Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Nakada, Akira; Seya, Natsumi; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-052, 118 Pages, 2024/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2022. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Yoshida, Hisao*; Yamamoto, Akira*; Hosokawa, Saburo*; Yamazoe, Seiji*; Kikkawa, Soichi*; Hara, Kenji*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Tanaka, Tsunehiro*
Topics in Catalysis, 64(9-12), p.660 - 671, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.54(Chemistry, Applied)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 O
O by
by  inelastic neutron scattering and their reactivity with ethylene
inelastic neutron scattering and their reactivity with ethyleneYamazoe, Seiji*; Yamamoto, Akira*; Hosokawa, Saburo*; Fukuda, Ryoichi*; Hara, Kenji*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Tsukuda, Tatsuya*; Yoshida, Hisao*; Tanaka, Tsunehiro*
Catalysis Science & Technology, 11(1), p.116 - 123, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:34.43(Chemistry, Physical)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Kitamura, Seiji; Iwasaki, Akihisa*; Matsubara, Shinichiro*; Okamura, Shigeki*
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/07
To design fast reactor (FR) components, seismic response must be evaluated in order to ensure structural integrity. Therefore, a sophisticated analysis method has to be developed to study the seismic response of FR core. The fast reactors are made of several hundred core assemblies in hexagonal arrangement. When a big earthquake occurs, large horizontal displacement and impact force of each core assembly may cause a trouble for control rod insertability and core assembly intensity. Therefore, a seismic analysis method of fast reactor core considering horizontal nonlinear behavior, such as impact, fluid-structure interaction, etc. is needed. Validation of the core assembly vibration analysis code in three dimension (REVIAN-3D) was conducted by a full scale experiment. In this validation, the vertical behavior (raising displacement) and horizontal behavior (Impact force, horizontal response) of the analysis result agreed very well with the experiments.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Onoe, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-050, 114 Pages, 2014/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2012. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2012, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Uchida, Shunsuke*; Wada, Yoichi*; Yamamoto, Seiji*; Takagi, Junichi*; Hisamune, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(1), p.24 - 36, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:57.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)ECP in the BWR primary cooling system can be measured only in the restricted region. In order to determine ECP at any location, ECP should be evaluated by computer simulation codes consisting of water radiolysis models to determine the concentrations of corrosive radiolytic species and mixed potential models to determine ECP based on corrosive species. Mitigation of SCC crack growth rate due to decreasing ECP can be authorized by the JSME Standards, while mitigation of ECP due to hydrogen addition has not been authorized yet. In the paper, standard procedures to authorize the computer simulation codes based on the verification and validation method are proposed. The numerical justification of every code applied as a standard code should be verified and its accuracy and applicability for plant analysis should be validated. Benchmark problems for verification processes are proposed and comparison of the calculated results with the measured ones for the plant of evaluation is required.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-018, 169 Pages, 2013/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in 2011 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2011, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Yamamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwano, Keita*; Namikawa, Tadashi*; Morikawa, Seiji*; Seno, Shoji*; Tabei, Kazuto*; Toida, Masaru*; Yokota, Hideharu
JAEA-Research 2013-003, 252 Pages, 2013/06
This study reconsiders rock's mechanical and hydrological parameters based on additional  data given in this year, and conducts the mechanical-hydrological analysis using the Micromechanics-Based Continuum (MBC) model which can consider the behavior of fracture. The acquired analysis results are compared with actual test data such as drift convergence and hydraulic pressure around the drift. Then, following knowledge is obtained.
data given in this year, and conducts the mechanical-hydrological analysis using the Micromechanics-Based Continuum (MBC) model which can consider the behavior of fracture. The acquired analysis results are compared with actual test data such as drift convergence and hydraulic pressure around the drift. Then, following knowledge is obtained.
Nagane, Satoru; Matsuno, Satoru; Yamamoto, Makoto; Tobinai, Kazuhito; Hori, Hiroshi; Kitahara, Katsumi; Yoshikawa, Seiji
JAEA-Review 2011-001, 49 Pages, 2011/03
Nuclear Facilities Management Section is liquid nuclear waste facility, a small nuclear fuel treatment facility, operation, maintenance and decommissioning of the nuclear ship "MUTSU", which carried out the operation and maintenance services of solid waste facilities. This paper, for the Nuclear Facilities Management Section FY2009 (April 2009 - March 2010) summarized results of operations.
Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Entani, Shiro; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Yamamoto, Shunya
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 131, 2011/01
Ion implantation technique is expected to be useful in fabrication of diluted magnetic semiconductors (DMS) that require high concentration magnetic atom doping without a secondary phase formation. However, ion implantation surely introduces irradiation-induced vacancies into crystals. Recent calculation studies have suggested a presence of vacancies affect the magnetic properties in DMS. In this study, magnetic ions were implanted into compound semiconductor crystals by using ion implantation. N-type ZnO(0001) crystals were implanted with 380 keV maximum energy Cr ions to a dose of 1
ions to a dose of 1 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . After ion implantation, isochronal annealing in steps of 30 min/100
. After ion implantation, isochronal annealing in steps of 30 min/100  C was performed. From the measurement results, irradiation-induced vacancies were annealed out at 900
C was performed. From the measurement results, irradiation-induced vacancies were annealed out at 900  C. From XRD measurements after annealing at 1100
C. From XRD measurements after annealing at 1100  C, no secondary phase peaks were observed. However, from SQUID measurement, a clear magnetic hysteresis was not observed.
