Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Si
Si ; Our current understanding
; Our current understandingKambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Walstedt, R. E.*; Harima, Hisatomo*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011035_1 - 011035_5, 2020/03
Owing to recent investigations, understanding of the symmetry of hidden order and superconductivity in URu Si
Si is fairly progressed. It seems that we are not far from the answer. Following issues and perspectives will be discussed.
is fairly progressed. It seems that we are not far from the answer. Following issues and perspectives will be discussed.
 In NQR study in dual-Ce sites heavy fermion superconductor Ce
In NQR study in dual-Ce sites heavy fermion superconductor Ce PtIn
PtIn
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Walstedt, R. E.*; Kratoch lov
lov , M.*; Uhlirova, K.*; Custers, J.*
, M.*; Uhlirova, K.*; Custers, J.*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 29, p.011009_1 - 011009_5, 2020/02
Zero field  In Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR) measurements at ambient pressure have been carried out on a single crystal of Ce
In Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR) measurements at ambient pressure have been carried out on a single crystal of Ce PtIn
PtIn , a heavy fermion compound exhibiting two magnetic transitions at T1 = 2.2 K and TN = 2 K prior to entering a superconducting state below Tc =0.32 K.
, a heavy fermion compound exhibiting two magnetic transitions at T1 = 2.2 K and TN = 2 K prior to entering a superconducting state below Tc =0.32 K.
 In NQR study with evidence for two magnetic quantum critical points in dual Ce site superconductor Ce
In NQR study with evidence for two magnetic quantum critical points in dual Ce site superconductor Ce PtIn
PtIn
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Walstedt, R. E.*; Kratoch lov
lov , M.*; Uhlirova, K.*; Custers, J.*
, M.*; Uhlirova, K.*; Custers, J.*
Physical Review B, 101(8), p.081103_1 - 081103_5, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:46.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study Ce PtIn
PtIn using NQR, and found two QCP behaviors.
using NQR, and found two QCP behaviors.
 Si
Si ; Conclusions from Si and Ru NMR measurements
; Conclusions from Si and Ru NMR measurementsKambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Hattori, Taisuke; Higa, Nonoka; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Walstedt, R. E.*; Harima, Hisatomo*
Physical Review B, 97(23), p.235142_1 - 235142_10, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:66.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Hattori, Taisuke; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Walstedt, R. E.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 969(1), p.012033_1 - 012033_6, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:49.05(Physics, Applied)High quality URu Si
Si enriched in
enriched in  Si isotope, which is an NMR nucleus, by 52% was prepared. Since the natural abundance ratio of
Si isotope, which is an NMR nucleus, by 52% was prepared. Since the natural abundance ratio of  Si isotope is about 4%, the accumulated measurement time can be shortened to about one hundredth by this concentration. Results of the Si-NMR linewidth of hidden ordered phase using this single crystal sample have already been reported. In this report, we will report more detailed analysis on the magnetic field, temperature and angle of this line width We also discuss the possibility of distribution of magnetic susceptibility in two-fold symmetry by RKKY model.
Si isotope is about 4%, the accumulated measurement time can be shortened to about one hundredth by this concentration. Results of the Si-NMR linewidth of hidden ordered phase using this single crystal sample have already been reported. In this report, we will report more detailed analysis on the magnetic field, temperature and angle of this line width We also discuss the possibility of distribution of magnetic susceptibility in two-fold symmetry by RKKY model.
 Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Hattori, Taisuke; Walstedt, R. E.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 868(1), p.012003_1 - 012003_7, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)In the hidden-ordered state of URu Si
Si , a modest breaking of the fourfold symmetry was suggested in previous
, a modest breaking of the fourfold symmetry was suggested in previous  Si NMR basal-plane field rotation measurements. Based on the detail analysis of
Si NMR basal-plane field rotation measurements. Based on the detail analysis of  Si NMR linewidth, the occurrence of a distribution of twofold local fields at the Si sites is suggested even in a high-quality single crystal. A possible picture for the distributed two-fold ordering will be discussed.
