Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nasu, Mitsunori*; Yanai, Hiroshi*; Hirayama, Naoki*; Adachi, Hironori*; Kakizawa, Yu*; Shirase, Yuto*; Nishiyama, Hiromichi*; Kawamoto, Teppei*; Inukai, Junji*; Shinohara, Takenao; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 530, p.231251_1 - 231251_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:88.86(Chemistry, Physical)Takeuchi, Ryuji; Onoe, Hironori; Murakami, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Yusuke; Mikake, Shinichiro; Ikeda, Koki; Iyatomi, Yosuke; Nishio, Kazuhisa*; Sasao, Eiji
JAEA-Review 2021-003, 63 Pages, 2021/06
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of geological disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment in the crystalline rock (granite) at Mizunami City, Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. On the occasion of JAEA reformation in FY2014, JAEA identified three remaining important issues on the geoscientific research program based on the synthesized latest results of research and development (R&D): "Development of countermeasure technologies for reducing groundwater inflow", "Development of modeling technologies for mass transport" and "Development of drift backfilling technologies". At the MIU, the R&D are being pursued with a focus on the remaining important issues from FY2015, and satisfactory results have been achieved. Based on this situation, the R&D on the MIU Project were completed at the end of FY2019. In this report, the results of R&D and construction activities of the MIU Project in FY2019 are summarized.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-007, 249 Pages, 2020/10
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting "Long-term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminants in the Environment of Fukushima" concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-002, 235 Pages, 2019/08
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (hereinafter referred to 1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, JAEA has been conducting Long-term Environmental Dynamics Research concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Onoe, Hironori; Kohashi, Akio; Watanabe, Masahisa
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2015/05
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Company is facing contaminated water issues. The amount of contaminated water is continuously increasing due to groundwater leakage into the underground part of reactor and turbine buildings. Therefore, it is important to understand the groundwater flow conditions at the site and to predict the impact of countermeasures taken for isolating groundwater from the source of the contamination, i.e. the reactor buildings. Installations, such as of land-side and sea-side impermeable walls have been planned as countermeasures. In this study, groundwater flow modeling has been performed to estimate the response of groundwater flow conditions to the countermeasures. From the modeling, groundwater conditions and changes in response to implementation of the countermeasures could be reasonably estimated. The results indicate that the countermeasures will decrease the volume of inflow into underground part of the buildings. This means that the countermeasures will be effective in reducing the discharge volume of contaminated groundwater to ocean.
Funaki, Hironori; Ishiyama, Koji*; Waseda, Amane*; Kato, Susumu*; Watanabe, Kunio*
Chigaku Zasshi, 121(6), p.929 - 945, 2012/12
Molecular and carbon isotope compositions of hydrocarbon gas have information related to their generation, migration and accumulation, and serve evaluations of gas permeability in sedimentary rocks. We conducted headspace gas analysis at the cores (below 500 m depth) to evaluate gas permeability in Neogene sedimentary rocks in the Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan. As a result, it was shown that hydrocarbon gases were almost biogenic methane. Further analysis of these data indicated that concentration and carbon isotope of methane varied carbon isotopic fractionation during anaerobic microbial oxidation and migration near the faults. A formation of high concentration and light carbon isotope of methane at present in the study area is low gas permeability and is less affected by secondary post-generic process.
Watanabe, Hironori; Tamai, Hidesada; Sato, Takashi; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Mitsutake, Toru*
Flow Measurement, p.95 - 106, 2012/03
In Boiling Water Reactor (BWR), reactor power, fuel conversion ratio and reactor cooling capacity changes by the void fraction in the core. We have developed a capacitance method (C method) to measure the void fraction under the condition of high temperature and high pressure of 7MPa, simulating reactor. This C method is based on the principle that the capacitance in the two-phase flow is a function of void fraction. Using this method, we can measure void fractions in real time, at all region of void fractions, and with a small error of measurement, which was not realized by usual techniques up to now.
