Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ichikawa, Tsubasa*; Hakoshima, Hideaki*; Inui, Koji*; Ito, Kosuke*; Matsuda, Ryo*; Mitarai, Kosuke*; Miyamoto, Koichi*; Mizukami, Wataru*; Mizuta, Kaoru*; Mori, Toshio*; et al.
Nature Reviews Physics (Internet), 6(6), p.345 - 347, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:99.15(Physics, Applied)Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Masatoshi*; Ishimaru, Sora*; Yamauchi, Sara*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Watanabe, Masao; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011010_1 - 011010_7, 2024/05
Okuno, Hiroshi; Kawakami, Takeshi; Watanabe, Fumitaka; Horikoshi, Hidehiko*
Journal of Disaster Research, 18(8), p.911 - 917, 2023/12
In response to residents' concerns about the radiation health effects following the nuclear accidents at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of the Tokyo Electric Power Company in March 2011, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) established a telephone consultation system. Eight toll-free telephone lines were prepared, and employees with knowledge of radiation health effects were assigned for consultation. Approximately 35,000 consultations were conducted from March 17, 2011, to September 18, 2012. The results of the text mining analysis revealed that the greatest source of anxiety was the impact on children's health from radiation. The JAEA's system for telephone consultation was improved following this telephone consultation experience. The description of telephone hotlines in the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) guide, GSG-14, was discussed for further improvements of the JAEA's telephone consultation system.
Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Sadamatsu, Hiroki*; Araki, Shohei; Nakano, Keita; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01041_1 - 01041_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Intensive fast neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for the study of medical RI production, radiation damage for fusion reactor materials, nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste, and so on. Neutron production data from various materials bombarded by deuterons are required for the design of such neutron sources. In the present work, we have conducted a systematic measurement of double-differential neutron production cross sections (DDXs) for a wide atomic number range of targets (Li, Be, C, Al, Cu, Nb, In, Ta, and Au) at an incident energy of 200 MeV in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP), Osaka University. A deuteron beam accelerated to 200 MeV was transported to the neutron experimental hall and focused on a thin target foil. Emitted neutrons from the target were detected by two different-size EJ301 liquid organic scintillators located at two distances of 7 m and 20 m, respectively. The neutron DDXs were measured at six angles from 0 to 25
to 25 ). The neutron energy was determined by a conventional time-of-flight (TOF) method. The measured DDXs were compared with theoretical model calculations by the DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS) and PHITS. The result indicated that the DEURACS calculation provides better agreement with the measured DDXs than the PHITS calculation.
). The neutron energy was determined by a conventional time-of-flight (TOF) method. The measured DDXs were compared with theoretical model calculations by the DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS) and PHITS. The result indicated that the DEURACS calculation provides better agreement with the measured DDXs than the PHITS calculation.
Nagata, Shuhei*; Ogawa, Yusuke*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Mitsui, Seiichiro
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.21 - 22, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Jeon, H.*; Hou, Y.*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Aze, Takahiro*; Miyairi, Yosuke*; Yokoyama, Yusuke*; Ogawa, Hiroshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, p.1 - 6, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The measurement the radiocarbon of dissolved organic matter (DO C) in seawater can provide information about a timescale of the dynamics of dissolved organic matter as well as about its sources in the ocean. Due to the low DOC concentration in seawater, in spite of the development of accelerator mass spectrometry, a relatively large volume of seawater (
C) in seawater can provide information about a timescale of the dynamics of dissolved organic matter as well as about its sources in the ocean. Due to the low DOC concentration in seawater, in spite of the development of accelerator mass spectrometry, a relatively large volume of seawater ( 1 L) is required for that analysis. In addition, complicated processing such as UV irradiation that emits high heat is required. In this study, we have developed a safer and easier method to analyze DO
1 L) is required for that analysis. In addition, complicated processing such as UV irradiation that emits high heat is required. In this study, we have developed a safer and easier method to analyze DO C in seawater than the conventional method. A particularly significant change was the adoption of a low-pressure mercury lamp in the decomposition system, which enabled direct decomposition of organic matter at lower temperatures. We also propose a method to quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of this system by analyzing simulated seawater consists of a soluble reference material of organic matter and sodium chloride. This method is expected to be applied not only to carbon isotope ratio analysis but also to analysis of trace elements and isotopes of various dissolved organic substances.
C in seawater than the conventional method. A particularly significant change was the adoption of a low-pressure mercury lamp in the decomposition system, which enabled direct decomposition of organic matter at lower temperatures. We also propose a method to quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of this system by analyzing simulated seawater consists of a soluble reference material of organic matter and sodium chloride. This method is expected to be applied not only to carbon isotope ratio analysis but also to analysis of trace elements and isotopes of various dissolved organic substances.
