Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 @C
@C ; Photoelectron spectroscopy of the Li
; Photoelectron spectroscopy of the Li @C
@C [PF
[PF
 ] salt and STM of the single Li
] salt and STM of the single Li @C
@C molecules on Cu(111)
molecules on Cu(111)Yamada, Yoichi*; Kuklin, A. V.*; Sato, Sho*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Sumi, Naoya*; Zhang, C.*; Sasaki, Masahiro*; Kwon, E.*; Kasama, Yasuhiko*; Avramov, P. V.*; et al.
Carbon, 133, p.23 - 30, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:51.01(Chemistry, Physical)We report first STM observation of the Li ion endohedral C
ion endohedral C , which is of a new class of endohedral fullerenes, prepared by means of evaporation of high-purity Li
, which is of a new class of endohedral fullerenes, prepared by means of evaporation of high-purity Li @C
@C [PF
[PF
 ] salt in ultra-high vacuum. Prior to the STM measurements, the electronic structure of Li
] salt in ultra-high vacuum. Prior to the STM measurements, the electronic structure of Li @C
@C in the Li
in the Li @C
@C [PF
[PF
 ] salt was also precisely determined. In the salt, it is shown that Li and PF
] salt was also precisely determined. In the salt, it is shown that Li and PF have nearly single positive and negative charge, respectively, and the C
have nearly single positive and negative charge, respectively, and the C cage is nearly neutral, suggesting that Li
cage is nearly neutral, suggesting that Li @C
@C in the salt retains its original electronic state.
in the salt retains its original electronic state.
 -FeSi
-FeSi
Yamada, Yoichi*; Mao, W.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Esaka, Fumitaka; Udono, Haruhiko*; Tsuru, Tomohito
Physics Procedia, 11, p.67 - 70, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:81.09(Optics)Clean surfaces of the single crystalline  -FeSi
-FeSi have been prepared and investigated. From XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy) measurements of the surface oxide, it is found that the surface Si is mainly oxidized while Fe isn't. After removing the surface oxide, clean surface can be obtained showing reasonable structure in LEED (Low-Energy Electron Diffraction) and STM (Scanning Tunneling Microscope). No drastic surface reconstruction is found reflecting strong Fe-Si bond. DFT (Density Functional Theory) calculation suggests the spin polarized surface DOS (Density Of State) when Fe comes at the surface.
have been prepared and investigated. From XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy) measurements of the surface oxide, it is found that the surface Si is mainly oxidized while Fe isn't. After removing the surface oxide, clean surface can be obtained showing reasonable structure in LEED (Low-Energy Electron Diffraction) and STM (Scanning Tunneling Microscope). No drastic surface reconstruction is found reflecting strong Fe-Si bond. DFT (Density Functional Theory) calculation suggests the spin polarized surface DOS (Density Of State) when Fe comes at the surface.
 -FeSi
-FeSi thin films fabricated by ion beam sputter deposition
thin films fabricated by ion beam sputter depositionEsaka, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Yamada, Yoichi*; Sasase, Masato*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Shamoto, Shinichi; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi
Applied Surface Science, 256(10), p.3155 - 3159, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:55.47(Chemistry, Physical)A combination of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) using synchrotron radiation is applied to clarify surface chemical states of  -FeSi
-FeSi films fabricated by an ion-beam sputtering deposition method. The differences in the chemical states of the films fabricated at substrate temperatures of 873, 973 and 1173 K are investigated.
films fabricated by an ion-beam sputtering deposition method. The differences in the chemical states of the films fabricated at substrate temperatures of 873, 973 and 1173 K are investigated.
Oba, Hironori; Suzuki, Hiroshi*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Sasase, Masato*; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 52(6), p.292 - 295, 2009/07
no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 52(6), p.369 - 371, 2009/07
no abstracts in English
Kurosaki, Yukio*; Yamachi, Hiroshi*; Katsunuma, Yoshio*; Nakata, Masao*; Kuwahara, Hideki*; Yamada, Fumitaka*; Matsushita, Kiyoshi*; Sato, Toshinori*
JAEA-Research 2008-048, 274 Pages, 2008/03
A junction space between a super deep shaft and horizontal drifts forms a 3-dimensional geo-structure, which would take a complicated mechanical behavior during a junction excavation. However, a quantitative design method for a deep junction has not yet established. In order to examine a collapse mechanism of super deep shaft junction, we have conducted literature surveys and interview studies concerned with a collapses. Considering the results of investigations with reviews of intellectuals, the collapse mechanism depends on both a construction procedure of shaft junction and a geological condition. On the other hand, where a deep junction intersects faults and/or fractures with a large angle, a collapse called taka-nuke may occur and a numerical studies that can simulate a practical rock mass behavior around a shaft junction should be carry out. We demonstrate finite difference method is most adequate for these simulations with intellectual review.