Watanabe, Hironori; Mitsutake, Toru*; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Takase, Kazuyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 76(769), p.1379 - 1385, 2010/09
The electro void fraction meter (Capacitance type meter) was applied to high temperature and high pressure condition measurement with various shapes of flow conduits such as rod bundle and pipe geometries. The principle of the meter is that the electrical capacitance of a gas liquid two phase flow changes with the void fraction. High frequency power supply enables to measure the electrical capacitance of the ion exchanged water with even though conductivity of pure water. It was confirmed by steam water boiling two phase flow experiments that void fraction can be obtained in real time way. Void fraction ranging from 0 to 0.9 at maximum was successfully measured under steam water boiling two phase flow conditions of 2 MPa through 18 MPa pressure.
Watanabe, Hironori; Mitsutake, Toru*; Kakizaki, Sadayuki*; Takase, Kazuyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 75(751), p.155 - 157, 2009/03
Capacitance type electro-void fraction meters with various shapes of electrodes were developed for two-phase flow measurement in tubes of 1mm in the smallest diameter. Ring and wire- type electrodes were applied to measure void fraction. The principle of the meter is that the electrical capacitance of a gas-liquid two-phase flow changes with void fraction. A high-frequency power supply enables to measure the low electrical capacitance of the water including pure water. It was confirmed by the air-water two-phase flow experiments that void fraction can be obtained in real time way every 50 millisecond. Void fraction in the experiment ranged from 0 to higher than 0.9. The void fraction was correlated with the electric capacitance by a linear function for the ring-electrode and hyperbolic function for the opposite wires-electrode under the atmospheric condition.
Watanabe, Hironori; Mitsutake, Toru*; Kakizaki, Sadayuki*; Takase, Kazuyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 74(742), p.1257 - 1262, 2008/06
Tamai, Hidesada; Kureta, Masatoshi; Liu, W.; Sato, Takashi; Nakatsuka, Toru; Watanabe, Hironori; Onuki, Akira; Akimoto, Hajime
JAEA-Data/Code 2007-011, 126 Pages, 2007/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performing tight-lattice rod bundle thermal-hydraulic tests to realize essential technologies for the technological and engineering feasibility of super high burn-up water-cooled breeder reactor featured by a high breeding ratio and super high burn-up by reducing the core water volume in water-cooled reactor. The tests were performing to make clear the fundamental subjects related to the boiling transition (BT) (Subjects: BT criteria under a highly tight-lattice rod bundle, effects of gap-width between rods and of rod-bowing) using 37-rod bundles (Base case test section (1.3 mm gap-width), Two parameter effect test sections (Gap-width effect one (1.0 mm) and Rod-bowing one)). In the present report, we summarize the test results from the rod-bowing effect test section. The thermal-hydraulic characteristics were obtained for the critical power under the steady-state and transient conditions, the pressure drop and the wall heat transfer within a wide range of pressure, flow rate, etc. including normal operational conditions of the designed reactor. Then the rod-bowing effects were also investigated based on the comparison between the results using the base case test section and the rod-bowing effect one.
Tamai, Hidesada; Kureta, Masatoshi; Liu, W.; Sato, Takashi; Watanabe, Hironori; Onuki, Akira; Akimoto, Hajime
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-016, 134 Pages, 2006/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performing tight-lattice rod bundle thermal-hydraulic tests to realize essential technologies for the technological and engineering feasibility of super high burn-up water-cooled breeder reactor featured by a high breeding ratio and super high burn-up by reducing the core water volume in water-cooled reactor. The tests are performing to make clear the fundamental subjects related to the boiling transition (BT)(Subjects: BT criteria under a highly tight-lattice rod bundle, effects of gap-width between rods and of rod-bowing) using 37-rod bundles (Base case test section (1.3mm gap-width), Two parameter effect test sections (Gap-width effect one (1.0mm) and Rod-bowing one)). In the present report, we summarize the test results from the gap-width effect section. The thermal-hydraulic characteristics were obtained for the critical power under the steady-state and transient conditions, the pressure drop and the wall heat transfer within a wide range of pressure, flow rate, etc. including normal operational conditions of the designed reactor. Then the gap-width effects were also obtained from the comparison between the results using the base case test section and the gap-width effect one.
