Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10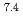 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Nakayoshi, Akira; Arai, Yoichi; Sato, Takumi; Ohgi, Hiroshi; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Morishita, Kazuki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-005, 418 Pages, 2023/12
For safe and steady decommissioning of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), information concerning composition and physical/chemical properties of fuel debris generated in the reactors should be estimated and provided to other projects conducting the decommissioning work including the retrieval of fuel debris and the subsequent storage. For this purpose, in FY2021, samples of contaminants (the wiped smear samples and the deposits) obtained through the internal investigation of the 1F Unit 2 were analyzed to clarify the components and to characterize the micro-particles containing uranium originated from fuel (U-bearing particles) in detail. This report summarized the results of analyses performed in FY2021, including the microscopic analysis by SEM and TEM, radiation analysis, and elemental analysis by ICP-MS, as a database for evaluating the main features of each sample and the probable formation mechanism of the U-bearing particles.
 solution in the gigapascal pressure range
solution in the gigapascal pressure rangeYamaguchi, Toshio*; Fukuyama, Nami*; Yoshida, Koji*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Liquids, 3(3), p.288 - 302, 2023/09
We report the structure of an aqueous 2 mol/kg MgCl solution at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 4 GPa and temperatures from 300 to 500 K revealed by X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. The scattering data are analyzed by empirical potential structure refinement (EPSR) modeling to derive the pair distribution functions, coordination number distributions, angle distributions, and spatial density functions as a function of pressure and temperature. Mg
solution at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 4 GPa and temperatures from 300 to 500 K revealed by X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. The scattering data are analyzed by empirical potential structure refinement (EPSR) modeling to derive the pair distribution functions, coordination number distributions, angle distributions, and spatial density functions as a function of pressure and temperature. Mg forms rigid solvation shells extended to the third shell; the first solvation shell of six-fold octahedral coordination with about six water molecules at 0 GPa transforms into about five water molecules and one Cl
forms rigid solvation shells extended to the third shell; the first solvation shell of six-fold octahedral coordination with about six water molecules at 0 GPa transforms into about five water molecules and one Cl due to the formation of the contact ion pairs in the GPa pressure range. The Cl
due to the formation of the contact ion pairs in the GPa pressure range. The Cl solvation shows a substantial pressure dependence; the coordination number of a water oxygen atom around Cl
solvation shows a substantial pressure dependence; the coordination number of a water oxygen atom around Cl increases from 8 at 0.1 MPa/300 K to 10 at 4 GPa/500 K. The solvent water transforms the tetrahedral network structure at 0.1 MPa/300 K to a densely packed structure in the GPa pressure range; the number of water oxygen atoms around a central water molecule gradually increases from 4.6 at 0.1 MPa/298 K to 8.4 at 4 GPa/500 K.
increases from 8 at 0.1 MPa/300 K to 10 at 4 GPa/500 K. The solvent water transforms the tetrahedral network structure at 0.1 MPa/300 K to a densely packed structure in the GPa pressure range; the number of water oxygen atoms around a central water molecule gradually increases from 4.6 at 0.1 MPa/298 K to 8.4 at 4 GPa/500 K.
Toyoda, Shin*; Inoue, Kazuhiko*; Yamaguchi, Ichiro*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Hirota, Seiko*; Oka, Toshitaka; Shimazaki, Tatsuya*; Mizuno, Hideyuki*; Tani, Atsushi*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1557 - 1564, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Interlaboratory comparison studies are important for radiation dosimetry in order to demonstrate how the technique is universally available. The set of standard samples are examined in each participating laboratory in the present study. After a set of standard samples together with the samples with unknown doses, which were prepared in the same laboratory as the standard samples, are measured at a participating laboratory, those samples are sent to another participating laboratory for next measurement. There is some small difference observed in the sensitivity (the slope of the dose response line) of the standard samples while the differences in the obtained doses for the samples with unknown doses are rather systematic, implying that the difference is mostly due to the samples but not to measurements.
