Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wada, Yuki; Furuichi, Noriyuki*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*
European Journal of Mechanics B, Fluids, 91, p.233 - 243, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:21.05(Mechanics) He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation) He
He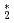 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.76(Physics, Applied)Wada, Yuki; Furuichi, Noriyuki*; Kusano, Eisuke*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*
Proceedings of 11th International Symposium on Turbulence and Shear Flow Phenomena (TSFP-11) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2019/07
This paper reports characteristics of turbulence intensity profile obtained in high Reynolds number actual flow facility in Japan. The experiments were performed in a pipe flow with water, and the friction Reynolds number was varied up to 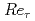 = 2.0
= 2.0  10
10 . The streamwise velocity was measured by laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV). The new procedure to correct the measurement volume effect of LDV is suggested and we discuss turbulence intensity issues such as the inner peak Reynolds number dependence and the outer logarithmic behavior, it was found that these characteristic behaviors are consistent with previous turbulence studies.
. The streamwise velocity was measured by laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV). The new procedure to correct the measurement volume effect of LDV is suggested and we discuss turbulence intensity issues such as the inner peak Reynolds number dependence and the outer logarithmic behavior, it was found that these characteristic behaviors are consistent with previous turbulence studies.
Wada, Yuki; Furuichi, Noriyuki*; Kusano, Eisuke*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Flow Dynamics (ICFD 2018) (USB Flash Drive), p.778 - 779, 2018/11
Spatial resolution effect of LDV (Laser Doppler Velocimetry) on the time-averaged statistics is presented in high Reynolds number turbulent pipe flow. Employing PDF (Probability Density Function) of streamwise velocity, we report the study of overestimation of time-averaged statistics based on the size of measurement volume. We proposed a simple equation to estimate their spatial resolution effect. Using the proposed equation, the measurement position and the measurement volume calculated precisely based on experimental setup, it was found that the correction for spatial resolution effect is possible. Analyzing the pipe flow data measured by LDV, we estimated the expected turbulence intensity profile. The validity of the present correction method was confirmed by comparing the correction result based on the low-resolution experimental result with the high-resolution experimental result.
Furuichi, Noriyuki*; Terao, Yoshiya*; Wada, Yuki; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*
Physics of Fluids, 30(5), p.055101_1 - 055101_7, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:73.01(Mechanics)Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hoashi, Eiji*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Yagi, Juro*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2014 (PLASMA 2014) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2014/11
In the IFMIF/EVEDA (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility/ Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity), the validation tests of the EVEDA lithium test loop with the world's highest flow rate of 3000 L/min was succeeded in generating a 100 mm-wide and 25 mm-thick free-surface lithium flow steadily under the IFMIF operation condition of a high-speed of 15 m/s at 250 C in a vacuum of 10
C in a vacuum of 10  Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Ida, Mizuho*; Ito, Yuzuru; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Edao, Yuki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 66(1), p.46 - 56, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Fukada, Satoshi*; Yagi, Juro*; Ida, Mizuho; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(12), p.691 - 705, 2012/12
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Kanemura, Takuji; Kondo, Hiroo; Ida, Mizuho; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Otaka, Masahiko; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(9-11), p.2491 - 2494, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)In IFMIF/EVEDA, tasks for lithium target system are shared to 5 validation tasks (LF1-5) and a design task (LF6). The purpose of LF1 task is to construct and operate the EVEDA lithium test loop, and JAEA has a main responsibility to the performance of the Li test loop. LF2 is a task for the diagnostics of the Li test loop and IFMIF design. Basic research for the diagnostics equipment has been completed, and the construction for the Li test loop will be finished before March in 2011. LF4 is a task for the purification systems with nitrogen and hydrogen. Basic research for the purification equipment has been completed, and the construction of the nitrogen system for the Li test loop will be finished before March in 2011. LF5 is a task for the remote handling system with the target assembly. JAEA has an idea to use the laser beam for cutting and welding of the lip part of the flanges. LF6 is a task for the design of the IFMIF based on the validation experiments of LF1-5.
