to construct the crystalline carbon materials with atomic-scale control.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Tang, J.*; Sekihata, Yuki*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(SM), p.SM0801_1 - SM0801_42, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.00(Physics, Applied)In this paper, we review the study of the unified Si oxidation reaction model mediated by point defect generation, in which O dissociative adsorption occurs at dangling bonds of point defects (emitted Si atoms and vacancies) at the SiO
dissociative adsorption occurs at dangling bonds of point defects (emitted Si atoms and vacancies) at the SiO /Si interface, and the point defect generation rate is given by a combination of oxidation-induced strain, thermal strain due to the difference in thermal expansion coefficient between Si and SiO
/Si interface, and the point defect generation rate is given by a combination of oxidation-induced strain, thermal strain due to the difference in thermal expansion coefficient between Si and SiO , thermal excitation of Si emission rate, and heat of adsorption.
, thermal excitation of Si emission rate, and heat of adsorption.
Tang, J.*; Yamamoto, Susumu*; Koitaya, Takanori*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Tokunaga, Takuma*; Mukai, Kozo*; Matsuda, Iwao*; Yoshinobu, Jun*
Applied Surface Science, 480, p.419 - 426, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54.32(Chemistry, Physical)Mass transports during hydrogen adsorption and absorption processes of PdCu alloys that has advantages of higher hydrogen diffusivity and economically lower-cost than the other Pd-alloys were studied. The research was made with a comparison of the well-known ordered phase of the bcc structure (the B2 phase) and a mixed phase of the fcc and B2 structures.  ultrahigh vacuum X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation were carried out to trace the chemical states of the Pd and Cu atoms as a function of temperatures. It is elucidated that the initial adsorption and absorption processes were similar in the two phases, but a hydrogen diffusion rate to the bulk was higher in the ordered phase than in the mixed one. We found the dynamics of the Pd and Cu atoms during the hydrogen adsorption/absorption processes largely depend on temperature. In the hydrogen atmosphere, the Pd atoms segregate at the surface below 373 K and Cu atoms segregate at the surface above 373 K. The present results agree well with the previous theoretical calculations and, thus, provide appropriate inputs toward developments of the hydrogen permeation materials.
ultrahigh vacuum X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation were carried out to trace the chemical states of the Pd and Cu atoms as a function of temperatures. It is elucidated that the initial adsorption and absorption processes were similar in the two phases, but a hydrogen diffusion rate to the bulk was higher in the ordered phase than in the mixed one. We found the dynamics of the Pd and Cu atoms during the hydrogen adsorption/absorption processes largely depend on temperature. In the hydrogen atmosphere, the Pd atoms segregate at the surface below 373 K and Cu atoms segregate at the surface above 373 K. The present results agree well with the previous theoretical calculations and, thus, provide appropriate inputs toward developments of the hydrogen permeation materials.
 H
H - C
- C F
F cocrystal towards graphane structure
cocrystal towards graphane structureWang, Y.*; Dong, X.*; Tang, X.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Lin, X.*; Fang, L.*; Sun, G.*; Chen, X.*; Xie, L.*; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 58(5), p.1468 - 1473, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:83.96(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatics is a novel method to construct sp -carbon frameworks, and nanothreads with diamond-like structures were synthesized by compressing benzene and its derivatives. Here by compressing benzene-hexafluorobenzene cocrystal(CHCF), we identified H-F-substituted graphane with a layered structure in the PIP product. Based on the crystal structure determined from the in situ neutron diffraction and the intermediate products identified by the gas chromatography-mass spectrum, we found that at 20 GPa CHCF forms tilted columns with benzene and hexafluorobenzene stacked alternatively, which leads to a [4+2] polymer, and then transfers to short-range ordered hydrogenated-fluorinated graphane. The reaction process contains [4+2] Diels-Alder, retro-Diels-Alder, and 1-1' coupling, and the former is the key reaction in the PIP. Our studies confirmed the elemental reactions of the CHCF for the first time, which provides a novel insight into the PIP of aromatics.
-carbon frameworks, and nanothreads with diamond-like structures were synthesized by compressing benzene and its derivatives. Here by compressing benzene-hexafluorobenzene cocrystal(CHCF), we identified H-F-substituted graphane with a layered structure in the PIP product. Based on the crystal structure determined from the in situ neutron diffraction and the intermediate products identified by the gas chromatography-mass spectrum, we found that at 20 GPa CHCF forms tilted columns with benzene and hexafluorobenzene stacked alternatively, which leads to a [4+2] polymer, and then transfers to short-range ordered hydrogenated-fluorinated graphane. The reaction process contains [4+2] Diels-Alder, retro-Diels-Alder, and 1-1' coupling, and the former is the key reaction in the PIP. Our studies confirmed the elemental reactions of the CHCF for the first time, which provides a novel insight into the PIP of aromatics.
Tang, C.*; Song, Q.*; Chang, C.-Z.*; Xu, Y.*; Onuma, Yuichi; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Liu, Y.*; Yuan, W.*; Yao, Y.*; Moodera, J. S.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 4(6), p.eaas8660_1 - eaas8660_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:83.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences) /Si(001) interfacial oxidation induced by thermal strain during rapid thermal oxidation
/Si(001) interfacial oxidation induced by thermal strain during rapid thermal oxidationOgawa, Shuichi*; Tang, J.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 145(11), p.114701_1 - 114701_7, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:17.36(Chemistry, Physical)Enhancement of SiO /Si(001) interfacial oxidation induced by thermal strain during rapid thermal oxidation was revealed by real time photoelectron spectroscopy using high intensity and high energy-resolution synchrotron radiation. This experimental result indicates the usefulness of the unified Si oxidation reaction model mediated by point defect generation.
/Si(001) interfacial oxidation induced by thermal strain during rapid thermal oxidation was revealed by real time photoelectron spectroscopy using high intensity and high energy-resolution synchrotron radiation. This experimental result indicates the usefulness of the unified Si oxidation reaction model mediated by point defect generation.
 7 surfaces studied by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy
7 surfaces studied by real-time photoelectron spectroscopyTang, J.*; Nishimoto, Kiwamu*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Watanabe, Daiki*; Teraoka, Yuden; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Surface and Interface Analysis, 46(12-13), p.1147 - 1150, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:1.56(Chemistry, Physical) /Si(001) interfaces during thermal oxidation
/Si(001) interfaces during thermal oxidationOgawa, Shuichi*; Tang, J.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Teraoka, Yuden; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(11), p.110128_1 - 110128_7, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:49.87(Physics, Applied)Tang, J.*; Nishimoto, Kiwamu*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Watanabe, Daiki*; Teraoka, Yuden; Takakuwa, Yuji*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 11, p.116 - 121, 2013/11
 pressure dependence of the initial oxide growth kinetics on Si(111) surfaces; Photoelectron spectroscopy observation and molecular orbital calculation of oxidation states
pressure dependence of the initial oxide growth kinetics on Si(111) surfaces; Photoelectron spectroscopy observation and molecular orbital calculation of oxidation statesTang, J.*; Nishimoto, Kiwamu*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Watanabe, Daiki*; Teraoka, Yuden; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Dai-18-Kai Getosutakku KenkyuKai Yokoshu, p.191 - 194, 2013/01
Chen, L.-M.; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Hong, W.*; Hua, J. F.*; Kameshima, Takashi; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Wen, X.*; Wu, Y.*; Tang, C.*; et al.
Chinese Optics Letters, 5(S1), p.S133 - S135, 2007/05