Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukunaga, Hisanori*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Tokuue, Koichi*; Omura, Motoko*
British Journal of Radiology, 93(1111), p.20200311_1 - 20200311_4, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:73.58(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) has attracted attention as a selective treatment approach for cancer cells while sparing surrounding normal cells. The basic concept of BNCT was developed in the 1930s, but it has not yet been commonly popular in clinical practice, even though there is now a large number of experimental and translational studies demonstrating its marked therapeutic potential. With the development of neutron accelerators that can be installed in medical institutions, accelerator-based BNCT is expected to become available at several medical institutes around the world in the near future. In this commentary, from the point of view of microdosimetry, we discuss the biological effects of BNCT, especially the underlying mechanisms of cell responses. The recent development of new treatment methods that combine proton beam sources and BNCT technology is expected to contribute significantly improving the prognosis of cancer treatment in the near future. Therefore, radiobiologists in the field of BNCT and related techniques will have a significant role to play in creating synergy effects in clinical oncology.
Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.94(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Matoba, Shiro*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012067_1 - 012067_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:73.22(Physics, Particles & Fields)Negative muonium atom ( e
e e
e , Mu
, Mu ) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu
) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu were 10
were 10 /s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu
/s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu averaged energy: it was 0.2
averaged energy: it was 0.2 0.1keV.
0.1keV.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 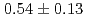 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.814 - 817, 2019/07
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Sue, Yuki*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Saito, Naohito; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2571 - 2574, 2019/06
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. Further improvement of the measurement system is needed to guarantee the required accuracy. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Yasue, Kenichi*; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Saiga, Atsushi; Shimizu, Mayuko; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-008, 83 Pages, 2018/12
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 2nd fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Otani, Masashi*; Sue, Yuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Iijima, Toru*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1067(5), p.052012_1 - 052012_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:47.2(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have measured the muon beam profile after acceleration using a radio frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). Positive muons are injected to an aluminum degrader and negative muoniums (Mu ) are generated. The generated Mu
) are generated. The generated Mu s are extracted by an electrostatic lens and accelerated to 89 keV by the RFQ. The accelerated Mu
s are extracted by an electrostatic lens and accelerated to 89 keV by the RFQ. The accelerated Mu s are transported to a beam profile monitor (BPM) through a quadrupole magnet pair and a bending magnet. The BPM consists of a micro-channel plate, a phospher screen, and a CCD camera. Measured profile in the vertical direction is consistent to the simulation. This profile measurement is one of milestones for realizing a muon linac for measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex.
s are transported to a beam profile monitor (BPM) through a quadrupole magnet pair and a bending magnet. The BPM consists of a micro-channel plate, a phospher screen, and a CCD camera. Measured profile in the vertical direction is consistent to the simulation. This profile measurement is one of milestones for realizing a muon linac for measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex.
Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Ojima, Mayumi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Ito, Takayoshi*; Gong, W.; Vogel, S. C.*; Inoue, Junya*; Tomota, Yo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51(3), p.746 - 760, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:90.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Bae, S.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 21(5), p.050101_1 - 050101_6, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.82(Physics, Nuclear)Muons have been accelerated by using a radio-frequency accelerator for the first time. Negative muonium atoms (Mu ), which are bound states of positive muons and two electrons, are generated from through the electron capture process in an aluminum degrader. The generated Mu
), which are bound states of positive muons and two electrons, are generated from through the electron capture process in an aluminum degrader. The generated Mu 's are initially electrostatically accelerated and injected into a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). In the RFQ, the Mu
's are initially electrostatically accelerated and injected into a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). In the RFQ, the Mu 's are accelerated to 89 keV. The accelerated Mu
's are accelerated to 89 keV. The accelerated Mu 's are identified by momentum measurement and time of flight. This compact muon linac opens the door to various muon accelerator applications including particle physics measurements and the construction of a transmission muon microscope.
's are identified by momentum measurement and time of flight. This compact muon linac opens the door to various muon accelerator applications including particle physics measurements and the construction of a transmission muon microscope.
Ojima, Mayumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Inoue, Junya*; Shobu, Takahisa; Xu, P. G.; Akita, Koichi; Nambu, Shoichi*; Koseki, Toshihiko*
Zairyo, 66(6), p.420 - 426, 2017/06
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji*; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-023, 91 Pages, 2017/02
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 1st fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Hama, Yuki
JAEA-Review 2016-016, 44 Pages, 2016/08
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in JAEA, in fiscal year 2016. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2016 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeda, Masaki; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-014, 274 Pages, 2016/08
We synthesized the research results from the Mizunami/Horonobe Underground Research Laboratories (URLs) and geo-stability projects in the second midterm research phase. This report can be used as a technical basis for the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan/Regulator at each decision point from siting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase).
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-019, 42 Pages, 2015/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in JAEA, in fiscal year 2015. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2015 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Shimada, Akiomi; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-012, 43 Pages, 2015/08
The concept of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan is based on a multibarrier system which combines a stable geological environment with an engineered barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in tectonically active zone. This report is to outline 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) of research and development (R&D) for geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the HLW in JAEA. Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance, and the past progress in this report. The objectives, outline, contents and schedule during the next 7 years are described in detail. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and Systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Yokota, Hideharu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2015-007, 269 Pages, 2015/08
We have synthesised the research results from Mizunami/Horonobe URLs and geo-stability projects in the second mid-term research phase. It could be used as technical bases for NUMO/Regulator in each decision point from sitting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase). High quality construction techniques and field investigation methods have been developed and implemented and these will be directly applicable to the National Disposal Program (along with general assessments of hazardous natural events and processes). It will be crucial to acquire technical knowledge on decisions of partial backfilling and final closure by actual field experiments in Mizunami/Horonobe URLs as main themes for the next phases.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Kokubu, Yoko; Kobori, Kazuo; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Matsubara, Akihiro; Shibata, Kenji; Tamura, Hajimu; Tanabe, Hiroaki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-033, 43 Pages, 2014/09
The concept of geological disposal of HLW in Japan is based on a multi-barrier system which combines a stable geological environment with a robust barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in a tectonically active zone. This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of HLW in JAEA, in fiscal year 2014. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2014 are described in detail based on the outline of 5 years plan (fiscal years 2010-2014). In addition, the planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Sueoka, Shigeru; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Ikuta, Masafumi; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-047, 109 Pages, 2014/03
This annual report documents the progress of R&D in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 2nd Midterm Plan (FY 2010 - 2014) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) development and systematization of investigation techniques for selecting suitable sites in geosphere stability, (2) development, application and verification of prediction models for evaluating the changes of geological environment in thermal, hydraulic, mechanical and geochemical conditions for a long period of time, and (3) development of new dating techniques for providing information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Okada, Hajime; Shimomura, Takuya; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Tanoue, Manabu; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Yogo, Akifumi; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 1, p.015095_1 - 015095_5, 2014/03
We present the design and characterization of a high-contrast, petawatt-class Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) laser system. Two saturable absorbers and low-gain optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) preamplifier in the double CPA laser chain have improved the temporal contrast to 1.4 10
10 on the subnanosecond time scale at 70 terawatt level. Final uncompressed broadband pulse energy is 28 J, indicating the potential for reaching peak power near 600 terawatt. We also discuss our upgrade to over petawatt level at a 0.1 Hz repetition rate briefly.
on the subnanosecond time scale at 70 terawatt level. Final uncompressed broadband pulse energy is 28 J, indicating the potential for reaching peak power near 600 terawatt. We also discuss our upgrade to over petawatt level at a 0.1 Hz repetition rate briefly.