Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Ono, Takuya; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Watanabe, Koji*; Abe, Hitoshi; Yamane, Yuichi
Nuclear Technology, 211(3), p.429 - 438, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Contributing to the confinement safety evaluation of glove-box (GB) connected with high efficiency particle air (HEPA) filters for radioactive materials under fire accidents, combustion tests of a flammable polymer, Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), and a flame retardant polymer, Polycarbonate (PC), as typical GB panel resins have been conducted with an engineering-scale combustion apparatus. The combustion properties such as the mass loss rate (MLR) and the heat release rate (HRR) of PMMA and PC were investigated in the combustion tests. In the tests with the same shapes, it was found the followings; MLRs and HRRs of PMMA were larger than those of PC under the same supply flow rate into the combustion cell (Fv); MLRs and HRRs of PMMA and PC were constant under different Fv. Moreover, in the tests of PMMA with different cross section areas (S), MLRs and HRRs were found to be proportional to S. Using these results, the relationships of MLR and HRR to S of PMMA and PC were deduced.
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Ono, Takuya; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Abe, Hitoshi
Nuclear Technology, 208(7), p.1205 - 1213, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A clogging behavior of a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter at solvent fire accidents for reprocessing facilities has been studied. In this study, the burning rates of 30% tri-butyl phosphate (TBP)/dodecane (DD) mixed solvent and DD solvent and the differential pressure ( P) of a high airflow typed HEPA filter applied in the actual facilities in Japan were measured. It was confirmed that the mainly burned was DD at the early stage of the mixed solvent burning and the TBP at the late stage. Furthermore, it was found that the
P) of a high airflow typed HEPA filter applied in the actual facilities in Japan were measured. It was confirmed that the mainly burned was DD at the early stage of the mixed solvent burning and the TBP at the late stage. Furthermore, it was found that the  P rapidly rose at the late stage of the mixed solvent burning. The increase of the release ratio of the unburned particulate composition (TBP, its degraded solvent and inorganic phosphorus (P
P rapidly rose at the late stage of the mixed solvent burning. The increase of the release ratio of the unburned particulate composition (TBP, its degraded solvent and inorganic phosphorus (P O
O )) was considered to contribute to the rapid rise. The correlating formulas with the
)) was considered to contribute to the rapid rise. The correlating formulas with the  P and the mass of the loading particulates, except for the region of the rapid rise of
P and the mass of the loading particulates, except for the region of the rapid rise of  P, could be induced.
P, could be induced.
Yamane, Yuichi; Amano, Yuki; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Abe, Hitoshi; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Yoshida, Kazuo; Ishikawa, Jun
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(6), p.783 - 789, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The release behavior of radioactive materials from high active liquid waste (HALW) has been experimentally investigated under boiling accident conditions. In the experiments using HALW obtained through laboratory scale reprocessing, release ratio was measured for the FP nuclides such as Ru,  Tc, Cs, Sr, Nd, Y, Mo, Rh and actinides such as
Tc, Cs, Sr, Nd, Y, Mo, Rh and actinides such as  Cm,
Cm,  Am. As a result, the release ratio was 0.20 for Ru and 1
Am. As a result, the release ratio was 0.20 for Ru and 1
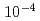 for the FP and Ac nuclides. Ru was released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas. For its released amount, weak dependency was found to the initial concentration in the test solution. The release ratio decreased with the initial concentration. For other FP nuclides and actinides as non-volatile, released into the gas phase in the form of mist, the released amount increased with the initial concentration. The release ratio of Ru and NOx concentration increased with temperature of the test solutions. They were released almost at the same temperature between 200 and 300
for the FP and Ac nuclides. Ru was released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas. For its released amount, weak dependency was found to the initial concentration in the test solution. The release ratio decreased with the initial concentration. For other FP nuclides and actinides as non-volatile, released into the gas phase in the form of mist, the released amount increased with the initial concentration. The release ratio of Ru and NOx concentration increased with temperature of the test solutions. They were released almost at the same temperature between 200 and 300 C. Size distribution of the mist and other particle was measured.