Nasu, Mitsunori*; Yanai, Hiroshi*; Hirayama, Naoki*; Adachi, Hironori*; Kakizawa, Yu*; Shirase, Yuto*; Nishiyama, Hiromichi*; Kawamoto, Teppei*; Inukai, Junji*; Shinohara, Takenao; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 530, p.231251_1 - 231251_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:88.86(Chemistry, Physical) -decay spectroscopy of
-decay spectroscopy of  Ta
TaMukai, Momo*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Watanabe, Hiroshi*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Jeong, S. C.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Brunet, M.*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; Kondev, F. G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 105(3), p.034331_1 - 034331_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:72.81(Physics, Nuclear)Inagawa, Jun; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Takano, Masahide; Akie, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Osamu; Komuro, Michiyasu; Oura, Hirofumi*; Nagai, Isao*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-001, 144 Pages, 2021/08
Plutonium Research Building No.1 (Pu1) was qualified as a facility to decommission, and preparatory operations for decommission were worked by the research groups users and the facility managers of Pu1. The operation of transportation of whole nuclear materials in Pu1 to Back-end Cycle Key Element Research Facility (BECKY) completed at Dec. 2020. In the operation included evaluation of criticality safety for changing permission of the license for use nuclear fuel materials in BECKY, cask of the transportation, the registration request of the cask at the institute, the test transportation, formulation of plan for whole nuclear materials transportation, and the main transportation. This report circumstantially shows all of those process to help prospective decommission.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:96.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
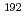 Re
ReWatanabe, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Andreyev, A. N.; Hashimoto, Takashi*; Kondev, F. G.*; Lane, G. J.*; Litvinov, Yu. A.*; Liu, J. J.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 814, p.136088_1 - 136088_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:58.46(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-007, 249 Pages, 2020/10
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting "Long-term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminants in the Environment of Fukushima" concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
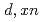 ) reaction for the development of accelerator-based neutron sources
) reaction for the development of accelerator-based neutron sourcesWatanabe, Yukinobu*; Sadamatsu, Hiroki*; Araki, Shohei*; Nakano, Keita*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.20012_1 - 20012_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:80.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)Accelerator-based neutron sources induced by deuteron beams are attractive for study of nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste as well as radiation damage for fusion reactor materials. In the present work, we have carried out a Double Differential cross section (DDX) measurement for Li at 200 MeV in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP), Osaka University. A deuteron beam accelerated to 200 MeV was transported to the neutron experimental hall and focused on a thin Li target. Emitted neutrons from the target were detected by two different-size EJ301 liquid organic scintillators located at two distances of 7 m and 20 m, respectively. The neutron DDXs were measured at six angles from 0 to 25
to 25 ). The neutron detection efficiencies of the detectors were calculated by SCINFUL-QMD code. We will present the results of the present DDX measurement and compare them with theoretical model calculations with DEURACS and PHITS.
). The neutron detection efficiencies of the detectors were calculated by SCINFUL-QMD code. We will present the results of the present DDX measurement and compare them with theoretical model calculations with DEURACS and PHITS.
 Cs on paved surfaces affected by the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
Cs on paved surfaces affected by the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accidentYoshimura, Kazuya; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Kurikami, Hiroshi
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 217, p.106213_1 - 106213_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:18.37(Environmental Sciences) Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targets
Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targetsSun, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Aikawa, Masayuki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; Kawakami, Shunsuke*; Koyama, Shumpei*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064623_1 - 064623_12, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.65(Physics, Nuclear)The spallation and fragmentation reactions of  Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-002, 235 Pages, 2019/08
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (hereinafter referred to 1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, JAEA has been conducting Long-term Environmental Dynamics Research concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Watanabe, Tamaki*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Hanamura, Kotoku*; Imao, Hiroshi*; Kamigaito, Osamu*; Kamoshida, Atsushi*; Kawachi, Toshihiko*; Koyama, Ryo*; Sakamoto, Naruhiko*; Fukunishi, Nobuhisa*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1105 - 1108, 2019/07
Upgrades for the RIKEN heavy-ion linac (RILAC) involving a new superconducting linac (SRILAC) are currently underway at the RIKEN radioactive isotope beam factory (RIBF). It is crucially important to develop nondestructive beam measurement diagnostics. We have developed a beam energy position monitor (BEPM) system which can measure not only the beam position but also the beam energy simultaneously by measuring the time of flight of the beam. We fabricated 11 BEPMs and completed the position calibration to obtain the sensitivity and offset for each BEPMs. The position accuracy has been achieved to be less than  0.1 mm by using the mapping measurement.
0.1 mm by using the mapping measurement.
Kawamura, Seiko; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Masatoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Kambara, Wataru*; Aoyama, Kazuhiro*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; et al.
Journal of Neutron Research, 21(1-2), p.17 - 22, 2019/05
The Cryogenics and Magnets group in the Sample Environment team is responsible for operation of cryostats and magnets for user's experiments at the MLF in J-PARC. We have introduced a top-loading  He cryostat, a bottom-loading
He cryostat, a bottom-loading  He cryostat, a dilution refrigerator insert and a superconducting magnet. The frequency of use of them dramatically becomes higher in these two years, as the beam power and the number of proposal increase. To respond such situation, we have made efforts to enhance performance of these equipment as follows. The
He cryostat, a dilution refrigerator insert and a superconducting magnet. The frequency of use of them dramatically becomes higher in these two years, as the beam power and the number of proposal increase. To respond such situation, we have made efforts to enhance performance of these equipment as follows. The  He cryostat originally involves an operation software for automatic initial cooling down to the base temperature and automatic re-charge of
He cryostat originally involves an operation software for automatic initial cooling down to the base temperature and automatic re-charge of  He. Recently we made an additional program for automatic temperature control with only the sorb heater. Last year, a new outer vacuum chamber of the magnet with an oscillating radial collimator (ORC) was fabricated. The data quality was drastically improved by introducing this ORC so that the magnet can be used even for the inelastic neutron scattering experiments.
He. Recently we made an additional program for automatic temperature control with only the sorb heater. Last year, a new outer vacuum chamber of the magnet with an oscillating radial collimator (ORC) was fabricated. The data quality was drastically improved by introducing this ORC so that the magnet can be used even for the inelastic neutron scattering experiments.
 Sn; First measurement of low-lying
Sn; First measurement of low-lying  -emitting isomers in
-emitting isomers in 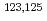 Ag
AgChen, Z. Q.*; Li, Z. H.*; Hua, H.*; Watanabe, Hiroshi*; Yuan, C. X.*; Zhang, S. Q.*; Lorusso, G.*; Orlandi, R.; 60 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 122(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:78.87(Physics, Multidisciplinary)