C, no secondary phase peaks were observed. However, from SQUID measurement, a clear magnetic hysteresis was not observed.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Nagane, Satoru; Matsuno, Satoru; Yamamoto, Makoto; Tobinai, Kazuhito; Ozaki, Shinji; Sato, Yasuo; Kitahara, Katsumi; Yoshikawa, Seiji
JAEA-Review 2009-018, 39 Pages, 2009/08
Nuclear Facilities Management Section is, Liquid nuclear waste facility, a small nuclear fuel treatment facility, operation, maintenance and decommissioning of the nuclear ship "MUTSU", which carried out the operation and maintenance services of solid waste facilities. This paper, the nuclear facilities Management Section, Office of FY2008 year (April 2008-March 2009) summarized results of operations.
Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Saeki, Riuji; Toyokawa, Ryoji; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Arakawa, Dai*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Lee, S.*; Sato, Kenichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.1125 - 1127, 2008/06
A 3-GeV Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) has been commissioned recently. During its beam commissioning, various beam diagnostic instrumentation has been used. The multi-wire profile monitor (MWPM) is used to establish injection and H0 dump line. The electron catcher confirms that the beam hits a charge exchange carbon foil and the specified current monitor limits the beam current to the H0 dump. Single pass BPMs and ionization profile monitors (IPM) help to check the one pass orbit without circulation of the beam. The beam position monitor (BPM) can measure both COD and turn-by-turn position. Tune monitor system consists of exciter and its own BPM. The exciter shakes the beam and coherent oscillation. Dedicated BPMs, Fast CT (FCT) and Wall Current Monitor (WCM) are used for RF feedback or feedfoward control. It will describe the performance of each instruments and how they are contributed to the successful beam commissioning.
Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Saeki, Riuji; Toyokawa, Ryoji*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Arakawa, Dai*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Lee, S.*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Tejima, Masaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.1128 - 1130, 2008/06
The Beam Position Monitor (BPM) system of the J-PARC RCS has been fabricated, installed and operated successfully during the beam commissioning. There are 54 BPMs around the ring and most of them are placed inside steering magnets. The BPM is electro static type and it has four electrodes. A pair of electrode gives a linear response with diagonal cut shape and they were calibrated before their installation. The signal processing unit, which is equipped with 14-bit 14MSPS ADC and 600MHz DSP, has been developed for the system. In order to measure small signal, especially during the initial phase of the commissioning, careful design also done for cabling. The paper presents the current performance of the system.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Saeki, Riuji; Toyama, Takeshi*; Teshima, Masaki*; Sato, Kenichiro*
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.382 - 384, 2008/06
Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Saha, P. K.; Saeki, Riuji; Toyokawa, Ryoji*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Arakawa, Dai*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Lee, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of 5th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 33rd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.243 - 245, 2008/00
The J-PARC RCS has been beam commissioned since fall 2007. During such a short period, the following items have been established. Establishment of the injection orbit, beam circulation, acceleration up to 3GeV, optics parameters measurements and it achieved 50 kW beam power (4 10
10 ppb). The beam monitor system has an important role for smooth beam commissioning. This paper describes the status of the beam monitor system, BPM, Injection monitors, IPM, current monitor, tune meter and BLM of the RCS.
ppb). The beam monitor system has an important role for smooth beam commissioning. This paper describes the status of the beam monitor system, BPM, Injection monitors, IPM, current monitor, tune meter and BLM of the RCS.
Nagata, Shinji*; Higashi, Seijiro*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; To, Kentaro*; Shikama, Tatsuo*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Ozaki, Koichi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Inoue, Aichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 257(1-2), p.420 - 423, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)Structural modification and primary precipitates in the Zr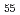 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu alloy films (50-100
alloy films (50-100  m thickness) caused by radiation with 300-500 keV H, Ag, Cu and Au ions has been studied. The results of XRD indicated that a metastable primary phase was formed in the alloy by the heat treatment after ion irradiation, but no difference was observed just after the ion irradiation at room temperature. Furthermore, higher incident Au ion fluence effectively suppressed thermal precipitation of the Zr
m thickness) caused by radiation with 300-500 keV H, Ag, Cu and Au ions has been studied. The results of XRD indicated that a metastable primary phase was formed in the alloy by the heat treatment after ion irradiation, but no difference was observed just after the ion irradiation at room temperature. Furthermore, higher incident Au ion fluence effectively suppressed thermal precipitation of the Zr Ni type crystalline phase in the alloy. The deposited energy dependence of the precipitation behavior indicated an increase of the nucleation sites by the implanted metal atoms, simultaneously with a decrease of the growth rate by higher energy deposition density.
Ni type crystalline phase in the alloy. The deposited energy dependence of the precipitation behavior indicated an increase of the nucleation sites by the implanted metal atoms, simultaneously with a decrease of the growth rate by higher energy deposition density.
Sato, Kenichiro; Hiroki, Seiji; Lee, S.*; Hayashi, Naoki; Yamamoto, Kazami; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Arakawa, Dai*; Igarashi, Zenei*; Saeki, Riuji
Proceedings of 4th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 32nd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.297 - 299, 2007/00
At the injection and H0 dump line of J-PARC RCS, different beam monitors have been installed. Main purpose of the beam monitors in the injection line is to generate a beam position and profile to adjust the injection trajectory to the RCS ring. To guide the injected beam precisely is, needless to say, required to reduce the beam loss in the ring. Hence the monitor system is one of the most essential to operate the RCS. At the injection point, there are also some beams that are not match the RCS ring, that is negative and neutral proton beam. H0 dump accepts the unsuitable beams through the H0 dump line. The power limitation of the H0 dump is 4 kW. The monitor system in the dump line is to handle the beam and to monitor the dumped beam power. At the conference these monitor systems will be outlined.