Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
松下 慧*; 土田 紀之*; 石丸 詠一郎*; 平川 直樹*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 33(13), p.6352 - 6361, 2024/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This study investigated the anisotropy of the tensile properties in a duplex stainless steel of 24Cr-5Ni-0.18N based on in situ neutron diffraction experiments. The 24Cr-5Ni-0.18N steel showed a better balance of tensile strength (TS) and uniform elongation (U.El) compared with 329J4L and 329J1 steels. The Lankford value ( -value) of the 24Cr-5Ni-0.18N steel was comparable to other duplex stainless steels while showing a larger TS. Regarding the anisotropy of the mechanical properties, the results for a test specimen oriented at 45
-value) of the 24Cr-5Ni-0.18N steel was comparable to other duplex stainless steels while showing a larger TS. Regarding the anisotropy of the mechanical properties, the results for a test specimen oriented at 45 showed a low yield strength (YS) and TS, but a better U.El and
showed a low yield strength (YS) and TS, but a better U.El and  -value. The neutron diffraction results are discussed to explain the mechanical properties.
-value. The neutron diffraction results are discussed to explain the mechanical properties.
上路 林太郎*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; 木村 勇次*; 井上 忠信*; 土田 紀之*
ISIJ International, 64(2), p.459 - 465, 2024/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:41.92(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) during tensile or compressive deformations of the bainitic steels with various carbon content (0.15%C, 0.25%C, 0.62%C) was studied. In all of the bainitic steels, the tensile deformation exhibited larger work hardening than the compression. This difference indicates the suppression of the DIMT at the compression, and actually the measurements of electron back scattering diffraction (EBSD) confirmed the less reduction of retained austenite at the compression of all the bainitic steels. Additionally, the steel with the highest carbon content was examined by in situ neutron diffraction and clarified the difference similar to that obtained by the EBSD measurement. The regression of the relation between the fraction of austenite and applied strain with the conventional empirical equation revealed that the kinetic of DIMT is strongly dependent with the stress polarity, but not significantly changed by the carbon content.
土田 紀之*; Kuramoto, Shota*; 上路 林太郎*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 廣井 孝介; 河村 幸彦*
ISIJ International, 64(2), p.354 - 360, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The effects of pre-strain on the mechanical properties of high strength martensitic steels were investigated using either strain tempering (ST) or quenching and tempering (QT) samples. In the tensile tests at deformation temperatures between 296 and 573 K, the ST sample exhibited an increase in both the tensile strength (TS) and uniform elongation (U El) at 473 to 523 K, whereas the QT sample showed an increase in U El with little change in the TS and yield strength (YS). The results of in situ neutron diffraction experiments revealed an increase in the stress partitioning to the bcc phase with an increase in the deformation temperature from 296 to 523 K. The difference in the phase stress between the bcc and cementite phases decreased with an increase in the temperature due to the decrease in the cementite strength. Pre-strain of 0.5% increased the YS at 296 K with a slight work hardening; the initial dislocation density ( ) decreased at 523 K, but increased significantly after yielding, leading to a better combination of TS and U.El. The combination of pre-strain, tempering, and deformation temperatures caused the change in
) decreased at 523 K, but increased significantly after yielding, leading to a better combination of TS and U.El. The combination of pre-strain, tempering, and deformation temperatures caused the change in  before deformation and the increase in
before deformation and the increase in  after yielding of the martensitic steel.
after yielding of the martensitic steel.
土田 紀之*; 上路 林太郎*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
Scripta Materialia, 222, p.115002_1 - 115002_6, 2023/01
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:55.35(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The present study investigated the tensile deformation behavior of quenched and tempered martensite steels at various austenitization and tempering temperatures using in situ neutron diffraction experiments. Phase lattice strains in the bcc and cementite ( ) phases and dislocation structures in the bcc phase were analyzed. The phase lattice strain in bcc became almost stagnant after yielding as the tempering temperature increased. The phase lattice strain in
) phases and dislocation structures in the bcc phase were analyzed. The phase lattice strain in bcc became almost stagnant after yielding as the tempering temperature increased. The phase lattice strain in  increased linearly with an increase in the flow stress, independent of the austenitization and tempering temperatures. The stress partitioning between bcc and
increased linearly with an increase in the flow stress, independent of the austenitization and tempering temperatures. The stress partitioning between bcc and  was confirmed after the yielding of bcc, which contributed to the work hardening. The phase stresses of bcc and
was confirmed after the yielding of bcc, which contributed to the work hardening. The phase stresses of bcc and  and their stress partitioning improve the mechanical properties of martensite steels, which can be summarized by the systematic changes in phase lattice strain and dislocation properties due to the austenitization and tempering temperatures.
and their stress partitioning improve the mechanical properties of martensite steels, which can be summarized by the systematic changes in phase lattice strain and dislocation properties due to the austenitization and tempering temperatures.
