Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room Temperature Semiconductor Detector Conference (2022 IEEE NSS MIC RTSD) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/11
A real-time data display and storage module was developed for time-of-flight neutron measurement. The module can display real-time experimental data from two-dimensional neutron detector in a two-dimensional image, one-dimensional projection images in X- and Y-axis, and time-of-flight spectra. The module has two modes of operation: standard mode, and simple-display mode. The simple-display mode only displays the experimental results on the monitor and can operate faster than that in the standard mode because the module uses the limited function. Therefore, the simple-display mode is also useful for measurement of high-counting rate neutrons. Operation test using test pulses were performed to confirm the operating speed of the module. The module in standard and simple-display mode could measure the continuous test pulses without counting losses with a frequency of 1.0 and 1.6 MHz, respectively.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.447 - 449, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A real-time data display and storage device was developed for pulsed neutron scattering experiments using the time-of-flight method. The device contains two sets of field programmable gate arrays and on-board microcomputers for data display and storage. The developed device can determine the time-of-flight and time-resolved neutron position data with a time range from 0 to 40 ms using a beam of pulsed neutrons at 25 Hz from an experimental facility. Operation tests were performed using test signals that simulate the neutron detector output signals. It was found that the device could separate double pulses with a time interval of 1  s; furthermore, it could measure the continuous pulses with a frequency of 1 MHz. Consequently, it was confirmed that the developed device demonstrated a counting rate capability of beyond 1 Mcps.
s; furthermore, it could measure the continuous pulses with a frequency of 1 MHz. Consequently, it was confirmed that the developed device demonstrated a counting rate capability of beyond 1 Mcps.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(12), p.C12011_1 - C12011_8, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)A neutron-detection element using circular cathode bumps was developed for two-dimensional neutron measurement, and an irradiation experiment was performed using a  Cf neutron source. The element has triangularly arranged small-sized circular cathode bumps, and the bumps are linked together in the x- and y-directions for the detection of incident neutrons. The element was arranged in the pressure vessel with a fill gas of composition He/(15%)CF
Cf neutron source. The element has triangularly arranged small-sized circular cathode bumps, and the bumps are linked together in the x- and y-directions for the detection of incident neutrons. The element was arranged in the pressure vessel with a fill gas of composition He/(15%)CF at 0.7 MPa. The detector system using bump cathode element exhibited a two-dimensional uniformity with a response of 10.1%. The average intrinsic spatial resolution was 1.89 mm full width at half maximum in the sensitive region, calculated by taking into account the track lengths of the secondary particles.
at 0.7 MPa. The detector system using bump cathode element exhibited a two-dimensional uniformity with a response of 10.1%. The average intrinsic spatial resolution was 1.89 mm full width at half maximum in the sensitive region, calculated by taking into account the track lengths of the secondary particles.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2016) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2016/00
A ceramic-insulated ball-anode (CiB) element that consists of a ceramic insulator, cathode lines, ball-shaped anodes, and anode lines was developed, and an irradiation experiment was performed using a Cf-252 neutron source. An electric field simulation of CiB element was conducted and strong electric fields of more than 10 V/m was obtained by the calculation using the finite element method. The neutron-induced signals of all pixels were observed using 8
V/m was obtained by the calculation using the finite element method. The neutron-induced signals of all pixels were observed using 8  8 pixel small-sized test element under Cf-252 neutron irradiation.
8 pixel small-sized test element under Cf-252 neutron irradiation.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 784, p.194 - 197, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)A novel ceramics insulated detector element was developed for neutron measurement. The developed detector element consists of a ceramics insulator, cathode lines on the insulator, and ball-shaped anodes. The incident neutrons are usually scattered by the detector element itself because it acts as scatterer. To estimate the effects of scattering, we calculated the amount of neutrons scattered by the developed element. By the calculation results by a Monte Carlo simulation using PHITS, it is found that the developed element is effective to reduce the scattered neutrons. The number of scattered neutrons of the developed element is 40% smaller than that of polymer insulated element, which is widely used in micro-pattern element. Finally, neutron-induced signals were clearly observed using the developed detector element.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2015), 2 Pages, 2015/00
A two-dimensional gas-based neutron detector system that can be operated under high-pressure was developed, and an irradiation experiment was performed using a Cf-252 neutron source. The pressure vessel of the developed detector system has 256 feedthroughs insulated by alumina ceramics for neutron-induced signals and 6 connectors for high voltage. The vessel could withstand pressures of up to 0.8 MPa and with a helium leakage of less than 10 Pam
Pam /s. The signals from neutrons clearly observed and can be discriminated from background signals such as
/s. The signals from neutrons clearly observed and can be discriminated from background signals such as  -ray and electrical noises. The flat-field image showed good homogeneity and an average gain spread of approximately 7.7%. The system exhibits a
-ray and electrical noises. The flat-field image showed good homogeneity and an average gain spread of approximately 7.7%. The system exhibits a  -ray sensitivity of 1.1
-ray sensitivity of 1.1 10
10 .