Si NMR linewidth, the occurrence of a distribution of twofold local fields at the Si sites is suggested even in a high-quality single crystal. A possible picture for the distributed two-fold ordering will be discussed.
 dependence of nuclear spin-echo decay at low temperatures in YbRh
dependence of nuclear spin-echo decay at low temperatures in YbRh Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Hattori, Taisuke; Lapertot, G.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Knebel, G.*; Flouquet, J.*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review B, 95(19), p.195121_1 - 195121_8, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The authors report  Si nuclear spin-echo oscillations and decay measurements on a single crystal of YbRh
Si nuclear spin-echo oscillations and decay measurements on a single crystal of YbRh Si
Si . These quantities are found to be
. These quantities are found to be  independent from 300 K down to
independent from 300 K down to  20 K, showing, however, a strong
20 K, showing, however, a strong  dependence below 20 K. These results indicate that electronic states near the Fermi level are modified at low temperatures. The observed spin-echo oscillations can be interpreted with the Ruderman-Kittel and pseudo-dipolar interactions between nearest-neighbor Si nuclei driven by conduction electron scattering at the Fermi surface. Possible modifications to the Fermi surface at low temperatures are discussed.
dependence below 20 K. These results indicate that electronic states near the Fermi level are modified at low temperatures. The observed spin-echo oscillations can be interpreted with the Ruderman-Kittel and pseudo-dipolar interactions between nearest-neighbor Si nuclei driven by conduction electron scattering at the Fermi surface. Possible modifications to the Fermi surface at low temperatures are discussed.
 Si NMR spin-echo decay in YbRh
Si NMR spin-echo decay in YbRh Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Hattori, Taisuke; Lapertot, G.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Knebel, G.*; Flouquet, J.*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 683(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_7, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)By means of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spin-lattice relaxation time ( ) measurements on a single crystal sample YbRh
) measurements on a single crystal sample YbRh Si
Si , the magnetic excitations around quantum critical phase transition is investigated. It is revealed that the coexisting Fermi and non-Fermi states appears near the quantum critical phase transition. Such a mottled state is considered to have remained hidden in Ce and U heavy fermion compounds, owing presumably to short lifetimes for the two states. The mottled state is highly anisotropic to applied magnetic field, which is consistent with previous studies. The origin of mottled state will be discussed.
, the magnetic excitations around quantum critical phase transition is investigated. It is revealed that the coexisting Fermi and non-Fermi states appears near the quantum critical phase transition. Such a mottled state is considered to have remained hidden in Ce and U heavy fermion compounds, owing presumably to short lifetimes for the two states. The mottled state is highly anisotropic to applied magnetic field, which is consistent with previous studies. The origin of mottled state will be discussed.
 Si
Si
Walstedt, R. E.*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori
Physical Review B, 93(4), p.045122_1 - 045122_8, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A well-known analytic model for Lorentzian broadening of metallic NMR lines by dilute localized magnetic centers embedded in a lattice has been applied to the case of the twofold-symmetry magnetism in URu Si
Si . The observed Lorentzian spectra are accounted for with a simple formula giving the
. The observed Lorentzian spectra are accounted for with a simple formula giving the  Si NMR linewidth in terms of the susceptibility of the magnetic broadening centers and a Ruderman-Kittel-Kasuya-Yosida (RKKY) coupling parameter.
Si NMR linewidth in terms of the susceptibility of the magnetic broadening centers and a Ruderman-Kittel-Kasuya-Yosida (RKKY) coupling parameter.
 Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Lapertot, G.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Knebel, G.*; Flouquet, J.*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 592(1), p.012085_1 - 012085_5, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.72(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Recently there is renewed interest in quantum critical phase transitions (QCPT) at 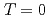 K in metallic strongly-correlated electron systems. From early experimental results, the QCPT in the Kondo-lattice compound YbRh
K in metallic strongly-correlated electron systems. From early experimental results, the QCPT in the Kondo-lattice compound YbRh Si
Si is not a case of the ordinary spin density wave (SDW) instability observed in Ce-based Kondo-lattices, but a candidate for a novel locally critical case In new observations reported here, we find that coexisting, static Fermi liquid (FL) and non-Fermi liquid (NFL) states are a key feature of the QCPT in YbRh
is not a case of the ordinary spin density wave (SDW) instability observed in Ce-based Kondo-lattices, but a candidate for a novel locally critical case In new observations reported here, we find that coexisting, static Fermi liquid (FL) and non-Fermi liquid (NFL) states are a key feature of the QCPT in YbRh Si
Si . Such a pair of states has remained hidden in Ce compounds, owing presumably to short lifetimes for the two states. A new scaling law for the occupation ratio of the two states is derived, and could be widely applicable to Kondo-lattice systems.