土田 紀之*; Harjo, S.
Metals, 11(12), p.2053_1 - 2053_16, 2021/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:10.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To improve uniform elongation (U.El) due to the TRIP effect, it is important to control deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) until the late part of deformation. In the present study, tensile tests with decreasing deformation temperatures were conducted to achieve continuous DIMT up to the late part of deformation. As a result, the U.El was improved by approximately 1.5 times compared with that in the tensile test conducted at 296 K. The enhancement of the U.El in the temperature change test was discussed with the use of neutron diffraction experiments.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 土田 紀之*; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.
鉄と鋼, 107(10), p.887 - 896, 2021/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In situ neutron diffraction measurements of two low-alloy TRIP steels and a 304-type stainless steel during tensile and creep tests were performed at room temperature. Changes in the diffraction pattern, the peak integrated intensities of austenite ( ) and the peak positions of
) and the peak positions of  were analyzed and discussed to understand a relationship between intergranular stress in
were analyzed and discussed to understand a relationship between intergranular stress in  and the occurrence of martensitic transformation during deformation. From tensile loading, it was found that the susceptibility of martensitic transformation depended on
and the occurrence of martensitic transformation during deformation. From tensile loading, it was found that the susceptibility of martensitic transformation depended on  -(
-(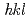 ) grains, in which
) grains, in which  -(111) grains underwent martensitic transformation at the latest. The
-(111) grains underwent martensitic transformation at the latest. The  -(
-(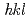 ) dependence in the susceptibility of martensitic transformation was found to be controlled by the shear stress levels in
) dependence in the susceptibility of martensitic transformation was found to be controlled by the shear stress levels in  -(
-(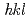 ) grains, which were affected by the intergranular stress partitioning during deformation.
) grains, which were affected by the intergranular stress partitioning during deformation.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 土田 紀之*; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.*
ISIJ International, 61(2), p.648 - 656, 2021/02
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:46.82(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) neutron diffraction measurements of two low-alloy steels and a 304-type stainless steel during tensile and creep tests were performed at room temperature. Changes in the diffraction pattern, the integrated peak intensities of austenite (
neutron diffraction measurements of two low-alloy steels and a 304-type stainless steel during tensile and creep tests were performed at room temperature. Changes in the diffraction pattern, the integrated peak intensities of austenite ( ), and the peak positions of
), and the peak positions of  were analyzed and discussed to elucidate the relationship between intergranular stress in
were analyzed and discussed to elucidate the relationship between intergranular stress in  and the occurrence of martensitic transformation during deformation. Tensile loading experiments revealed that the susceptibility to martensitic transformation depended on the
and the occurrence of martensitic transformation during deformation. Tensile loading experiments revealed that the susceptibility to martensitic transformation depended on the  -(hkl) grains, where
-(hkl) grains, where  -(111) grains underwent martensitic transformation at the latest. The
-(111) grains underwent martensitic transformation at the latest. The  -hkl dependence of the susceptibility to martensitic transformation was found to be controlled by the shear stress levels in
-hkl dependence of the susceptibility to martensitic transformation was found to be controlled by the shear stress levels in  -(hkl) grains, which were affected by the intergranular stress partitioning during deformation.
-(hkl) grains, which were affected by the intergranular stress partitioning during deformation.
土田 紀之*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of International Conference on Martensitic Transformations: Chicago, p.43 - 46, 2018/00
In order to investigate TRIP (transformation induced plasticity) effect in different deformation style, a room temperature creep test under the constant load was conducted by using a TRIP-aided multi-microstructure steel. As a result, the volume fraction of deformation-induced martensite in the constant load creep test was larger than that in the tensile test. In situ neutron diffraction experiments during the constant load creep test were performed to discuss its reason. It is found from the in situ neutron diffraction experiments during the constant load creep tests that the phase strain of the austenite phase in the creep tests was larger than that in the tensile tests at the same applied stress.