Yamada, Fumitaka; Sonobe, Hitoshi; Igarashi, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2007-061, 67 Pages, 2008/02
In JAEA, various systems associated with the collaboration with industries and universities are enacted. These systems have been operated considering the needs of JAEA's program, industry and academia, resultantly contributed, for example, to basic research and the project development. Activities under these systems contain personal exchanges, the publication of the accomplishments and utilization of those, in R&D concerning geological disposal technology of HLW. These activities have progressed in PNC and JNC, through JAEA. The accomplishments from these systems have contributed to the advancement of the national program on the geological disposal of HLW. In this report, the progress of the R&D under these systems was investigated from the beginning of their operation. The contribution to the R&D on geological disposal technology of HLW was also studied. On the basis of these studies, the future utilization of the systems of the collaboration was also discussed.
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yamada, Yoichi; Sasase, Masato*; Esaka, Fumitaka
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 100, p.012044_1 - 012044_4, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:87.53(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Non-destructive depth profile analysis with better depth resolution is required for the characterization of nano-materials. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is the typically non-destructive analysis, however, XPS with fixed excitation energy source cannot provide depth profile without additional technique. On the other hand, analyzing depth of XPS can be varied with the energy tunable excitation source, such as the synchrotron-radiation (SR), since the escape depth of the photoelectrons depends on their kinetic energy. In the present study, Ge thin films (2,4 nm) on two different Si substrates (hydrogen terminated, native oxide) has been analyzed to obtain depth profile of the thin film and buried interface of Ge/Si under the film with two different Si substrates. The XPS spectra clearly show the difference obtained from the varied analyzing depth. These results suggest that the SR-XPS can be applicable for non-destructive depth profile analysis of surface and buried interface.
Yamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Oba, Hironori; Sasase, Masato*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Udono, Haruhiko*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Hojo, Kiichi
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 68(11), p.2204 - 2208, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.23(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) Si in natural Si has been widely used for a doping source, since
Si in natural Si has been widely used for a doping source, since  Si can be transmuted into
Si can be transmuted into 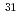 P by thermal neutron (Neutron Transmutation Doping, NTD). NTD of nanostructure fabricated from
P by thermal neutron (Neutron Transmutation Doping, NTD). NTD of nanostructure fabricated from  Si-enriched materials can serve as a controlled local doping method with tunable dopant concentration, which cannot be realized by conventional doping methods such as ion implantation. In the present study,
Si-enriched materials can serve as a controlled local doping method with tunable dopant concentration, which cannot be realized by conventional doping methods such as ion implantation. In the present study,  Si-enriched thin film has been fabricated in order to demonstrate the local NTD. The
Si-enriched thin film has been fabricated in order to demonstrate the local NTD. The  Si-enriched film with thickness of 100 nm was deposited on the Si(100) substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition using
Si-enriched film with thickness of 100 nm was deposited on the Si(100) substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition using  Si-enriched SiF
Si-enriched SiF as the source gases. The film contains 7.1 % of
as the source gases. The film contains 7.1 % of  Si, which is twice higher than that of natural Si. Possible contaminant, fluorine, is lower than 0.6 at.% determined from X-ray photoelectron spectra. Nanostructure of films and changes of electronic properties by the neutron irradiation will also be discussed.
Si, which is twice higher than that of natural Si. Possible contaminant, fluorine, is lower than 0.6 at.% determined from X-ray photoelectron spectra. Nanostructure of films and changes of electronic properties by the neutron irradiation will also be discussed.
Aoyagi, Noboru; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yamada, Reiji
Chemistry Letters, 36(7), p.890 - 891, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)A high yield of H gas was unprecedentedly produced due to the radiolysis of water containing asbestos while the morphology of them turned fibrous bundles into non-fibrous particles in 0.40 M H
gas was unprecedentedly produced due to the radiolysis of water containing asbestos while the morphology of them turned fibrous bundles into non-fibrous particles in 0.40 M H SO
SO solution over 2.0 MGy dose of irradiation. In conclusion, irradiation against asbestos in solutions can promote the hydrogen gas production and cause the morphological change of chrysotile without providing heat or chemicals.
solution over 2.0 MGy dose of irradiation. In conclusion, irradiation against asbestos in solutions can promote the hydrogen gas production and cause the morphological change of chrysotile without providing heat or chemicals.
Yamada, Fumitaka*; Kita, Haruyuki*; Nakata, Masao*
PNC TJ7176 98-002, 135 Pages, 1998/03
None
 Si enriched thin film
Si enriched thin filmYamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Oba, Hironori; Sasase, Masato*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Udono, Haruhiko*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Hojo, Kiichi; Shamoto, Shinichi
no journal, ,
Neutron transmutation doping has been tried by using  Si enriched thin film in order to fabricate nano doping devices.
Si enriched thin film in order to fabricate nano doping devices.