. Such a pair of states has remained hidden in Ce compounds, owing presumably to short lifetimes for the two states. A new scaling law for the occupation ratio of the two states is derived, and could be widely applicable to Kondo-lattice systems.
 Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review B, 91(3), p.035111_1 - 035111_8, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:49.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In previous  Si NMR basal-plane field rotation measurements, a modest breaking of the fourfold symmetry was suggested in the hidden-order state of URu
Si NMR basal-plane field rotation measurements, a modest breaking of the fourfold symmetry was suggested in the hidden-order state of URu Si
Si . Here, the angular dependence of the
. Here, the angular dependence of the  Si NMR linewidth is analyzed in detail, indicating the occurrence of a distribution of twofold local fields at the Si sites even in a high-quality single crystal. The relation between sample quality and the occurrence of effects having twofold symmetry is discussed.
Si NMR linewidth is analyzed in detail, indicating the occurrence of a distribution of twofold local fields at the Si sites even in a high-quality single crystal. The relation between sample quality and the occurrence of effects having twofold symmetry is discussed.
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Lapertot, G.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Knebel, G.*; Flouquet, J.*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Nature Physics, 10(11), p.840 - 844, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:69.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In new observations reported here, we find that coexisting, static Fermi liquid and non-Fermi liquid states are a key feature of the QCPT in YbRh Si
Si . By means of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spin-lattice relaxation time measurements on a single crystal sample, it is revealed that the FL and NFL states are invariant,while their relative proportion in a crossover is field dependent near the QCPT. Such a pair of states has remained hidden in Ce compounds, owing presumably to short lifetimes for the two states. A new scaling law for the occupation ratio of the two states is derived, and could be widely applicable to Kondo-lattice systems
. By means of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spin-lattice relaxation time measurements on a single crystal sample, it is revealed that the FL and NFL states are invariant,while their relative proportion in a crossover is field dependent near the QCPT. Such a pair of states has remained hidden in Ce compounds, owing presumably to short lifetimes for the two states. A new scaling law for the occupation ratio of the two states is derived, and could be widely applicable to Kondo-lattice systems
 revealed by
revealed by  O-NMR
O-NMRTokunaga, Yo; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Ito, Akinori*; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Homma, Yoshiya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Aoki, Dai*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review B, 89(21), p.214416_1 - 214416_8, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:36.70(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic phase transition near 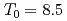 K in AmO
K in AmO has been investigated microscopically by means of
has been investigated microscopically by means of  O NMR. To avoid complexities arising from sample aging associated with the alpha decay of
O NMR. To avoid complexities arising from sample aging associated with the alpha decay of  Am, all measurements have been performed within 40 days after sample synthesis. Even during such a short period, however, a rapid change of NMR line shape has been observed at 1.5 K, suggesting that the ground state of AmO
Am, all measurements have been performed within 40 days after sample synthesis. Even during such a short period, however, a rapid change of NMR line shape has been observed at 1.5 K, suggesting that the ground state of AmO is very sensitive to disorder. We have also confirmed the loss of
is very sensitive to disorder. We have also confirmed the loss of  O NMR signal intensity over a wide temperature range below
O NMR signal intensity over a wide temperature range below 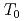 , and more than half of oxygen nuclei are undetectable at 1.5 K. This behavior reveals the persistence of slow and distributed spin fluctuations down to temperatures well below
, and more than half of oxygen nuclei are undetectable at 1.5 K. This behavior reveals the persistence of slow and distributed spin fluctuations down to temperatures well below 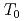 . In the paramagnetic state, strong NMR line broadening and spatially inhomogeneous spin fluctuations have been observed. The results are all indicative of short-range, spin-glass-like character for the magnetic transition in this system.