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*; 阿部 淳*; Gong, W.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.15149_1 - 15149_11, 2017/11
被引用回数:124 パーセンタイル:94.27(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Two TRIP-aided multiphase steels with different carbon contents were analyzed in situ during tensile deformation by time-of-flight neutron diffraction to clarify the deformation induced martensitic transformation behavior and its role on the strengthening mechanism. The difference in the carbon content affected mainly the difference in the phase fractions before deformation, where the higher carbon content increased the phase fraction of retained austenite ( ). However, the changes in the relative fraction of martensitic transformation with respect to the applied strain were found to be similar in both steels since the carbon concentrations in
). However, the changes in the relative fraction of martensitic transformation with respect to the applied strain were found to be similar in both steels since the carbon concentrations in  were similar. The stress contribution from martensite was observed increasing during plastic deformation while that from bainitic ferrite hardly changing and that from
were similar. The stress contribution from martensite was observed increasing during plastic deformation while that from bainitic ferrite hardly changing and that from  decreasing.
decreasing.
土田 紀之*; Nagahisa, N.*; Harjo, S.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 700, p.631 - 636, 2017/07
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:40.66(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)This study investigated room-temperature creep tests using a low-carbon TRIP steel to clarify the TRIP effect on tensile deformation behavior under constant load. Nominal strain and strain rate increased with an increase in applied stress and those were almost stagnated at holding times of about 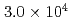 s. The volume fractions of deformation-induced martensite (
s. The volume fractions of deformation-induced martensite (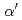 ) at a given true strain obtained from constant load creep tests were larger than those from tensile tests. From the in situ neutron diffraction experiments during the constant load creep tests, the phase strain of the austenite (
) at a given true strain obtained from constant load creep tests were larger than those from tensile tests. From the in situ neutron diffraction experiments during the constant load creep tests, the phase strain of the austenite ( ) phase in the creep tests was found to be larger than that in the tensile tests at the same applied stress. This means that the phase strain or true stress of the
) phase in the creep tests was found to be larger than that in the tensile tests at the same applied stress. This means that the phase strain or true stress of the  phase in the TRIP steel was associated with the difference in the volume fraction of
phase in the TRIP steel was associated with the difference in the volume fraction of 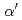 between the creep and the tensile tests.
between the creep and the tensile tests.
土田 紀之*; 川畑 拓司*; 石丸 栄一郎*; 高橋 明彦*; 鈴木 裕士; 菖蒲 敬久
ISIJ International, 53(7), p.1260 - 1267, 2013/07
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:71.21(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)二相ステンレス鋼の引張変形挙動を明らかにするため、中性子と放射光白色X線を利用したその場測定を行った。放射光白色X線の結果から、引張変形中でS32101の硬い相がフェライトからオーステナイトに変化した。これはより大きな力により後半の相へ変化したためであるといえる。中性子実験からは、S32101中のより高い応力下での 相の応力分配が見つかった。ゆえに、S32101中の加工硬化率は
相の応力分配が見つかった。ゆえに、S32101中の加工硬化率は 相と
相と 相の応力分配により説明することができる。
相の応力分配により説明することができる。
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*; Gong, W.; 阿部 淳; 相澤 一也
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1528 (Internet), 7 Pages, 2013/01
鉄鋼材料の強化機構の中で、高強度,高延性、優れた高速変形挙動が期待されるものにTRIP効果がある。TRIP効果は鉄鋼材料に発現する特徴的な強化機構であり、オーステナイト組織( )の一部が強度の高いマルテンサイト組織(
)の一部が強度の高いマルテンサイト組織( ')に変態する(加工誘起変態)ことにより高強度,高延性が得られると言われている。ところが、TRIP効果にもたらす変形中の加工誘起変態挙動,
')に変態する(加工誘起変態)ことにより高強度,高延性が得られると言われている。ところが、TRIP効果にもたらす変形中の加工誘起変態挙動,  ,フェライト組織(
,フェライト組織( )及び
)及び '組織の役割に関する定量的な研究がほとんどないため、TRIP鋼の変形中のその場中性子回折実験を行った。実験及び結果の詳細を紹介し議論する。
'組織の役割に関する定量的な研究がほとんどないため、TRIP鋼の変形中のその場中性子回折実験を行った。実験及び結果の詳細を紹介し議論する。
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*; 川崎 卓郎; 諸岡 聡
no journal, ,
TRIP鋼のマルテンサイト変態において、ひずみ誘起相変態が支配的であるか、変形中のその場中性子回折によって検証した。引張変形中のその場中性子回折実験をJ-PARCのBL19匠にて実施し、ピーク積分強度, 格子ひずみ等の解析をRietveld法等で行った。マクロ降伏の後にマルテンサイト変態の相対量が増加しはじめ、負荷応力の増加に伴い増加し続けた。この負荷応力にはベイナイト-フェライト及び変態で発生したマルテンサイトも寄与している。また、マルテンサイト変態量に 相応力との相関があることを示唆している。
相応力との相関があることを示唆している。
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*; 中本 建志*; 相澤 一也; 阿部 淳*; Gong, W.