Aoyagi, Noboru; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yamada, Reiji
no journal, ,
Interfacial reaction on chrysotile in acidic aqueous solutions which is promoted by irradiation of  Co
Co  -ray or electron beam was studied by analyzing the production of hydrogen gas and morphological alteration offibril structure. The amount of generated hydrogen gas was proportional to the dose of irradiation and larger than the other particles such as alumina or silica known as a reactive surface donor for radicals. An expedited reaction in which chrysotile fibrous structure fell apart and come into particles was found more in SEM-EDX measurement with increasing the concentrations of sulfuric acid as 0.2M, 0.4M, 0.8M and 2.0M.
-ray or electron beam was studied by analyzing the production of hydrogen gas and morphological alteration offibril structure. The amount of generated hydrogen gas was proportional to the dose of irradiation and larger than the other particles such as alumina or silica known as a reactive surface donor for radicals. An expedited reaction in which chrysotile fibrous structure fell apart and come into particles was found more in SEM-EDX measurement with increasing the concentrations of sulfuric acid as 0.2M, 0.4M, 0.8M and 2.0M.
 -FeSi
-FeSi
Mao, W.; Wakaya, Ippei*; Yamada, Yoichi; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Shamoto, Shinichi; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Udono, Haruhiko*
no journal, ,
Thin films of semiconducting  -FeSi
-FeSi keep attracting considerable attentions for their promising applicability to the Si-based optoelectronics devices. Recently, large single-crystalline
keep attracting considerable attentions for their promising applicability to the Si-based optoelectronics devices. Recently, large single-crystalline  -FeSi
-FeSi has successfully been synthesized, providing a substrate for a well-defined homoepitaxy film. As a first step toward good homoepitaxy of
has successfully been synthesized, providing a substrate for a well-defined homoepitaxy film. As a first step toward good homoepitaxy of  -FeSi
-FeSi , we prepare and characterize low-index surfaces of
, we prepare and characterize low-index surfaces of  -FeSi
-FeSi single crystal. Both LEED and STM reveal the absence of the long-ranged surface reconstruction for each face, which is favorable for the homoepitaxy on this substrate. On the other hand, STM suggests a presence of a significant amount of surface defects for each face, which should be improved in the next step. In addition to structural analysis, the stoichiometry of clean surfaces will be discussed on the basis of XPS and SIMS measurements.
single crystal. Both LEED and STM reveal the absence of the long-ranged surface reconstruction for each face, which is favorable for the homoepitaxy on this substrate. On the other hand, STM suggests a presence of a significant amount of surface defects for each face, which should be improved in the next step. In addition to structural analysis, the stoichiometry of clean surfaces will be discussed on the basis of XPS and SIMS measurements.
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yamada, Yoichi; Matsue, Hideaki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Esaka, Fumitaka; Sasase, Masato*
no journal, ,
Non-destructive depth profiling of steel surface by quantum beam has been introduced. Hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation and neutron depth profiling using reactor have been applied for surface analysis.
Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yokoyama, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Si-enriched thin films for local neutron transmutation doping
Si-enriched thin films for local neutron transmutation dopingYamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Oba, Hironori; Sasase, Masato*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Udono, Haruhiko*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Hojo, Kiichi
no journal, ,
Fabrication and estimation of  Si-enriched thin films for local neutron transmutation doping has been attempted.
Si-enriched thin films for local neutron transmutation doping has been attempted.
Saeki, Morihisa; Oba, Hironori; Yamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yokoyama, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Asai, Shiho; Esaka, Fumitaka; Shinohara, Nobuo; Hirota, Hideyuki*; Yamada, Shinsuke*; Miyoshi, Kazuyoshi*; Saito, Kyoichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -FeSi
-FeSi films by synchrotron radiation fabricated with ion beam sputter deposition
films by synchrotron radiation fabricated with ion beam sputter depositionEsaka, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Yamada, Yoichi*; Sasase, Masato*; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Shamoto, Shinichi
no journal, ,
Synchrotron radiation excited XPS and XAS were utilized to investigate chemical states of the surface of  -FeSi
-FeSi films fabricated by ion beam sputter deposition. The analysis was performed at the BL-13C of the Photon Factory in KEK. In the XPS analysis, depth profiling was carried out by changing the kinetic energy of photoelectrons. As a result, the relative ratios of SiO
films fabricated by ion beam sputter deposition. The analysis was performed at the BL-13C of the Photon Factory in KEK. In the XPS analysis, depth profiling was carried out by changing the kinetic energy of photoelectrons. As a result, the relative ratios of SiO and SiO
and SiO increased with decreasing the kinetic energy of photoelectrons. Simulation results indicated that the SiO
increased with decreasing the kinetic energy of photoelectrons. Simulation results indicated that the SiO formed at the upper layer and the SiO
formed at the upper layer and the SiO formed at the lower layer of the surface. These results show that these analytical methods enable us to investigate chemical states of solid surfaces in detail.
formed at the lower layer of the surface. These results show that these analytical methods enable us to investigate chemical states of solid surfaces in detail.