Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sweet, M.*; Mishima, Kenji*; Harada, Masahide; Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi; Tasaki, Seiji*; Kikuchi, Norio*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 9(2), p.11_1 - 11_17, 2025/04
Neutron beam, being electrically neutral and highly penetrating, offers unique advantages for irradiation of biological species such as plants, seeds, and microorganisms. We comprehensively investigated the potential of neutron irradiation for inducing genetic mutations using simulations of J-PARC BL10, JRR-3 TNRF, and KUANS for spallation, reactor, and compact neutron sources.
Okita, Shoichiro; Abe, Yutaka*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Fukaya, Yuji
Radioisotopes, 73(3), p.233 - 240, 2024/11
Okita, Shoichiro; Tasaki, Seiji*; Abe, Yutaka*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 19(3), p.178 - 184, 2020/09
The Kyoto University Accelerator-based Neutron Source (KUANS) is a compact neutron source that is mainly used for spectrometer and detector development. In addition, it is also suited for experiments to study the neutronic design of moderators owing to the relatively low neutron generation yield by  Be(p,n). We present a neutronic design of the neutron moderator on a reentrant-hole configuration for KUANS to enhance the neutron emission, and some experiments are conducted at KUANS for verification. A polyethylene moderator on a reentrant-hole configuration is designed by PHITS calculation and is introduced to KUANS to obtain intense oblong neutron beams. The intensity of the pulsed neutron beam is experimentally measured. The results reveal that the intensity becomes approximately 1.9 times stronger than that of the conventional rectangular design. In addition, the ratio of its intensity to the conventional intensity increases to approximately threefold as the neutron wavelength increases. It is interesting to note that the longer the neutron wavelength, the more efficiently they are extracted from the inside of the moderator owing to the existence of the reentrant-hole configuration.
Be(p,n). We present a neutronic design of the neutron moderator on a reentrant-hole configuration for KUANS to enhance the neutron emission, and some experiments are conducted at KUANS for verification. A polyethylene moderator on a reentrant-hole configuration is designed by PHITS calculation and is introduced to KUANS to obtain intense oblong neutron beams. The intensity of the pulsed neutron beam is experimentally measured. The results reveal that the intensity becomes approximately 1.9 times stronger than that of the conventional rectangular design. In addition, the ratio of its intensity to the conventional intensity increases to approximately threefold as the neutron wavelength increases. It is interesting to note that the longer the neutron wavelength, the more efficiently they are extracted from the inside of the moderator owing to the existence of the reentrant-hole configuration.
Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Tasaki, Seiji*; Hino, Masahiro*; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 634(1, Suppl.), p.S90 - S93, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)In a neutron spin interferometer (NSI), incident neutrons are in states of up- and down-spin eigenstates and a phase difference between the eigenstates is observed after transmission through a magnetic sample. Since the phase difference is proportional to an integral of magnetic field along a trajectory of neutrons, NSI imaging provides projection images of a distribution of magnetic field in the sample. We tried to visualize magnetic field in permalloy film with and without stress as a demonstration of the NSI imaging. An experiment was carried out at C3-1-2-2, MINE2 port at the neutron guide hall of JRR-3M with wavelength of 0.88nm and wavelength resolution of 0.3% in FWHM. Permalloy film with thickness of 0.1 mm was used as a sample and was stressed by bending with angles of 45 and 180  . As a result, images of decrease of a saturated magnetization and an increase of leak magnetic field with increasing the bending angle were obtained.
. As a result, images of decrease of a saturated magnetization and an increase of leak magnetic field with increasing the bending angle were obtained.
Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Maruyama, Ryuji*; Tasaki, Seiji*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 356(1-4), p.174 - 177, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.87(Physics, Condensed Matter)Drabkin energy filter could be used as a fast chopper for pulsed neutrons by varying the resonant wavelength 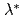 fast in such a way that resonant wavelength matches neutron wavelength at a small time region. The faster
fast in such a way that resonant wavelength matches neutron wavelength at a small time region. The faster 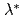 are varied, the smaller time window we could obtain. Neutron pulses could be sharpened much more effectively for a small wavelength band than in the wide-band pulse-shaping mode in which
are varied, the smaller time window we could obtain. Neutron pulses could be sharpened much more effectively for a small wavelength band than in the wide-band pulse-shaping mode in which 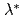 is varied in synchronization with the time-of-flight from the moderator. In our preliminary test of a chopper-mode with a prototype Drabkin energy filter, time-window of 0.21 ms was obtained while it was 1.08 ms with the filter driven stationary. Narrower time-window could have been obtained if we had more beam-time and it could be also narrowed with higher-resolution Drabkin filters.
is varied in synchronization with the time-of-flight from the moderator. In our preliminary test of a chopper-mode with a prototype Drabkin energy filter, time-window of 0.21 ms was obtained while it was 1.08 ms with the filter driven stationary. Narrower time-window could have been obtained if we had more beam-time and it could be also narrowed with higher-resolution Drabkin filters.
Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Torikai, Naoya*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Matsuoka, Hideki*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 356(1-4), p.229 - 233, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.87(Physics, Condensed Matter)The application of neutron reflectometry to study dynamic phenomena at surface and interfaces have been restricted so far. It was mainly due to the low intensity of neutron sources, but now high-intensity spallation neutron sources are under construction in Japan (J-PARC) and U.S. (SNS). We have a plan to install a spin-echo option on the J-PARC neutron reflectometer with horizontal sample geometry for studies on dynamics of surfaces and interfaces. This option is based on the resonance spin-echo method and aimed at dynamics upto hundreds of nanoseconds. In this contribution, the plan and status of development are introduced together with the principle and characteristics of this option.
Maruyama, Ryuji*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Hino, Masahiro*; Takeda, Masayasu; Ebisawa, Toru*; Kawabata, Yuji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 530(3), p.505 - 512, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.82(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron resonance spin echo (NRSE) spectroscopy enables us to measure neutron quasielastic scattering with high energy resolution. It is desirable to apply NRSE spectroscopy to pulsed neutron sources because this application allows a very wide range of the spin echo time. We have already developed the neutron resonance spin flipper applicable to a polychromatic pulsed neutron beam, which is necessary for the TOF-NRSE method. Using this flipper, we have succeeded in observing spin echo signals with visibility higher than 0.65 for the pulsed neutron beam with wavelength from 0.3 to 0.9 nm. We discuss the prospect of the NRSE spectrometer with high energy resolution on the basis of the present result.
Oku, Takayuki*; Sakai, Kenji*; Adachi, Tomohiro*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Maruyama, Ryuji*; Hino, Masahiro*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 335(1-4), p.226 - 229, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.69(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tamura, Itaru; Tasaki, Seiji*
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 1, p.407 - 415, 2003/06
Drabkin energy filters extract neutrons of required wavelength using spatial neutron spin resonance. If they are applied to pulsed neutrons, they could sharpen pulse width and cut tail neutrons without reducing band-width or peak-intensity. Shaping of J-PARC coupled-moderator pulse by a Drabkin energy filter was simulated. In the simulation, discrete field gradient to Bx is introduced and total field B is varied in accordance with the dominant wavelength at each moment at the filter position. The results suggest that about 90 % or more of tail neutrons from coupled moderator are cut and a fliter with fields of 200 periods could reduce pulse width up to that of decoupled moderator. Effects of fluctuations of width of each half period were studied and it was found that fluctuation within  1 % are tolerable for a flipper with field of 100 or 200 periods.
1 % are tolerable for a flipper with field of 100 or 200 periods.
Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tasaki, Seiji*
JAERI-Research 2003-009, 29 Pages, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Masayasu; Torikai, Naoya*; Ino, Takashi*; Tasaki, Seiji*
KENS Report-XIV, p.205 - 206, 2003/00
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Junichi; Tasaki, Seiji*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*
Applied Physics A, 74(Suppl.1), p.S308 - S310, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Junichi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Tasaki, Seiji*; Ebisawa, Toru*
JAERI-Conf 2001-002, p.547 - 550, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Kawabata, Yuji*; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Suzuki, Masatoshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAERI-Research 2000-019, p.20 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; ; ; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tasaki, Seiji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 35(11), p.750 - 758, 1998/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:59.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ebisawa, Toru*; Tasaki, Seiji*; ; ; Soyama, Kazuhiko; ;
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 213-214, p.901 - 903, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:86.15(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; Suzuki, Masatoshi; Kodaira, Tsuneo; Ebisawa, Toru*; ; Tasaki, Seiji*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 213-214, p.951 - 953, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.18(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Iikura, Hiroshi; Yasuda, Ryo; Sakai, Takuro; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Takenaka, Nobuyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Iikura, Hiroshi; Yasuda, Ryo; Sakai, Takuro; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Takenaka, Nobuyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Takenaka, Nobuyuki*; Kageyama, Masashi*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Hino, Masahiro*; Kawabata, Yuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Iikura, Hiroshi; Yasuda, Ryo; Sakai, Takuro; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Takenaka, Nobuyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English