Yoshimune, Wataru*; Higuchi, Yuki*; Kato, Akihiko*; Hibi, Shogo*; Yamaguchi, Satoshi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kato, Satoru*
ACS Energy Letters (Internet), 8(8), p.3485 - 3487, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.07(Chemistry, Physical)Hirata, Yoshinobu*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Kaneko, Koji; Hagihara, Masato; Yamaguchi, Hideyuki*; Omoto, Chie*; Katsuno, Nakako*; Imaizumi, Teppei*; Nishizu, Takahisa*
Food Hydrocolloids, 141, p.108728_1 - 108728_7, 2023/08
Crystallinity is reflected in the mechanical properties of foods and materials. Crystallinity should be related to the structural dynamics of starch. In this study, we used quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) to investigate changes in the molecular dynamics of cooked rice starch during retrogradation. The width of the measured QENS narrowed with retrogradation. The elastic incoherent structure factor (EISF) increased, which indicated that the molecular dynamics are spatially suppressed upon retrogradation. Analysis of EISF with a bimodal continuous diffusion model, where low and high mobilities are assumed to correspond to crystalline and amorphous phases, respectively, showed that the fraction of the low-mobility component increases with retrogradation.
Saito, Shigeru; Yamaguchi, Kazushi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu*; Obayashi, Hironari; Sasa, Toshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2022-032, 51 Pages, 2023/03
In the Accelerator Driven System (ADS) being studied by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) for transmutation of long-lived radioactive waste, lead-bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) is used as a spallation target and subcritical core coolant. A proton irradiation facility in J-PARC is considered to prepare a material irradiation database for ADS development. The proton irradiation facility is equipped with an LBE loop, which enables material irradiation tests in spallation environment under flowing LBE condition. The slow leakage of LBE is one of critical issue to use LBE safety. The slow leakage is caused by the biting slag and/or other materials at valve seal of drain valve. To solve this problem, JAEA examined the application of freeze-seal valve (FSV), which seal the piping by freezing LBE in specific position. Water-cooled and air-cooled freeze-seal valve test modules were fabricated, installed in the test section of the existing test stand for LBE technology development, and tested to confirm their operation and performance. As a result of the tests, it was confirmed that the water-cooled FSV test module worked well along to the design values. This report describes the outline and details of the test stand for LBE technology and each FSV test module, as well as the results of operation and performance verification tests.
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.9(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Yuji; Meigo, Shinichiro
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, 226 Pages, 2022/11
The 2021 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held as an online connection conference on November 18-19, 2021. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) in cooperation with the Sigma Investigative Advisory Committee of AESJ, J-PARC Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), and High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK). In the symposium, tutorials "New Developments in TALYS and TENDL-2021" and "Role of ADS and its Development Issues" were proposed and held. Three sessions of lectures and discussions were held: "J-PARC and JAEA Facilities", "Current Status and Future Prospects of Nuclear Data Research", and "Medical, Isotope Production, and Analysis". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, nuclear theory, evaluation, benchmark, and applications were presented in the poster session. The total number of participants was 132 participants. Each oral and poster presentation was followed by an active question and answer session. This report consists of a total of 36 papers including 14 oral and 22 poster presentations.
Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Yoshida, Koji*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 365, p.120181_1 - 120181_10, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.81(Chemistry, Physical)Neutron scattering measurements were performed on an aqueous 3 mol/kg NaCl solution in D O at temperature and pressure conditions of 0.1 MPa/298K, 1 GPa/298K, 1 GPa/523K, and 4 GPa/523K. The empirical potential structure refinement method was applied to the obtained data to extract the pair correlation function, coordination number distribution, angular distribution (orientation correlation), and spatial density function (3-D structure). From those results, pressure and temperature dependence of solvation and association of ions and solvent-water structure were discussed.
O at temperature and pressure conditions of 0.1 MPa/298K, 1 GPa/298K, 1 GPa/523K, and 4 GPa/523K. The empirical potential structure refinement method was applied to the obtained data to extract the pair correlation function, coordination number distribution, angular distribution (orientation correlation), and spatial density function (3-D structure). From those results, pressure and temperature dependence of solvation and association of ions and solvent-water structure were discussed.
