Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
山本 耀二郎*; 早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋
Computational Materials Science, 229, p.112389_1 - 112389_9, 2023/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:21.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ヘリウムバブルは、核融合炉条件下で生成する特有の微細構造である。これらのバブルは、自らの移動によって接近・融合し、微細構造や材料特性に大きな影響を与える。しかし複数の金属原子の移動が含まれるこれらのプロセスは、分子動力学(MD)では時間スケールの制約から扱うことができない。この研究では、自己発展原子論的キネティックモンテカルロ(SEAKMC)法により時間スケールを拡張し、Fe中のバブルの融合過程を再現した。He原子の微小な振動やFe原子の短距離変位など、活性化エネルギーが極めて低い些細なイベントを避けるため、SEAKMCに2つのアルゴリズムを導入した。He原子の微小な振動を回避するために二段階のサドルポイント検索を行い、Fe原子の短距離変位を避けるためにFe原子の変位距離に対する閾値を設定した。さらに、活性化エネルギーの上限を設定する別のアルゴリズムを追加することで、非現実的に高い活性化エネルギーを持つイベントの選択を防ぎ、MDの時間尺度よりも8桁長い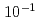 秒までのシミュレーション時間において、ダンベルから楕円形への構造の変化を再現することに成功した。開発された手法は、軽元素を含む金属材料の微細構造を分析するのに効果的であり、実験と比較可能な時間スケールに到達できる唯一の手法である。
秒までのシミュレーション時間において、ダンベルから楕円形への構造の変化を再現することに成功した。開発された手法は、軽元素を含む金属材料の微細構造を分析するのに効果的であり、実験と比較可能な時間スケールに到達できる唯一の手法である。
早川 頌*; 山本 耀二郎*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 218, p.111987_1 - 111987_10, 2023/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:5.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)On-the-fly kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC), a computational technique for atomistic simulations, has attracted attention because it increases the simulation timescale beyond that of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations while maintaining atomistic fidelity. However, for most kMC methods, when events with high and low activation energies coexist in the event list, trivial events with extremely low activation energies that do not essentially affect the phenomena of interest, so-called flicker events, are frequently selected, making it challenging to observe the key dynamics. In this study, we use Self-Evolving Atomistic kMC (SEAKMC), one of the on-the-fly kMC methods, to model the unstable-to-stable transformations of irregular three-dimensional self-interstitial-atom (SIA) clusters in Cu generated through collision cascade. By setting an activation energy threshold once every five steps, transformations into stable configurations are enhanced. The algorithm renders the simulation timescales one or two orders of magnitude longer than those possible with MD simulations. Further, the probability of transformations into stable configurations is increased by 40 times compared to that of the original SEAKMC method. In addition, we find that the stable configurations obtained by the transformation of the SIA clusters are mostly Frank loops. In summary, this new algorithm for the SEAKMC method helps to resolve the inefficiency of kMC methods resulting from the selection of flicker events and will aid the study of meso-timescale atomistic dynamics.
 O
O
吉岡 聰*; 鶴田 幸之介*; 山本 知一*; 安田 和弘*; 松村 晶*; 杉山 武晴*; 大場 洋次郎; 石川 法人; 小林 英一*; 奥平 幸司*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 103(8), p.4654 - 4663, 2020/08
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:30.42(Materials Science, Ceramics)高速重イオン照射によりMgAl O
O スピネルに形成された損傷組織をX線吸収端近傍構造解析(XANES)とX線小角散乱法(SAXS)を用いて調べた。照射量が増加するとSAXSとXANESの両方で変化が見られた。SAXSでは、照射部に直径5nmの円柱状のイオントラックが観測された。XANESの結果は、四面体位置と八面体位置の間でカチオンの無秩序化が生じていることを示すものであった。さらに、XANESスペクトルの定量的な解析により、高照射量ではカチオンが八面体位置を優先的に占有することがわかった。
スピネルに形成された損傷組織をX線吸収端近傍構造解析(XANES)とX線小角散乱法(SAXS)を用いて調べた。照射量が増加するとSAXSとXANESの両方で変化が見られた。SAXSでは、照射部に直径5nmの円柱状のイオントラックが観測された。XANESの結果は、四面体位置と八面体位置の間でカチオンの無秩序化が生じていることを示すものであった。さらに、XANESスペクトルの定量的な解析により、高照射量ではカチオンが八面体位置を優先的に占有することがわかった。
佐々木 宏和*; 西久保 英郎*; 西田 真輔*; 山崎 悟志*; 中崎 竜介*; 磯松 岳己*; 湊 龍一郎*; 衣川 耕平*; 今村 明博*; 大友 晋哉*; et al.
古河電工時報, (138), p.2 - 10, 2019/02
電子顕微鏡や放射光等の先端解析技術は、試料の構造や化学状態について多くの有用な情報をもたらし、材料研究に欠かせないツールとなっている。本稿では、これらの先端解析技術の中から、電子線ホログラフィや放射光を用いたX線小角散乱法(SAXS)等の手法を中心に、材料研究への応用事例を紹介する。これらの手法を活用することにより、未知であった材料の本質を明らかにすることができ、新製品開発の指針を定める上で重要な知見を得ることができる。