C. Size distribution of the mist and other particle was measured.
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Kazuo; Yamane, Yuichi; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(4), p.227 - 234, 2015/12
The release characteristics of Ru from highly active liquid waste (HALW) have been investigated under the condition of accidental evaporation to dryness by boiling of HALW. Using a laboratory-scale apparatus, non-radioactive simulated HALW (s-HALW) was heated with an external heater to dryness to observe the release characteristics of Ru and gaseous nitrogen oxides. As a result, Ru was significantly released between 120 and 300  C of the s-HALW. The cumulative release ratio of Ru was 0.088. It was also found that the partially released amount of Ru against the temperature of the s-HALW had two peaks with one maximal at about 140
C of the s-HALW. The cumulative release ratio of Ru was 0.088. It was also found that the partially released amount of Ru against the temperature of the s-HALW had two peaks with one maximal at about 140  C and maximum at about 240
C and maximum at about 240  C. Referring to the results of the release rate of gaseous nitrogen oxides and the volume of condensate, which was a collection of the mixed vapors of steam and nitric acid released from the s-HALW, we discussed the causes of Ru release around these peaks.
C. Referring to the results of the release rate of gaseous nitrogen oxides and the volume of condensate, which was a collection of the mixed vapors of steam and nitric acid released from the s-HALW, we discussed the causes of Ru release around these peaks.
Uchiyama, Gunzo; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi; Yamane, Yuichi; Yoshida, Kazuo; Ishikawa, Jun
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.1056 - 1063, 2015/09
The experimental study for source term data of radioactive materials has been conducted at a boiling accident of high active liquid waste (HALW) in reprocessing plants. In the study, three kinds of tests have been conducted including a cold small scale test, a cold engineering scale test and a hot small scale test. The following results were obtained: Ruthenium and Technetium were released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas under the boiling accident conditions of a simulated HALW. Non-volatile fission products (FPs) such as Nd and Cs were released into the gas phase in the form of mist. The release ratios of non-volatile FPs from a vessel of the simulated HALW were about 10 . The release ratios of actinide nuclides such as Am were almost the same as those of non-volatile FPs.
. The release ratios of actinide nuclides such as Am were almost the same as those of non-volatile FPs.
Amano, Yuki; Watanabe, Koji; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Yamane, Yuichi; Ishikawa, Jun; Yoshida, Kazuo; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(2), p.86 - 94, 2015/06
Radioactive materials could be released into air due to the accidental boiling of high active liquid waste (HALW) in reprocessing plants. Volatile radioactive nuclides, such as ruthenium, are released from the tanks into the atmosphere. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are also released due to the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates in HALW. The released NOx transport volatile ruthenium and cause redox reactions associated with the composition or decomposition of volatile ruthenium. In this study, NOx release data were obtained by heating simulated HALW up to 600 C. As a result, the release of NOx from the simulated HALW was observed from 200
C. As a result, the release of NOx from the simulated HALW was observed from 200 C to 600
C to 600 C, and the main release of NOx was observed at about 340
C, and the main release of NOx was observed at about 340 C. All the lanthanide nitrates were found to decompose in the simulated HALW, and the thermal decomposition temperature of the lanthanide nitrates decreased after the addition of ruthenium dioxide to the mixed lanthanide nitrates solution.
C. All the lanthanide nitrates were found to decompose in the simulated HALW, and the thermal decomposition temperature of the lanthanide nitrates decreased after the addition of ruthenium dioxide to the mixed lanthanide nitrates solution.
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi; Yamane, Yuichi; Yoshida, Kazuo
Nuclear Technology, 190(2), p.207 - 213, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)The release behavior of radioactive materials from high active liquid waste (HALW) has been investigated under boiling accident conditions. Results of the experiment using a nonradioactive simulated HALW found Ru to be a volatile element under the accident conditions and to be released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas. The Ru release rate and the apparent Ru volatilization rate constant were obtained under the boiling conditions of simulated HALW. The other fission product elements such as Cs were found to be nonvolatile and to be released into the gasphase in the form of mist. The mist size distribution near the surface of the simulated HALW in the reactor vessel was found to range from 0.05 to 20  m with a peak diameter of
m with a peak diameter of  2
2  m.
m.
 9 fuel
9 fuelSuyama, Kenya; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Miki; Yamamoto, Toru*; Suzuki, Motomu*
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.47 - 56, 2015/00
In fission products in used nuclear fuel, there are several stable isotopes which have large neutron absorption effect. It is known that there are several hardly measurable elements in such important fission products. JAEA had been developed the method to assess the amount of fission products which are hardly measurable and have large neutron capture cross section, under the auspices of the JNES. In this development, the measurement method was developed combining a simple and effective chemical separation scheme of fission products from used nuclear fuel and ICP-MS with high-sensitivity and high-precision. This method was applied to the measurement program for used BWR 9 9 fuel assembly. This method is applicable to the required measurement for the countermeasure to the accident of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plants of Tokyo Electric Power Company. This presentation describes the measurement method developed in the study as well as the future measurement plan in JAEA.