.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 9(11), p.C11019_1 - C11019_9, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)A multiwire-type two-dimensional neutron detector system using individual line readout and optical signal transmission method is developed for use in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The sensitive area was 128  128 mm
128 mm with a pitch of 1 mm in both directions (x and y), and the 256 signal lines are individually readout by signal-processing electronics. First irradiation experiments using pulsed neutrons are performed at the J-PARC/MLF. The developed detector could determine time-of-flight spectra and time-resolved two-dimensional images accurately with time range from 0 to 40 ms that arise from 25-Hz pulsed neutrons. Finally, the validity of the detector system is confirmed by a neutron reflectometry using Ni/Ti multilayer.
with a pitch of 1 mm in both directions (x and y), and the 256 signal lines are individually readout by signal-processing electronics. First irradiation experiments using pulsed neutrons are performed at the J-PARC/MLF. The developed detector could determine time-of-flight spectra and time-resolved two-dimensional images accurately with time range from 0 to 40 ms that arise from 25-Hz pulsed neutrons. Finally, the validity of the detector system is confirmed by a neutron reflectometry using Ni/Ti multilayer.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 528, p.012045_1 - 012045_6, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:77.09(Optics)A multiwire proportional chamber (MWPC) neutron detector system is developed for use in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. In the developed MWPC system, a short response time and high spatial resolution can be obtained through the use of an individual line readout method. The developed system consists of a 256 channel detector element (x: 128 lines, y: 128 lines) equipped with a pressure vessel, amplifier-shaper-discriminator (ASD) boards, optical signal transmission devices, position encoders with field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), and a data acquisition device. The measured uniformity of all pixels in the two-dimensional image was 7.9%. The average intrinsic spatial resolution was 1.55 mm full width at half-maximum in the sensitive region calculated by taking into account measured track lengths of secondary particles.
 B
B O
O ceramic scintillator detector as an alternative to a
ceramic scintillator detector as an alternative to a  He-gas-based detector for a plutonium canister assay system
He-gas-based detector for a plutonium canister assay systemNakamura, Tatsuya; Ozu, Akira; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Honda, Katsunori; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Takase, Misao; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 763, p.340 - 346, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)A neutron-sensitive ZnS/ B
B O
O ceramic scintillator detector was developed as an alternative to a
ceramic scintillator detector was developed as an alternative to a  He-gas-based detector for use in a plutonium canister assay system. The detector has a modular structure, with a flat ZnS/
He-gas-based detector for use in a plutonium canister assay system. The detector has a modular structure, with a flat ZnS/ B
B O
O ceramic scintillator strip that is installed diagonally inside a light-reflecting aluminium case with a square cross section. The prototype detectors, which have a neutron-sensitive area of 30 mm
ceramic scintillator strip that is installed diagonally inside a light-reflecting aluminium case with a square cross section. The prototype detectors, which have a neutron-sensitive area of 30 mm  250 mm, exhibited a sensitivity of 21.7-23.4
250 mm, exhibited a sensitivity of 21.7-23.4  0.1 cps
0.1 cps nv for thermal neutrons, a
nv for thermal neutrons, a  Cs
Cs  -ray sensitivity of 1.1-1.9
-ray sensitivity of 1.1-1.9 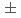 0.2
0.2  10
10 and a count variation of less than 6% over the detector length. A trial experiment revealed a temperature coefficient of less than -0.24
and a count variation of less than 6% over the detector length. A trial experiment revealed a temperature coefficient of less than -0.24 0.05% /
0.05% /  C over the temperature range of 20-50
C over the temperature range of 20-50 C.