Hirane, Nobuhiko; Ishikuro, Yasuhiro; Nagadomi, Hideki; Yokoo, Kenji; Horiguchi, Hironori; Nemoto, Takumi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Yagi, Masahiro; Arai, Nobuyoshi; Watanabe, Shukichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-028, 115 Pages, 2006/03
JRR-4, a light-water-moderated and cooled, swimming pool type research reactor using high-enriched uranium plate-type fuels had been operated from 1965 to 1996. In order to convert to low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuels, modification work had been carried out for 2 years, from 1996 to 1998. After the modification, start-up experiments were carried out to obtain characteristics of the low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuel core. The measured excess reactivity, reactor shutdown margin and the maximum reactivity addition rate satisfied the nuclear limitation of the safety report for licensing. It was confirmed that conversion to low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuels was carried out properly. Besides, the necessary data for reactor operation were obtained, such as nuclear, thermal hydraulic and reactor control characteristics. This report describes the results of start-up experiments and burnup experiments. The first criticality of low-enriched-uranium-silicied core was achieved on 14th July 1998, and the operation for joint-use has been carried out since 6th October 1998.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Sato, Takashi; Watanabe, Hironori; Onuki, Akira; Akimoto, Hajime
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-007, 90 Pages, 2006/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performing tight-lattice rod bundle thermal-hydraulic tests as one of essential technologies for the technological and engineering feasibility of super high burn-up water-cooled breeder reactor which aims to achieve a high breeding ratio and super high burn-up by innovative performance-up of water-cooled reactor. The tests are performing to make clear the fundamental subjects related to the boiling transition(BT)(Subjects:BT criteria under a highly tight-lattice rod bundle, effects of gap-width between rods and of rod-bowing) using 37-rod bundles (Base case test section (1.3mm gap-width), Two parameter effect test sections (Gap-width effect one (1.0mm) and Rod-bowing one)). In the present report, we summarize the test results from the base case test section. The thermal-hydraulic characteristics using the large scale test section were obtained for the critical power, the pressure drop and the wall heat transfer under a wide range of pressure, flow rate, etc. including normal operational conditions of the designed reactor. Effects of local peaking factor on the critical power were also obtained.
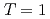 nucleus
nucleus  Cr
CrOnishi, Takeo*; Gelberg, A.*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Yoneda, Kenichiro*; Aoi, Nori*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Baba, Hidetada*; Von Brentano, P.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Ichikawa, Yuichi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 72(2), p.024308_1 - 024308_7, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:79.08(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Takase, Kazuyuki; Watanabe, Hironori; Akimoto, Hajime
Fusion Engineering and Design, 63-64, p.217 - 222, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Araya, Fumimasa; Nakatsuka, Toru; Yoritsune, Tsutomu; Kureta, Masatoshi; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Sato, Takashi; Watanabe, Hironori; Okubo, Tsutomu; Iwamura, Takamichi; et al.
JAERI-Research 2002-018, 37 Pages, 2002/10
no abstracts in English
Iguchi, Tadashi; Watanabe, Hironori; Kimura, Mamoru*; Anoda, Yoshinari
JAERI-Research 2001-032, 111 Pages, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Iguchi, Tadashi; Ito, Hideo; Kiuchi, Toshio; Watanabe, Hironori; Kimura, Mamoru*; Anoda, Yoshinari
JAERI-Data/Code 2001-013, 502 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Hironori; Iguchi, Tadashi; Kimura, Mamoru; Anoda, Yoshinari
JAERI-Research 2000-043, 77 Pages, 2000/11
no abstracts in English