9 fuel assembly. This method is applicable to the required measurement for the countermeasure to the accident of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plants of Tokyo Electric Power Company. This presentation describes the measurement method developed in the study as well as the future measurement plan in JAEA.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Yamane, Yuichi; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(4), p.155 - 166, 2014/12
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents to occur caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, a large amount of ruthenium (Ru) will be volatilized and transfer to the vapor phase in the tank, and could be released to the environment. Therefore, the quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the key issues in the assessment of the accident consequence. To resolve this issue, an empirical correlation for Ru transfer rate to vapor phase with the temperature, nitric acid mol fraction and activity of HLLW has been developed based on the data obtained from the accelerated experiments using simulated HLLW. A simulation study with the developed correlation demonstrated that amount of Ru transfer to vapor phase was in a good agreement with the long term experiment using actual HLLW.
 ray irradiation on pyrolysis properties of glove-box panel materials
ray irradiation on pyrolysis properties of glove-box panel materialsAbe, Hitoshi; Watanabe, Koji; Uchiyama, Gunzo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(4), p.136 - 144, 2014/12
The glove box (GB) is the equipment with some kinds of plastic components which is used for the containment of the radioactive material. In the MOX fuel fabrication facility, MOX is also handled in the GB. Since the plastic panel, which has the largest area of the GB, is used in the long period, it is exposed to high dose from MOX continuously. In this study, to confirm that containment capability of GB can be maintained even under external thermal stress, effect of the  -ray irradiation with
-ray irradiation with  Co on the pyrolysis properties of the common panel materials which were obtained by TG-DTA has been investigated. As a result, polymethylmethacrylate showed the large peak of mass loss rate at about 260 degrees under the non-irradiation and air condition but it separated into lower and higher temperature sides above 25 kGy. The effect was not observed up to 10 kGy for polymethylmethacrylate, and up to 880 kGy for polycarbonate. By comparing with the estimated total dose of which GB panel would be irradiated in the operation period, it was found that the irradiation from MOX does not have significant effect on the pyrolysis properties of GB panel in the actual facility.
Co on the pyrolysis properties of the common panel materials which were obtained by TG-DTA has been investigated. As a result, polymethylmethacrylate showed the large peak of mass loss rate at about 260 degrees under the non-irradiation and air condition but it separated into lower and higher temperature sides above 25 kGy. The effect was not observed up to 10 kGy for polymethylmethacrylate, and up to 880 kGy for polycarbonate. By comparing with the estimated total dose of which GB panel would be irradiated in the operation period, it was found that the irradiation from MOX does not have significant effect on the pyrolysis properties of GB panel in the actual facility.
Abe, Hitoshi; Masaki, Tomoo; Amano, Yuki; Uchiyama, Gunzo
JAEA-Research 2014-022, 12 Pages, 2014/11
To contribute safety evaluation of boiling and drying accident of high active liquid waste (HALW) in fuel reprocessing plant, release behavior of Ru, which was considered as an important nuclide for evaluating public dose from the volatile viewpoint, has been investigated. It has been reported that release of Ru becomes conspicuously after HALW is dried up. In this work, to grasp the release behavior of Ru, release ratio of Ru with thermal decomposition of Ru nitrate, which would be in the dried HALW, was measured and release rate constant of Ru from the nitrate was estimated. It was found that the calculation result of release rate of Ru from the nitrate with rise of temperature by using the constant could well simulate the result acquired from the beaker-scale experiment.
Uchiyama, Gunzo; Abe, Hitoshi
Proceedings of 20th International Solvent Extraction Conference (ISEC 2014), p.1167 - 1172, 2014/09
A simulation study and an experimental study were conducted for the consideration of a scenario of criticality accident at raffinate solution tanks in separation cycle in reprocessing plants. In a simulation study, transient extraction behavior of Pu has been studied with the solvent extraction simulation code, ESSCAR to understand the effect of process parameters in separation cycle. In the experimental study, extraction behaviors of nitrous acid and dibutyl phosphate (DBP) which influence the extraction behavior of Pu in separation cycles were investigated by using a mixer-settler under a  -ray irradiation condition. It was found that the concentrations of nitrous acid in both organic and aqueous phases were 1
-ray irradiation condition. It was found that the concentrations of nitrous acid in both organic and aqueous phases were 1  10
10 M and 2
M and 2  10
10 M, respectively. The concentrations of DBP in both organic and aqueous phases were 5
M, respectively. The concentrations of DBP in both organic and aqueous phases were 5  10
10 M and 8
M and 8  10
10 M, respectively.
M, respectively.