no journal, ,
Stress Induced Phase Transformation is one of the strengthening mechanisms in steels for the improvement in strength and ductility, which is well known as a TRIP effect. Two kinds of steels, type 304 stainless steel and TRIP-type multiphase carbon steel, were used in neutron diffraction measurements during tensile deformations. The type 304 stainless steel samples were deformed at RT and at 50K. There was no TRIP effect observed during the deformation at RT, while TRIP effects were observed at the onset of plastic region during deformation at 50K. The TRIP-type carbon steel was deformed at RT, and TRIP effects started at the onset of plastic deformation. The phases formed during TRIP effects were determined and stress partitioning among the constituent phases were evaluated. The details will be reported and the strengthening mechanisms of both steels during the TRIP effects will be discussed in the presentation.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 土田 紀之*; 諸岡 聡; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
Transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) phenomenon is paid attention because it gives a high work-hardening rate and a large uniform elongation as a result of deformation induced martensitic transformation during plastic loading. The deformation induced martensitic transformations in most metastable iron alloys occur after macro-yielding during deformation at room temperature (RT). There are arguments to explain whether the martensitic transformation during plastic loading is controlled by strain (the strain-induced transformation) or stress (the stress-assisted transformation). In this paper, we tried to observe the trigger of deformation induced martensitic transformation during tensile deformation by in situ tensile loading neutron diffraction (ND) of metastable iron alloys. In situ ND measurements during deformation have been confirmed as powerful tools to understand the strengthening mechanism during deformation of multiphase alloys.
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
鉄鋼材料の強化機構の中で、高強度,高延性、優れた高速変形挙動が期待されるものにTRIP効果がある。TRIP効果は準安定な組織(オーステナイト:A)を有する鉄鋼材料において塑性変形に伴い強度がより高い組織(マルテンサイト:M)に相変態することによって起こる。ところが、TRIP効果にもたらす変形中の加工誘起相変態挙動、すなわち、M相の強度への寄与に関する定量的な研究がほとんどないため、中性子回折法を使って変形中のその場測定を行い解明を試みた。匠は従来の装置に比べて約3倍も分解能が高いため今まで分離が難しかったフェライト母相とM相の回折情報を識別でき、全構成相の相ひずみの観察に成功した。加工誘起相変態で形成されたM相は最も高い応力を負担していることが実証できた。
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 阿部 淳; 相澤 一也; 土田 紀之*
no journal, ,
鉄鋼材料の強化機構の中で、高強度,高延性、優れた高速変形挙動が期待されるものにTRIP効果がある。TRIP効果は鉄鋼材料に発現する特徴的な強化機構であり、オーステナイト組織( )の一部が強度の高いマルテンサイト組織(
)の一部が強度の高いマルテンサイト組織( ')に変態する(加工誘起変態)ことにより高強度,高延性が得られると言われている。ところが、TRIP効果にもたらす変形中の加工誘起変態挙動,
')に変態する(加工誘起変態)ことにより高強度,高延性が得られると言われている。ところが、TRIP効果にもたらす変形中の加工誘起変態挙動, ,フェライト組織(
,フェライト組織( )及び
)及び '組織の役割に関する定量的な研究がほとんどないため、TRIP鋼の変形中のその場中性子回折実験を行った。本発表では実験結果を中心に紹介し、他の手法では得られない知見を議論する。
'組織の役割に関する定量的な研究がほとんどないため、TRIP鋼の変形中のその場中性子回折実験を行った。本発表では実験結果を中心に紹介し、他の手法では得られない知見を議論する。
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*
no journal, ,
TRIP-aided multiphase steels with different carbon contents were analyzed in situ during tensile deformation by TOF neutron diffraction to clarify the deformation induced martensitic transformation behavior and its role on the strengthening mechanism. The difference in the carbon content affected mainly the difference in the phase fractions, where the higher carbon content increased the fraction of retained austenite ( ). However, changes in the relative fraction of martensitic transformation during deformation were found to be similar in both steels. The relative fraction of martensitic transformation increased with increasing of
). However, changes in the relative fraction of martensitic transformation during deformation were found to be similar in both steels. The relative fraction of martensitic transformation increased with increasing of  phase stress. The martensite phase stress was much larger than that of
phase stress. The martensite phase stress was much larger than that of  or bainitic ferrite since the martensite was generated at the beginning of plastic deformation. The stress contribution from martensite increased during plastic deformation while that from bainitic ferrite hardly changed and that from
or bainitic ferrite since the martensite was generated at the beginning of plastic deformation. The stress contribution from martensite increased during plastic deformation while that from bainitic ferrite hardly changed and that from  decreased.