Ida, Mizuho; Fukada, Satoshi*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Kondo, Hiroo; Miyashita, Makoto; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sugiura, Hirokazu*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.1294 - 1298, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities (EVEDA) of the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) was started. As a Japanese activity for the target system, EVEDA Lithium Test Loop simulating hydraulic and impurity conditions of IFMIF is under design and preparation for fabrication. Feasibility of thermo-mechanical structure of the target assembly and the replaceable back-plate made of F82H (a RAFM) and 316L (a stainless steel) is a key issue. Toward final validation on the EVEDA loop, diagnostics applicable to a high-speed free-surface Li flow and hot traps to control nitrogen and hydrogen in Li are under tests. For remote handling of target assemblies and the replaceable back-plates activated up to 50 dpa/y, lip weld on 316L-316L by laser and dissimilar weld on F82H-316L are under investigation. As engineering design of the IFMIF target system, water experiments and hydraulic/thermo-mechanical analyses of the back-plate are going.
Ide, Hiroshi; Sakuta, Yoshiyuki; Hanawa, Yoshio; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Tsuboi, Kazuaki; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Miyazawa, Masataka
JAEA-Technology 2009-019, 28 Pages, 2009/06
The main body of the JMTR is composed of reactor pressure vessel, core and reactor pool. At the bottom of the reactor pool, the Diaphragm-seal (2.6m outer diameter, 2m inner diameter, thickness 1.5mm) of the JMTR made of stainless steel is installed to prevent the water leak of the reactor pool and to absorb the expansion of the reactor pressure vessel due to pressure and temperature changes. Prior to the refurbishment of the JMTR, the inspection device which is a deposition-collection apparatus with underwater-camera was developed, and the visual inspection was carried out to confirm the soundness of the diaphragm-seal. As a result, harmful flaws and/or corrosions were not inspected in the visual inspection, and the soundness of the diaphragm seal was confirmed. In future, the long-term integrity of the diaphragm-seal will could be achieved by conducting the periodic inspection.
Tanaka, Hirohiko*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kawashima, Hisato; Takamura, Shuichi*; Uesugi, Yoshihiko*; JT-60U Team
Nuclear Fusion, 49(6), p.065017_1 - 065017_7, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:78.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Comparison between fluctuation characteristics at high-field-side (HFS) and low-field-side (LFS) scrape off layers (SOLs) has been made, for the first time, in the L mode plasma of the JT-60U tokamak using reciprocating Langumuir probes. Statistical analysis based on probability distribution function (PDF) was employed to describe intermittent (non-diffusion) transport in SOL plasma fluctuations. The positive bursty events appeared most frequently at LFS midplane associated with blobby plasma transport, then the PDF is strongly skewed positively, while the PDF in HFS SOL is close to Gaussian distribution. Conditional averaging analysis of the positive bursty events at LFS midplane indicates the intermittent feature with a rapid increase and a slow decay is similar to that of plasma blobs theoretically predicted. Statistical self-similarity was also investigated with Fourier power spectrum and statistics of waiting-time and duration-time of the fluctuation.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Sakai, Takaaki; Kamide, Hideki; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Ezure, Toshiki; Uchibori, Akihiro; Ito, Kei; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Okamoto, Koji*; Tanaka, Nobuatsu*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-049, 44 Pages, 2008/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has conducted a conceptional design study of a sodium-cooled fast reactor in a frame work of the FBR feasibility study. The plant system concept for a commercial step is intended to minimize a vessel diameter to achieve an economical competitiveness. Therefore, the coolant in the vessel has relatively higher velocity and gas entrainment (GE) prevention from a liquid surface in the reactor vessel becomes one of important issues for the thermal-hydraulic design. In order to establish a design criteria for the GE prevention, the GE from vortex dimples at the liquid surface was investigated by a working group. The 1st proposal of "Design Guideline for Gas Entrainment Prevention Using CFD Method" was established based on the knowledge gained from the working group activities. This report introduces each study in the working group to clarify the basis of the design guideline.
Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kamide, Hideki
JNC TY9400 2005-017, 54 Pages, 2005/03
Compact reactor vessel is designed to reduce construction cost of a fast reactor. In a compact reactor vessel flow velocity will increase and it causes gas entrainment at free surface. Thus, gas entrainment is one of significant issue of the reactor design. In this study we carried out a water experiment on the gas entrainment, especially the onset condition of a dimple vortex, which causes the gas entrainment in order to establish a guide line in a deisgn.This study is planned to carry in three years from 2003 to 2005. The year of 2004 corresponds to the second term. In this year, water experiment was carried out using a flow channel, vertical suction pipe, and an obstacle in order to see influences of obstacles on the gas entrainment and dimple vortex. Onset conditions of the gas entrainment due to the dimple vortex were obtained with experimental parameters of flow velocity in the channel, water level, and free surface wave or disturbance. It was shown that the onset of gas entrainment needed vertical vortex, e.g. in a wake of an obstacle, and disturbance of free surface block the onset of the dimple vortex and the gas entrainment.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Fujita, Mitsutane*; Xu, Y.*; Yoshida, Kenji*; Mashiko, Shinichi*; Shimura, Kazuki*; Miyakawa, Shunichi*; Ashino, Toshihiro*
Data Science Journal (Internet), 3, p.88 - 94, 2004/07
The distributed material database system named "Data-Free-Way" has been developed by four organizations (the National Institute for Materials Science, the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute, and the Japan Science and Technology Corporation) under a cooperative agreement. In order to create additional values of the system, knowledge base system, in which knowledge extracted from the material database is expressed, is planned to be developed for more effective utilization of Data-Free-Way. XML (eXtensible Markup Language) has been adopted as the description method of the retrieved results and the meaning of them. One knowledge note described with XML is stored as one knowledge which composes the knowledge base. This paper describes the current status of Data-Free-Way, the description method of knowledge extracted from the material database with XML and the distributed material knowledge base system.
Obata, Takanori*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Kamide, Hideki
JNC TY9400 2004-017, 36 Pages, 2004/03
Gas entrainment at free surface is of importance due to higher flow velocity in a compact reactor vessel. Dimple-eddy is one of major reasons for gas entrainment in case of low flow velocity condition at free surface. Water experiment was carried out to see generation of dimple-eddy in this study. A round shape obstacle was set in an open channel. Eddies are generated in wake region behind the obstacle.Laser beam and photo acceptance unit of PSD were used to measure inclined angle of free surface and shape of dimple-eddy. The dimple depth is one of the key parameter of eddy development. Following findings were obtained from the experiment; 1) This laser-PSD system can measure the inclined angle of free surface and find the dimple-eddy, 2) Shape of the dimple-eddy can be estimated by statistics of the free surface angle-data.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactors (CD-ROM), p.1185 - 1190, 2004/01
The aim of this work is to evaluate corrosion behavior of irradiated materials for mechanistic understanding of irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC). Solution annealed high purity Fe-18Cr-12Ni specimens were used in this study. H and He were implanted during irradiation with 12MeV Ni ion at 573K and 673K. After corrosion procedure, the specimens were examined with atomic force microscope (AFM) to evaluate corrosion behavior. It was shown that the corroded volume of irradiated area increased with radiation damage. H implantation at lower temperature accelerated corrosion, but H implantation at higher temperature did not accelerate corrosion. He implantation suppressed corrosion, and corroded volume was larger for the specimens irradiated at 673K than these at 573K. It is suggested from this study that implantations of H and He affect the passivating behavior of Ni
ion at 573K and 673K. After corrosion procedure, the specimens were examined with atomic force microscope (AFM) to evaluate corrosion behavior. It was shown that the corroded volume of irradiated area increased with radiation damage. H implantation at lower temperature accelerated corrosion, but H implantation at higher temperature did not accelerate corrosion. He implantation suppressed corrosion, and corroded volume was larger for the specimens irradiated at 673K than these at 573K. It is suggested from this study that implantations of H and He affect the passivating behavior of Ni ion irradiated alloy.
ion irradiated alloy.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon AEM Gakkai-Shi, 11(4), p.242 - 248, 2003/12
no abstracts in English
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Abe, Hiroaki*; Sekimura, Naoto*
JAERI-Review 2003-033, TIARA Annual Report 2002, p.171 - 173, 2003/11
The aim of this work is to evaluate corrosion behavior of irradiated materials for mechanistic understanding of irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC). Solution annealed high purity Fe-18Cr-12Ni specimens were used in this study. H and He were implanted during irradiation with 12MeV Ni ion at 573K. After corrosion procedure, the specimens were examined with atomic force microscope (AFM) to evaluate corrosion behavior. It was shown that the corroded volume of irradiated area increased with radiation damage. H implantation at lower temperature accelerated corrosion. He implantation suppressed corrosion.
ion at 573K. After corrosion procedure, the specimens were examined with atomic force microscope (AFM) to evaluate corrosion behavior. It was shown that the corroded volume of irradiated area increased with radiation damage. H implantation at lower temperature accelerated corrosion. He implantation suppressed corrosion.