Uchiyama, Gunzo; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi; Yamane, Yuichi; Yoshida, Kazuo; Ishikawa, Jun
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposia 2014 (WM2014) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2014/05
The experimental study for source term data of radioactive materials has been conducted at a boiling accident of high active liquid waste (HALW) in a reprocessing plant. In the small scale cold test using a non-radioactive simulated HALW, the release behavior of FP elements from the simulated HALW were investigated under various boiling accident conditions. In the engineering scale cold test, the release behavior of FP elements at boiling accident conditions was investigated mainly as a spatial function. In the small scale hot test using a radioactive simulated HALW, the release behavior of radioactive materials (FP, alpha nuclides) were obtained under typical boiling accident conditions. In the small scale hot test, the release fractions of Ru and non-volatile FPs obtained were almost the same as those of the small scale cold test.
Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Suyama, Kenya; Sonoda, Takashi; Okubo, Kiyoshi; Umeda, Miki; Uchiyama, Gunzo
JAEA-Research 2013-020, 81 Pages, 2013/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency conducted a project "Isotopic Composition measurement of Fission Products in Spent Fuel from FY2008 to FY2011" by the entrustment of Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization. In that project, we measured the isotopic composition of neodymium isotopes which are important to evaluate the burnup value of spent nuclear fuel by using two different methods and obtained different results. So that we carried out the follow-up measurement in order to investigate the reason of the difference between two neodymium measurements. It was found that we needed correction to the measurement results of neodymium for two samples and a part of other fission products for all samples in total five samples. This report summarizes the all works carried out in this follow-up measurement and obtained results.
Amano, Yuki; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Abe, Hitoshi; Yamane, Yuichi; Yoshida, Kazuo
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference; Nuclear Energy at a Crossroads (GLOBAL 2013) (CD-ROM), p.1411 - 1417, 2013/09
Takeuchi, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Nakajima, Yasuo; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Nojima, Yasuo*; Fujine, Sachio*
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering, 7(6), p.1090 - 1096, 2013/06
The corrosion behavior of a titanium-5% tantalum alloy (Ti-5Ta) in hot nitric acid condensate was investigated to understand aging behavior of reprocessing equipments. On the basis of long-term immersion tests, it was determined that the corrosion of Ti-5Ta in nitric acid condensate is accelerated with an increase in the concentration. The corrosion rate was nearly constant during the immersion test and the coupons suffered from uniform corrosion. In addition, it is important to note that the nitric acid concentration in the condensate increased on addition of metal salts to the heated nitric acid solution. The larger valence of metal ions was contributed to the increase in the concentration of nitric acid condensate. Consequently, the metal salt in the heated nitric acid solution accelerates the corrosion of Ti-5Ta in the condensate. Therefore, the nitric acid condensate condition should be carefully considered for the corrosion environment of titanium and its alloys.

Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Ban, Yasutoshi; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Nojima, Yasuo*; Fujine, Sachio*
ECS Transactions, 53(21), p.45 - 55, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.37(Electrochemistry)Neptunium ion contained as one of the fission products in reprocessing solutions is known as a corrosion accelerator of the stainless steel. But it is not clear why remarkable acceleration of corrosion is caused by a slight amount of the Np ion in boiling nitric acid solution. Neptunium has several oxidation states in nitric acid solution. These changeable oxidation states of Np in nitric acid solution are regarded as the cause. Therefore an evaluation of the electrochemical behaviors on stainless steel in nitric acid solution related to the oxidation state of Np is required in order to understand the corrosion acceleration mechanism. A specially designed electrochemical test cell integrated with optical cell for spectroscopic analysis was used for this purpose. From results of electrochemical tests, cathodic reaction on stainless steel was activated by Np ions. Np(VI) ion made the corrosion potential shift nobler than Np(V) and nobler corrosion potential causes increasing corrosion current and accelerating corrosion of stainless steel in nitric acid solution. Np(V) was easily oxidized to Np(VI) in nitric acid solution and Np(VI) was the stable state in boiling 3M-HNO . It was considered that role of Np ions was that of mediator to accelerate corrosion due to activating cathodic reaction and re-oxidizing cycle in boiling 3M-HNO
. It was considered that role of Np ions was that of mediator to accelerate corrosion due to activating cathodic reaction and re-oxidizing cycle in boiling 3M-HNO .