 -iron
-ironHirayama, Shintaro*; Sato, Koichi*; Kato, Daiji*; Iwakiri, Hirotomo*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Watanabe, Yoshiyuki*; Nozawa, Takashi*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 31, p.101179_1 - 101179_9, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Zhang, W. Q.*; Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Fang, C. H.*; Yoshida, Koji*; Zhou, Y. Q.*; Zhu, F. Y.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Li, W.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 348, p.118080_1 - 118080_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.79(Chemistry, Physical)The ion hydration and association and hydrogen-bonded water structure in an aqueous 3 mol/kg RbCl solution were investigated at 298 K/0.1 MPa, 298 K/1 GPa, 523 K/1 GPa, and 523 K/4 GPa by neutron diffraction combined with EPSR methods. The second hydration layer of Rb and Cl
and Cl becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb
becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb (Cl
(Cl ) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb
) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl
and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb
does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb -Cl
-Cl decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.
decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.
Yin, Y.-G.*; Mori, Yoshinao*; Suzui, Nobuo*; Kurita, Keisuke; Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka*; Miyoshi, Yuta*; Nagao, Yuto*; Ashikari, Motoyuki*; Nagai, Keisuke*; Kawachi, Naoki*
New Phytologist, 232(5), p.1974 - 1984, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:65.39(Plant Sciences)Rice (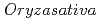 ) plants have porous or hollow organs consisting of aerenchyma, which is presumed to function as a low-resistance diffusion pathway for air to travel from the foliage above the water to submerged organs. However, gas movement in rice plants has yet to be visualized in real time. In this study involving partially submerged rice plants, the leaves emerging from the water were fed nitrogen-13-labeled nitrogen ([
) plants have porous or hollow organs consisting of aerenchyma, which is presumed to function as a low-resistance diffusion pathway for air to travel from the foliage above the water to submerged organs. However, gas movement in rice plants has yet to be visualized in real time. In this study involving partially submerged rice plants, the leaves emerging from the water were fed nitrogen-13-labeled nitrogen ([ N]N
N]N ) tracer gas, and the gas movement downward along the leaf blade, leaf sheath, and internode over time was monitored.
) tracer gas, and the gas movement downward along the leaf blade, leaf sheath, and internode over time was monitored.
Taguchi, Shigeo; Taguchi, Katsuya; Makino, Risa; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Suzuki, Kazuyuki; Takano, Masato; Koshino, Katsuhiko; Ishida, Michihiko; Nakano, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Toshiya
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-17-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.499 - 502, 2021/07
In 2018, Tokai Reprocessing Plan (TRP) shifted to the decommissioning stage. In order to proceed with steady decommissioning work, TRP effort to enhance project management function. This paper describes the establishment and role of the Decommissioning Project Management Office, effectiveness of applying the project management tool and its utilization concept, and the method of materialize the equipment dismantling plan.
Nugraha, E. D.*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Kusdiana*; Untara*; Mellawati, J.*; Nurokhim*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Ikram, A.*; Syaifudin, M.*; Yamada, Ryohei; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.14578_1 - 14578_16, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:84.25(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mamuju is one of the regions in Indonesia which retains natural conditions but has relatively high exposure to natural radiation. The goals of the present study were to characterize exposure of the entire Mamuju region as a high natural background radiation area (HNBRA) and to assess the existing exposure as a means for radiation protection of the public and the environment. A cross-sectional study method was used with cluster sampling areas by measuring all parameters that contribute to external and internal radiation exposures. It was determined that Mamuju was a unique HNBRA with the annual effective dose between 17 and 115 mSv, with an average of 32 mSv. The lifetime cumulative dose calculation suggested that Mamuju residents could receive as much as 2.2 Sv on average which is much higher than the average dose of atomic bomb survivors for which risks of cancer and non-cancer diseases are demonstrated. The study results are new scientific data allowing better understanding of health effects related to chronic low-dose-rate radiation exposure and they can be used as the main input in a future epidemiology study.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Ogura, Koya*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Suzuki, Takahito*; Yamada, Ryohei; Negemi, Ryoju*; Tsujiguchi, Takakiyo*; Yamaguchi, Masaru*; Shiroma, Yoshitaka*; Iwaoka, Kazuki*; et al.