C.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Hino, Masahiro*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 726, p.169 - 174, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.66(Instruments & Instrumentation)A multiwire-type two-dimensional neutron detector system with a sensitive area of 128  128 mm
128 mm is developed for use in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. The system can achieve a short response time and high spatial resolution using the individual line readout method. Optical devices have been incorporated in the system for long-distance signal transmission and insulation between a detector head in the neutron shielding and signal processing circuits in the data acquisition room. The detector system exhibits a pulse-pair resolution of 1
is developed for use in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. The system can achieve a short response time and high spatial resolution using the individual line readout method. Optical devices have been incorporated in the system for long-distance signal transmission and insulation between a detector head in the neutron shielding and signal processing circuits in the data acquisition room. The detector system exhibits a pulse-pair resolution of 1  s, an average spatial resolution of less than 2 mm full width at half-maximum in the sensitive region, and a two-dimensional homogeneity of 8.3% in all pixels.
s, an average spatial resolution of less than 2 mm full width at half-maximum in the sensitive region, and a two-dimensional homogeneity of 8.3% in all pixels.
Yamagishi, Hideshi*; To, Kentaro
JAEA-Research 2011-050, 16 Pages, 2012/10
For development of two-dimensional position sensitive (2-D) neutron detectors with fast response and high spatial resolution, an ASIC with fast response and low noise performances is required. The MP8 and MP16, consisting of p-MOSFETs, with high g and low noise have been proposed (1) to develop the ASIC. In this paper a simple low noise amplifier (LNA) was designed and the noise power and the noise figure were analytically calculated. The results were also applied to LNAs using MP8 or MP16 configuration. The results showed that the MP8 and MP16 had enough performances for the ASIC.
and low noise have been proposed (1) to develop the ASIC. In this paper a simple low noise amplifier (LNA) was designed and the noise power and the noise figure were analytically calculated. The results were also applied to LNAs using MP8 or MP16 configuration. The results showed that the MP8 and MP16 had enough performances for the ASIC.
Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Maruyama, Ryuji; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Kubota, Masato; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Chinese Journal of Physics, 50(2), p.161 - 170, 2012/04
Yamagishi, Hideshi*; To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Research 2011-051, 19 Pages, 2012/02
An ASD-ASIC (Amplifier-Shaper-Discriminator ASIC) with fast response and low noise performances has been designed for two-dimensional position sensitive neutron gas detectors (InSPaD). The InSPaD is a 2D neutron detector system with  He gas and provides a high spatial resolution by making distinction between proton and triton particles generated in the gas chamber. The new ASD-ASIC is required to have very low noise, a wide dynamic range, good output linearity and high counting rate. The new ASD-ASIC has been designed by using CMOS and consisted of 64-channel ASDs, a 16-channel multiplexer with LVTTL drivers and sum amplifier system for summing all analog signals. The performances were evaluated by the Spice simulation. It was confirmed that the new ASD-ASIC had very low noise performance, wide dynamic range and fast signal processing functions.
He gas and provides a high spatial resolution by making distinction between proton and triton particles generated in the gas chamber. The new ASD-ASIC is required to have very low noise, a wide dynamic range, good output linearity and high counting rate. The new ASD-ASIC has been designed by using CMOS and consisted of 64-channel ASDs, a 16-channel multiplexer with LVTTL drivers and sum amplifier system for summing all analog signals. The performances were evaluated by the Spice simulation. It was confirmed that the new ASD-ASIC had very low noise performance, wide dynamic range and fast signal processing functions.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 7(1), p.C01025_1 - C01025_6, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.72(Instruments & Instrumentation)We are currently developing a two-dimensional neutron detection system that can read out individual signals and consists of a micro-pixel detector element. By increasing the gas pressure, the spatial resolution and detection efficiency of a two-dimensional gas-based detector are improved but the output signal strength is decreased. Therefore, the supply voltage must be increased to obtain output signals under high pressure. In the present study, we have developed a micro-pixel detector element with a high-voltage resistance by an improved fabrication process. The voltage resistance of the element was improved, and the element could operate up to 750 V at a total pressure of 5 atm (4.1 atm of He and 0.9 atm of CF ). The measured gas gain was found to be approximately 100, and the thermal neutron detection efficiency was estimated to be 70%. A flat-field image showed good homogeneity, and the average gain spread was about 8.7%.