.
Abe, Hitoshi; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Watanabe, Koji; Uchiyama, Gunzo
JAEA-Research 2012-035, 26 Pages, 2013/01
To contribute on confirmation of safety of fuel cycle facilities, an evaluation method for soundness of confinement capability of the facilities under fire accident has been investigated. Organic extraction solvents, zinc stearate, which is added into MOX powder in MOX fuel preparation process, and typical lubricating oil were considered to be examination objects as the representative combustible materials in the facilities. Combustion property data, such as mass loss rate and soot release fraction, of them and clogging property data of HEPA filter with combustion of the organic extraction solvents were measured. As the results, it was found that soot release fraction from burning 30%TBP/70%dodecane was larger than that of the other materials including dodecane and very rapid rise of differential pressure of HEPA filter, which has not been reported, would be induced in the last stage of combustion of 30%TBP/70%dodecane. Furthermore, it was confirmed that zinc stearate, of which combustibility has not been considered, burned continuously in the condition which was heated from outside.
Takeuchi, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Nakajima, Yasuo; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Nojima, Yasuo*; Fujine, Sachio*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2012/07
A long-term corrosion tendency and metal salt effect in heating nitric acid solution on corrosion behavior of titanium-5% tantalum alloy (Ti-5Ta) in hot nitric acid condensate condition were mainly researched to discuss the aging behavior of reprocessing equipments such as evaporators made of titanium or its alloy. The hot pure nitric acid solution with continuous renewing such as the nitric acid condensate condition is severe corrosion environment for their materials because of the corrosion inhibition effect from titanium ions as corrosion products or oxidizing ions in nitric acid solution. From the results of the long-term corrosion test for total 11,000 hrs, the corrosion of Ti-5Ta in the nitric acid condensate was accelerated with increase of the nitric acid concentration in the condensate. The corrosion rate was nearly constant during the immersion time and the test coupons suffered a uniform corrosion. Thus, from the viewpoints of nitric acid corrosion, the life-time of the reprocessing equipments made of titanium or its alloy will be roughly estimated based on the results of average corrosion rate in operation. It was also found that the kind and concentration of metal salt in the heating nitric acid solution gave a remarkable effect on the concentration of nitric acid vapor and the corrosion of Ti-5Ta in the hot nitric acid condensate. Most of the evaporators for reprocessing plants include metal ions in the heating nitric acid solution, so the metal salt effect is one of the corrosion factors to control the corrosion behavior of titanium alloy in condensate. The nitric acid concentration in the condensate increases by adding the metal salts in the heating nitric acid solution, in addition, the larger valence of metal ions was contributed to the increase of nitric acid concentration in the condensate. Consequently, the metal salts effect in the heating nitric acid solution accelerates the corrosion of Ti-5Ta in the nitric acid condensate.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Shiraishi, Hironori; Inoue, Shun; Motooka, Takafumi; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Nojima, Yasuo*; Fujine, Sachio*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/07
In PUREX process for spent fuel reprocessing plants, heating portions in the components are severely corroded in the boiling solution under heat transfer (HT) conditions. In this paper, authors have focused on the effects of surface temperature and heat flux on corrosion rates (CRs) of stainless steels in boiling nitric acid under HT conditions. Two types of cells for HT and immersion conditions were applied for corrosion tests. Test solution used was 33 mol/m vanadium added to 3 kmol/m
vanadium added to 3 kmol/m nitric acid solution, and was heated at boiling temperature under atmospheric pressure. Additionally, a boiling curve which was indicated the relation between heat flux and degree of superheating was investigated experimentally. Surface temperatures during corrosion tests were estimated from a boiling curve. The results showed that CR did not depend on heat flux, but depended on surface temperature. Arrhenius plots on CRs indicated that CR was accelerated by solution boiling against non-boiling.
nitric acid solution, and was heated at boiling temperature under atmospheric pressure. Additionally, a boiling curve which was indicated the relation between heat flux and degree of superheating was investigated experimentally. Surface temperatures during corrosion tests were estimated from a boiling curve. The results showed that CR did not depend on heat flux, but depended on surface temperature. Arrhenius plots on CRs indicated that CR was accelerated by solution boiling against non-boiling.