. In the paramagnetic state, strong NMR line broadening and spatially inhomogeneous spin fluctuations have been observed. The results are all indicative of short-range, spin-glass-like character for the magnetic transition in this system.
 Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Lapertot, G.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Knebel, G.*; Flouquet, J.*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review B, 91(16), p.161110_1 - 161110_5, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Based on  Si nuclear spin-lattice relaxation time (
Si nuclear spin-lattice relaxation time ( ) data on a single crystal of YbRh
) data on a single crystal of YbRh Si
Si , the coexisting Fermi liquid (FL) and non-Fermi liquid (NFL) states around the quantum critical phase transition have been found to be sensitive to the direction of the applied magnetic field. Augmented scaling analysis shows that the anisotropic characteristic temperature and field are roughly 10 times larger for
, the coexisting Fermi liquid (FL) and non-Fermi liquid (NFL) states around the quantum critical phase transition have been found to be sensitive to the direction of the applied magnetic field. Augmented scaling analysis shows that the anisotropic characteristic temperature and field are roughly 10 times larger for 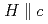 than for
than for 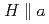 , consistent with a previously obtained anisotropic phase diagram.
, consistent with a previously obtained anisotropic phase diagram.
 Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Fisk, Z.; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review Letters, 110(24), p.246406_1 - 246406_5, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:83.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report  Si NMR spectra and Knight shift measurements as a function of applied field orientation in the (001) basal plane of URu
Si NMR spectra and Knight shift measurements as a function of applied field orientation in the (001) basal plane of URu Si
Si . Observed linewidth oscillations confirm the in-plane 2-fold ordered domain state observed in recent magnetic susceptibility measurements. Analysis of our linewidth data leads to the estimate
. Observed linewidth oscillations confirm the in-plane 2-fold ordered domain state observed in recent magnetic susceptibility measurements. Analysis of our linewidth data leads to the estimate 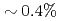 for the 2-fold intrinsic (mono-domain) susceptibility anisotropy in the basal plane, a value
for the 2-fold intrinsic (mono-domain) susceptibility anisotropy in the basal plane, a value 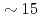 times smaller than that obtained from recent susceptibility measurements.
times smaller than that obtained from recent susceptibility measurements.
 Np nuclear relaxation rate in heavy fermion superconductor NpPd
Np nuclear relaxation rate in heavy fermion superconductor NpPd Al
Al
Chudo, Hiroyuki; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Onuki, Yoshichika; Yasuoka, Hiroshi; Aoki, Dai*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 84(9), p.094402_1 - 094402_5, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Onuki, Yoshichika*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.A), p.SA009_1 - SA009_3, 2011/07
We report an  In NMR study of a single-crystal sample of the heavy fermion superconductor CeIrIn
In NMR study of a single-crystal sample of the heavy fermion superconductor CeIrIn . The observed non-linear variation of Knight Shift with static susceptibility in the normal state is consistent with the two-fluid (components) model of Nakatsuji et al, indicating that two individual contributions to static susceptibility exist. However, our results can also be understood in terms of a T-dependent hyperfine coupling, which accounts for the spin-lattice relaxation data naturally on the basis of a one-component dynamical susceptibility. In addition, the observed T-dependence of the hyperfine coupling is scaled to a density of states given by dynamical mean field theory (DMFT). We believe that this contrast between the static and dynamical properties is a crucial dual nature of the heavy fermion crossover, which related with the coherence between localized and itinerant excitations.
. The observed non-linear variation of Knight Shift with static susceptibility in the normal state is consistent with the two-fluid (components) model of Nakatsuji et al, indicating that two individual contributions to static susceptibility exist. However, our results can also be understood in terms of a T-dependent hyperfine coupling, which accounts for the spin-lattice relaxation data naturally on the basis of a one-component dynamical susceptibility. In addition, the observed T-dependence of the hyperfine coupling is scaled to a density of states given by dynamical mean field theory (DMFT). We believe that this contrast between the static and dynamical properties is a crucial dual nature of the heavy fermion crossover, which related with the coherence between localized and itinerant excitations.

Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review B, 82(14), p.144503_1 - 144503_7, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:53.50(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Based on analysis of nuclear ( In) spin-lattice relaxation time measurements on the heavy fermion superconductor CeIrIn
In) spin-lattice relaxation time measurements on the heavy fermion superconductor CeIrIn ,
, 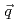 ,
, 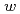 , and temperature-dependences of the dynamical susceptibility Im
, and temperature-dependences of the dynamical susceptibility Im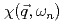 near the antiferromagnetic wave vector
near the antiferromagnetic wave vector 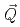 at low energy
at low energy 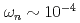 meV have been estimated. The
meV have been estimated. The  -dependences found, Im
-dependences found, Im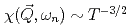 and antiferromagnetic correlation length
and antiferromagnetic correlation length 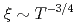 , are consistent with quantum critical behavior for a three dimensional antiferromagnet (
, are consistent with quantum critical behavior for a three dimensional antiferromagnet ( =3,
=3, 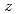 =2) having a spin density wave instability.
=2) having a spin density wave instability.
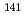 Pr nuclear spin dynamics in PrPb
Pr nuclear spin dynamics in PrPb ;
;  La NMR study in Pr
La NMR study in Pr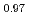 La
La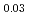 Pb
Pb
Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Kambe, Shinsaku; Yasuoka, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Walstedt, R. E.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Aoki, Dai*; Shiokawa, Yoshinobu*
Physical Review B, 82(10), p.104401_1 - 104401_6, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.09(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) La NMR studies have been performed on PrPb
La NMR studies have been performed on PrPb substituted with 3% La. The temperature dependence of the local magnetic susceptibility around La ions has been extracted from the
substituted with 3% La. The temperature dependence of the local magnetic susceptibility around La ions has been extracted from the  La Knight shift. These data show that the non-magnetic
La Knight shift. These data show that the non-magnetic  crystalline-electric-field (CEF) ground state (GS) is preserved even at the nearest neighboring Pr ions, although their CEF level scheme is slightly modified due to the La substitution. On the other hand, the temperature dependence of the nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rate
crystalline-electric-field (CEF) ground state (GS) is preserved even at the nearest neighboring Pr ions, although their CEF level scheme is slightly modified due to the La substitution. On the other hand, the temperature dependence of the nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rate  is found to be well reproduced by assuming the same CEF level scheme over a wide temperature range. However,
is found to be well reproduced by assuming the same CEF level scheme over a wide temperature range. However,  shows a strong upturn below 10 K, which is not expected from the non-magnetic CEF GS. We show that the low temperature anomaly can be quantitatively understood in terms of a cross-relaxation process between
shows a strong upturn below 10 K, which is not expected from the non-magnetic CEF GS. We show that the low temperature anomaly can be quantitatively understood in terms of a cross-relaxation process between 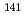 Pr and
Pr and  La nuclear spins.
La nuclear spins.

Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review B, 81(14), p.140405_1 - 140405_4, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:60.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report an  In NMR study of a single-crystal sample of the heavy fermion compound CeIrIn
In NMR study of a single-crystal sample of the heavy fermion compound CeIrIn . The observed non-linear variation of Knight shift with static susceptibility is consistent with the two-fluid model of Nakatsuji
. The observed non-linear variation of Knight shift with static susceptibility is consistent with the two-fluid model of Nakatsuji  . However, our results can also be understood in terms of a
. However, our results can also be understood in terms of a  -dependent hyperfine coupling, which accounts for the spin-lattice relaxation data naturally on the basis of a one-component dynamical susceptibility. In addition, the observed
-dependent hyperfine coupling, which accounts for the spin-lattice relaxation data naturally on the basis of a one-component dynamical susceptibility. In addition, the observed  -dependence of the hyperfine coupling is scaled to a density of states given by dynamical mean field theory.
-dependence of the hyperfine coupling is scaled to a density of states given by dynamical mean field theory.