). The measured gas gain was found to be approximately 100, and the thermal neutron detection efficiency was estimated to be 70%. A flat-field image showed good homogeneity, and the average gain spread was about 8.7%.
Yamagishi, Hideshi*; To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 6(12), p.C12025_1 - C12025_7, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.40(Instruments & Instrumentation)We are currently developing a multiwire-type two-dimensional neutron detector system for use at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at J-PARC. This system can attain high response time and high spatial resolution by using the individual line readout method. The performance parameters of a gas-based two-dimensional neutron detector, such as spatial resolution and detection efficiency, strongly depend on the mixture gas condition. We developed a simulation program for our multiwire-type two-dimensional neutron detector system to determine the gas condition. Further, a small test system was fabricated to evaluate the simulation program. Experimental results obtained using the small test system agreed well with the simulation results, thus, it was confirmed that the simulation program can be effectively used to determine the gas condition when the required spatial resolution and detection efficiency are known.
Yamagishi, Hideshi*; To, Kentaro
JAEA-Technology 2010-030, 16 Pages, 2010/09
In two-dimensional position sensitive (2-D) neutron detectors used for neutron scattering experiments in the J-PARC, it is required that very small pulse signals consisted of several hundred channels should be measured with discriminating form noises and  ray signals and converted from analogue to digital signals in real time. To establish performances of neutron detectors such as fast response and a very small spatial resolution, multi-channel small signals should be measured and the signal processing should be carried out with high S/N ratios. For development of multi-channel electronics with fast response and very low noise, manufacture of an application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) with high performances is indispensable for the 2-D neutron detectors. Therefore, MOSFETs with high gm and low noise required for the ASIC were designed and the noise performances were studied and estimated.
ray signals and converted from analogue to digital signals in real time. To establish performances of neutron detectors such as fast response and a very small spatial resolution, multi-channel small signals should be measured and the signal processing should be carried out with high S/N ratios. For development of multi-channel electronics with fast response and very low noise, manufacture of an application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) with high performances is indispensable for the 2-D neutron detectors. Therefore, MOSFETs with high gm and low noise required for the ASIC were designed and the noise performances were studied and estimated.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Tanaka, Hiroki; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya; Ochi, Atsuhiko*; Tanimori, Toru*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 573(1-2), p.187 - 190, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have been developing a neutron imaging gas detector with a high spatial resolution and with a high temporal response for the neutron scattering instruments at the pulsed neutron source in the Japan proton accelerator research complex. The gas detector system with individual read-outs was developed to meet the requirements for the instruments for neutron reflectometry or for small angle neutron scattering. The performances of the prototype detector using a multi-wire (MW) or micro-strip (MS) detector head were evaluated using a collimated neutron beam, and we confirmed the MS detector exhibiting a spatial resolution of 1.5 mm and a pulse-pair resolution of about 100 ns with a gas pressure of 6 atm helium with a mixture of 30% CF . The performances for the MS detector were also evaluated up to the total gas pressure of 8 atm.
. The performances for the MS detector were also evaluated up to the total gas pressure of 8 atm.
Yamagishi, Hideshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-004, 15 Pages, 2007/02
Two-dimensional position sensitive neutron detectors that have performances of a fast response and a very small spatial resolution are required for various neutron scattering experiments using high-intensity pulse-neutron sources in a high-intensity proton accelerator facility. We put forward the development of a micro-pixel gas chamber (MPGC) filled with helium-3 gas as the two-dimensional position sensitive neutron detector. The MPGC provides fast responses and very small signals and requires more than 500 signal channels. Therefore, development of an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is essential for processing of multi-channel signals from the MPGC. Design and study of the ASIC was performed.
Yamagishi, Hideshi; Kakuta, Tsunemi*
Kyodo Kenkyu Seika Gaiyo, Shoraigata Genshiryoku Hatsuden Gijutsu No Kodoka Ni Kansuru Kenkyu, p.197 - 211, 2006/06
no abstracts in English