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), p.978_1 - 978_16, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:68.83(Environmental Sciences)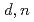 ) reaction at 12, 20, and 30 MeV
) reaction at 12, 20, and 30 MeVPatwary, M. K. A*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Aoki, Katsumi*; Yoshinami, Kosuke*; Yamaguchi, Masaya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(2), p.252 - 258, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)While designing deuteron accelerator neutron sources for radioisotopes production, nuclear data for light elements such as Li, Be, and C have been systematically measured in the deuteron energy range from a few MeV to around 50 MeV. Currently, the experimental data available on double-differential thick-target neutron yields (DDTTNYs) is insufficient, especially for deuteron energies between 18 and 33 MeV. In this study, we measured the DDTTNYs of (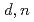 ) reactions on
) reactions on  C target for incident deuteron energies of 12, 20, and 30 MeV using the multiple-foils activation method to improve nuclear data insufficiency. We applied the GRAVEL code for the unfolding process to derive the DDTTNYs. The results were compared with the calculation by DEURACS. The present data were also used to confirm the systematics of the differential neutron yields at 0
C target for incident deuteron energies of 12, 20, and 30 MeV using the multiple-foils activation method to improve nuclear data insufficiency. We applied the GRAVEL code for the unfolding process to derive the DDTTNYs. The results were compared with the calculation by DEURACS. The present data were also used to confirm the systematics of the differential neutron yields at 0 and total neutron yield per incident deuteron in the wide range of deuteron energy.
and total neutron yield per incident deuteron in the wide range of deuteron energy.
Nagae, Daisuke*; Abe, Yasushi*; Okada, Shunsuke*; Omika, Shuichiro*; Wakayama, Kiyoshi*; Hosoi, Shun*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Moriguchi, Tetsuro*; Amano, Masamichi*; Kamioka, Daiki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 986, p.164713_1 - 164713_7, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)Hosoda, Masahiro*; Nugraha, E. D.*; Akata, Naofumi*; Yamada, Ryohei; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Sasaki, Michiya*; Kelleher, K.*; Yoshinaga, Shinji*; Suzuki, Takahito*; Rattanapongs, C. P.*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 750, p.142346_1 - 142346_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:86.19(Environmental Sciences)The biological effects of low dose-rate radiation exposures on humans remains unknown. In fact, the Japanese nation still struggles with this issue after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Recently, we have found a unique area in Indonesia where naturally high radiation levels are present, resulting in chronic low dose-rate radiation exposures. We aimed to estimate the comprehensive dose due to internal and external exposures at the particularly high natural radiation area, and to discuss the enhancement mechanism of radon. A car-borne survey was conducted to estimate the external doses from terrestrial radiation. Indoor radon measurements were made in 47 dwellings over three to five months, covering the two typical seasons, to estimate the internal doses. Atmospheric radon gases were simultaneously collected at several heights to evaluate the vertical distribution. The absorbed dose rates in air in the study area vary widely between 50 nGy h and 1109 nGy h
and 1109 nGy h . Indoor radon concentrations ranged from 124 Bq m
. Indoor radon concentrations ranged from 124 Bq m to 1015 Bq m
to 1015 Bq m . That is, the indoor radon concentrations measured exceed the reference levels of 100 Bq m
. That is, the indoor radon concentrations measured exceed the reference levels of 100 Bq m recommended by the World Health Organization. Furthermore, the outdoor radon concentrations measured were comparable to the high indoor radon concentrations. The annual effective dose due to external and internal exposures in the study area was estimated to be 27 mSv using the median values. It was found that many residents are receiving radiation exposure from natural radionuclides over the dose limit for occupational exposure to radiation workers. This enhanced outdoor radon concentration might be as a result of the stable atmospheric conditions generated at an exceptionally low altitude. Our findings suggest that this area provides a unique opportunity to conduct an epidemiological study related to health effects due to chronic low dose-rate radiation exposure.
recommended by the World Health Organization. Furthermore, the outdoor radon concentrations measured were comparable to the high indoor radon concentrations. The annual effective dose due to external and internal exposures in the study area was estimated to be 27 mSv using the median values. It was found that many residents are receiving radiation exposure from natural radionuclides over the dose limit for occupational exposure to radiation workers. This enhanced outdoor radon concentration might be as a result of the stable atmospheric conditions generated at an exceptionally low altitude. Our findings suggest that this area provides a unique opportunity to conduct an epidemiological study related to health effects due to chronic low dose-rate radiation exposure.