decreased.
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*; Gong, W.; 阿部 淳; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
2種類のTRIP型複相の炭素鋼、0.4C TRIP鋼及び0.2C TRIP鋼を用意し、室温引張変形中のその場測定をJ-PARC物質・生命科学実験施設(MLF)工学材料回折装置「匠」を用いて行った。試験片を横にして、入射ビームに対して45 水平方向に置き、外力を加えて、引張軸方向とその垂直方向からの回折パターンを散乱角2
水平方向に置き、外力を加えて、引張軸方向とその垂直方向からの回折パターンを散乱角2 が90
が90 のペアの検出器バンクで同時に収集した。引張試験は、弾性域では5分間の段階的な荷重制御、塑性域ではクロスヘッド一定の連続試験を行った。塑性域での回折パターンは実験後に5分間ごとにスライスし、解析を行った。本発表では、得られた実験結果を紹介し、TRIP効果に伴う強化機構及び本試料における炭素量の影響等についての議論を行う。
のペアの検出器バンクで同時に収集した。引張試験は、弾性域では5分間の段階的な荷重制御、塑性域ではクロスヘッド一定の連続試験を行った。塑性域での回折パターンは実験後に5分間ごとにスライスし、解析を行った。本発表では、得られた実験結果を紹介し、TRIP効果に伴う強化機構及び本試料における炭素量の影響等についての議論を行う。
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*; 阿部 淳*; 川崎 卓郎
no journal, ,
TRIP steels contain several tens of percent of metastable retained austenite ( ) that transform to martensite (
) that transform to martensite ( ') during deformation, leading to the improvement of strength and ductility. Deformation induced martensitic transformation behavior and its effect on the strengthening mechanism in two TRIP-aided multiphase steels with different carbon contents (0.2 and 0.4 wt.%) were monitored using in situ neutron diffraction experiments during tensile tests to clarifying the effect of TRIP on the improvement of strength. The results suggest that
') during deformation, leading to the improvement of strength and ductility. Deformation induced martensitic transformation behavior and its effect on the strengthening mechanism in two TRIP-aided multiphase steels with different carbon contents (0.2 and 0.4 wt.%) were monitored using in situ neutron diffraction experiments during tensile tests to clarifying the effect of TRIP on the improvement of strength. The results suggest that  ' plays an important role in increasing the strength during tensile deformation.
' plays an important role in increasing the strength during tensile deformation.
Harjo, S.; 土田 紀之*; 川崎 卓郎
no journal, ,
Transformation Induced Plasticity (TRIP) effect is one of important strengthening mechanism of advanced steels, to achieve high strength and relatively large ductility in the same time. TRIP occurs and uses the deformation induced martensitic transformation. It is well known that the retained austenite still exists in TRIP steels near the fracture in tensile deformation. Recently we have found that the amount of transformed martensite was much larger in a creep test under constant load than in tensile deformation of a metastable austenitic 304 steel that shows also TRIP phenomenon. In this study, we will pay attention on crystallographic microstructure properties including dislocation information during tensile and creep deformations, by means of in situ neutron diffraction, to clarify the relationship among martensitic transformation, crystallographic properties and mechanical properties.